Medieval Castles - Features and History
- History of Castles. Castles are an innovation of the European and they emerged in the 9 th and 10 th centuries. ...
- Purposes of Castles. Castles served a wide range of purposes. The most distinct purposes were domestic, administrative, and military.
- Features of Castles. Initially, castles were constructed using earth and timber. ...
When were castles first built a why?
Castle History. Castle, a strongly fortified residence. Castles developed in western Europe in the late 10th century as the private strongholds of kings and noblemen and played an important role in the feudal system. Castles were built not only in Europe, but also in the Middle East (during the Crusades) and in parts of the Far East.
What life was really like in a medieval castle?
Life in a medieval castle would have been ordered and organised, full of pomp and ceremony, and also very cold and smelly! Essentially, castles were at the heart of Medieval society. Castles were built in England and Wales after 1066.
What are facts about medieval castles?
Medieval Castles Facts. Medieval castles were built during the Middle Ages in Europe and the Middle East as a structure to provide protection for nobility from invaders. Not to be confused with palaces, castles were fortified structures that began to be built in the 9 th and 10 th centuries, and continued to be built for roughly 900 years.
What were castles used for?
What were castles originally used for? Medieval castles were built mainly for protection for the nobility, which is the noble class of a country such as royalty and important public figures. The natural resources of the land were used as a first line of defense for intruders, and the features of the castles served as even more protection.

What was the function of a castle quizlet?
Live in them and defend and administer their land; they were also used as courts and prisons and major festivals and banquets were held in them. What were the first castles made of? Why were castles often built on hills?
What was the main reason for building castle?
Medieval castles were built from the 11th century CE for rulers to demonstrate their wealth and power to the local populace, to provide a place of defence and safe retreat in the case of attack, defend strategically important sites like river crossings, passages through hills, mountains and frontiers, and as a place of ...
Why did kings live in castles?
he castle was a fortified building or set of buildings used to provide permanent or temporary protection and accommodation for kings and queens or important noblemen and their families. The castle provided the centre for political and administrative power for the region.
Who made castles first?
The first castles Even before the battle, William the Conqueror built a castle at Hastings, near his landing place. Over the next 150 years, the Normans covered the country with them, and built around 1,000 in England and Wales. Castles were something quite new in England.
When was the first castle built in Ghana?
George's d'Elmina Castle, built in 1482, is one of the oldest European buildings outside Europe, and the historic town of Elmina is believed to be the location of the first point of contact between Europeans and sub-Saharan Africans.
What was the first castle ever built?
The Citadel of Aleppo is the oldest castle in the world, with some parts of the structure dating back to 3000 BC. Built in 1070 AD, Windsor Castle is the oldest castle that is still actively used today.
How did castle design develop?
The first castles, built in the Early Middle Ages (early Medieval period), were 'earthworks' – mounds of earth primarily built for defence, as enemies struggled to climb them. During the 1000s, the Normans developed these into Motte and Bailey castle designs.
Why were there medieval castles?
Medieval castles were built mainly for protection for the nobility, which is the noble class of a country such as royalty and important public figures. The natural resources of the land were used as a first line of defense for intruders, and the features of the castles served as even more protection.
Why Do We Care About Castles?
From the Middle Ages to today's world, the planned communities and system of the social order of medieval life have become romanticized, transformed into a time of honor, chivalry, and other knightly virtues. America's fascination with wizardry didn't begin with Harry Potter or even " Camelot ". The 15th-century British writer Sir Thomas Malory compiled the medieval legends we've come to know — the stories of King Arthur, Queen Guinevere, Sir Lancelot and the Knights of the Round Table. Much later, Medieval life was satirized by the popular American author Mark Twain in the 1889 novel "A Connecticut Yankee in King Arthur's Court". Later still, Walt Disney placed the castle, modeled after Neuschwanstein in Germany, at the heart of his theme parks.
What is a castle?
Originally, a castle was a fortress built to protect strategic locations from enemy attack or to serve as a military base for invading armies. Some dictionaries describe a castle simply as "a fortified habitation.". The earliest "modern" castle design dates from Roman Legionary Camps.
Why were castles important in the Renaissance?
People seeking protection from invading armies built villages around established castles. Local nobility took the safest residences for themselves — inside the castle walls. Castles became homes, and also served as important political centers. As Europe moved into the Renaissance, the role of castles expanded.
Why is the first floor of Castle Ashby shaped like an E?
The first-floor plan was shaped like an "E" to celebrate the rule of Queen Elizabeth I. In 1635, additions squared off the design to create the inner courtyard — a more traditional floor plan for a fortified habitation (view floor plan of Castle Ashby's first floor).
Why were the plantation castles in Northern Ireland fortified?
Still others, like the plantation castles of Northern Ireland, were large homes, fortified to protect immigrants like the Scots from the resentful local Irish inhabitants.
What were the fortifications of the 13th century?
Over the next three centuries, wooden fortifications evolved into imposing stone walls. High parapets, or battlements, had narrow openings ( embrasures) for shooting. By the 13th century, lofty stone towers were popping up across Europe. The Medieval castle at Penaranda de Duero, northern Spain is often how we imagine castles.
What is a Roman castle?
Castle Details Handed Down. The English word "castle" is from the Latin word castrum, meaning a fort or fortified habitation. The Roman castrum had a particular design — rectangular, enclosed by walls with towers and four gates, the interior space divided into four quadrants by two main streets.
Why did the Lord of the Castle have a castle?
Due to the lord's presence in a castle, it was a centre of administration from where he controlled his lands. He relied on the support of those below him, as without the support of his more powerful tenants a lord could expect his power to be undermined. Successful lords regularly held court with those immediately below them on the social scale, but absentees could expect to find their influence weakened. Larger lordships could be vast, and it would be impractical for a lord to visit all his properties regularly, so deputies were appointed. This especially applied to royalty, who sometimes owned land in different countries.
What is a castle?
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble.
What are baileys in castles called?
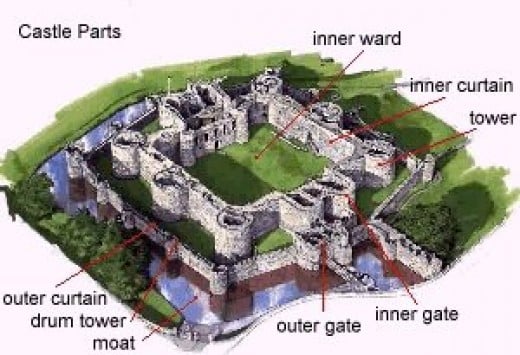
From the late 12th century there was a trend for knights to move out of the small houses they had previously occupied within the bailey to live in fortified houses in the countryside. Although often associated with the motte-and-bailey type of castle, baileys could also be found as independent defensive structures. These simple fortifications were called ringworks. The enceinte was the castle's main defensive enclosure, and the terms "bailey" and "enceinte" are linked. A castle could have several baileys but only one enceinte. Castles with no keep, which relied on their outer defences for protection, are sometimes called enceinte castles; these were the earliest form of castles, before the keep was introduced in the 10th century.
Why did castles rise in Europe?
Discussions have typically attributed the rise of the castle to a reaction to attacks by Magyars, Muslims, and Vikings and a need for private defence. The breakdown of the Carolingian Empire led to the privatisation of government, and local lords assumed responsibility for the economy and justice. However, while castles proliferated in the 9th and 10th centuries the link between periods of insecurity and building fortifications is not always straightforward. Some high concentrations of castles occur in secure places, while some border regions had relatively few castles.
How did the castle evolve?
It is likely that the castle evolved from the practice of fortifying a lordly home. The greatest threat to a lord's home or hall was fire as it was usually a wooden structure. To protect against this, and keep other threats at bay, there were several courses of action available: create encircling earthworks to keep an enemy at a distance; build the hall in stone; or raise it up on an artificial mound, known as a motte, to present an obstacle to attackers. While the concept of ditches, ramparts, and stone walls as defensive measures is ancient, raising a motte is a medieval innovation.
How tall was the wall in the castle?
A typical wall could be 3 m (10 ft) thick and 12 m (39 ft) tall, although sizes varied greatly between castles.
When did gunpowder start to affect castles?
Some grand castles had long winding approaches intended to impress and dominate their landscape. Although gunpowder was introduced to Europe in the 14th century, it did not significantly affect castle building until the 15th century, when artillery became powerful enough to break through stone walls.
What was the principle of the medieval castle?
The principle governing the design of the new forts constructed all over Europe was that the whole building should be concentrated in one compact block.
What is a castle in medieval times?
castle, medieval stronghold, generally the residence of the king or lord of the territory in which it stands. Strongholds designed with the same functionality have been built throughout the world, including in Japan, India, and other countries. The word castle is sometimes applied to prehistoric earthworks, such as Maiden Castle in England, and is also applied, in various linguistic forms (e.g., château, castello, and Burg ), to princely mansions or country seats.
What is the moat of the Tower of London?
Tower of London. Its moat and two concentric “curtains,” or walls, surround the White Tower. Jupiterimages. The baileys at the foot of the mound were enclosed by palisades and later by walls and towers of masonry.
What were castles in England?
Castles, which were virtually unknown in pre-Conquest England and could only be built with royal permission, provided bases for administration and military organization. They were an essential element in the Norman settlement of England.…
What was the development of the use of guns in the 15th and 16th centuries?
Development in the use of firearms was so rapid during the 15th and 16th centuries as to require a radical change in military architecture. French troops marched through Italy in 1494 and, with their guns, reduced castle after castle with astonishing rapidity. The age of the medieval castle came to an end, and the era of modern military fortification opened. The principle governing the design of the new forts constructed all over Europe was that the whole building should be concentrated in one compact block. Its low walls could then be defended all around by artillery, the guns being mounted on bastions and redans.
What was the main defense of the Third Crusade?
The main defense was concentrated in the direction of approach, where there were often two or three lines of advance fortifications.
What was the name of the castle in the 11th century?
During the 11th century this type of private fortress, known as the “motte [mound] and bailey” castle, spread throughout western Europe. Château of the dukes of Anjou, Saumur, France. Art Resource, New York. The thickness of castle walls varied according to the natural strength of the sites they occupied, often diverging greatly at different points ...
Why were castles built?
Where possible, castles were built to take advantage of the surrounding terrain. Those on rugged hills or ridges were harder to assault than those on flat land. A river or swamp providing water for a moat often helped decide where a castle was built. But a source of drinking water was always the determining factor of a castle's site. A garrison could store enough food to withstand a siege (one Crusader castle held a five-year supply of grain), but it had to be located where springs or wells provided a constant supply of fresh water.
What was the evolution of the castle?
The evolution of the castle coincided with the emergence of a new political system called feudalism. For several centuries, castles played a crucial role in European history. However, by the end of the thirteenth century they had lost their military, political, and social significance and were being abandoned.
How did castles evolve?
Since there was only room on the motte for very small towers (with deplorable sanitary conditions), castle construction quickly evolved. By the early twelfth century, stone began replacing timber in the towers and walls. Because skilled masons were needed for this work, only the wealthier, higher-ranking nobles could now afford to build castles. As nobles built larger dwellings, the motte was too small for their foundations. It disappeared and the defensive emphasis shifted to strengthening the tower (called the keep or donjon) and the outer walls of the bailey. Ditches surrounded these outer walls and wherever possible were filled with water for further protection. Access to the castle was controlled by a drawbridge which spanned the ditch or moat. By the late twelfth century, the "concentric" castle evolved, with a strong outer wall to keep sappers (tunnelers who removed the foundations of a wall causing it to collapse) and catapults away from the main fortification. This was a higher, stronger inner wall that surrounded the bailey and a massive keep. The Crusaders' Crac des Chevaliers and Richard I 's Château Gaillard at Les Andelys in France were the most famous concentric castles.
How many castles were built in England?
We will never know how many castles were built since the majority were of the timber motte and bailey type, which have vanished leaving no trace. In England alone, at least half the 1,500 castles built since 1066 were deserted by 1300. In those that were still inhabited, the nobles spent their money seeking comfort, not protection. The castle was evolving into the manor house; in France, "château" no longer meant feudal castle, but rather a large country house.
Why did the nobles need strongholds?
To protect themselves from sudden raids by the Vikings, the nobles needed strongholds to which they could retreat until they gathered their vassals for battle. These strongholds were the first castles. In 1066, the castle and feudal system were forcibly introduced into England in the Norman Conquest.
Why were cities fortified?
In the ancient world cities were often fortified, especially if they were vulnerable to attack by outside forces. The purpose of these defensive walls was to protect the public; they were group strongholds. Over time, attackers developed techniques to penetrate these fortifications, ranging from scaling the walls with ladders, to tunneling under them, or using rams to batter them down. Machines were invented to assist in assaults: towers that could be rolled against the walls and artillery such as catapults to hurl missiles over them. Defenders, however, found ways to counter each of these methods of attack.
When did the castle system start?
In 1066, the castle and feudal system were forcibly introduced into England in the Norman Conquest. Soon, feudalism and castles were established all over Europe. As the outside threats faded, nobles fought power struggles with each other and with monarchs anxious to restore central authority.
What were the purposes of castles?
Purposes of Castles. Castles served a wide range of purposes. The most distinct purposes were domestic, administrative, and military. Castles also served as offensive tools and could be used a base of operations in foreign territories.
What were castles built of?
Initially, castles were constructed using earth and timber. Later, stone replaced the castles’ defences. Early castles relied on a central keep and exploited natural defences. They often lacked advanced features such as arrowslits and towers. A specific approach to castle defence arose in the 12th and 13th centuries. A proliferation of towers occurred and great emphasis was made on flanking fire. The castles relied on concentric defence and had various stages of defence that could all function at the same time. This helped to intensify the castle's firepower.
What is a medieval castle?
European nobles built and occupied castles. There are many stunning examples of medieval castles that still stand today. The word castle comes from the Latin word castellum, derived from the word castrum meaning a fortified place. Scholars define a castle as a fortified residence of a noble or a lord. A castle is different from a palace, as ...
How are castles different from palaces?
A castle is different from a palace, as a palace is not fortified. A castle is also distinct from a fortress, as a fortress was not always occupied by a noble. For the period of 900 years when castles were built, they adopted many designs. However, the castles shared some features such as arrowslits and curtain walls.
Why did castles lose their military significance?
This was due to the advancement of strong canons and the prevalence of artillery fortifications, which could withstand the canons.
How many castles did William the Conqueror have?
By building castles, William was able to secure the land he had conquered. Between the years 1066 and 1087, he has established 36 castles. These castles are some of the oldest in Europe.
Why did the Carolingian Empire build castles?
The nobles took the initiative to build castles in order to defend the acquired territories. The castles offered protection from enemies. They also formed a base from which raids and battles were planned and launched. Besides their military purposes, castles also acted as symbols of power and served as centers of administration. Castles constructed in rural areas were located near important features such as fertile land, water sources, and mills. In urban areas, castles helped control local populace and travel routes.
What was the purpose of the kitchen in a castle?
The most elaborate kitchens would have been all-set to cook and prepare game and fish , which had been caught when hunting in the castle grounds.
Why were castles built on the turbulent borders of England and Wales?
For example, a castle built on the turbulent borders of England and Wales might have been built to be as strong and as defensive as possible.
What was the name of the castle that was built for the Hungerford family?
Farleigh Hungerford Castle was, first and foremost, a grand residence for the Hungerford family. However, the design of the castle still included many defensive elements, such as towers, a barbican, a gatehouse and a moat. It did play a small part in the English Civil War.
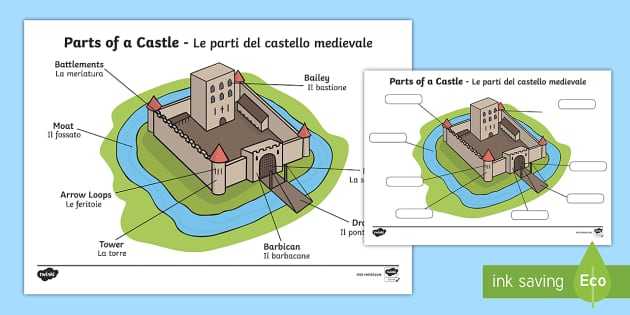
Why did the castles have round towers?
Although round towers of Farleigh Hungerford castle were predominately decorative, many other castles built towers for practical purposes – to provide a vantage-point for archers to shoot at oncoming attackers.
Why were moats important in castles?
Although moats were great for defence – they partially prevented attackers from burrowing beneath the castle walls, for example – a stagnant moat would have been pretty unpleasant. Sewage would have been tipped straight into the stagnant water – imagine the smell in the summer!
Why didn't castles have dungeons?
In Early Medieval times, castles didn’t really have dungeons – simply because the idea of keeping someone prisoner was, back then, a very strange punishment. However, as the Middle Ages developed, more castles became to be equipped with space for prisoners.
What was the most fortified part of a castle?
The keep was traditionally the strongest and the most fortified part of a castle – and, in early Medieval times, it’s where the nobles would have lived. In later Medieval times, as castles began to morph into grand residential buildings (from being fortresses), the nobles began to live in warmer, comfier chambers – and the keep became a strong-hold.
Overview
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a pleasance which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settl…
Definition
The word castle is derived from the Latin word castellum, which is a diminutive of the word castrum, meaning "fortified place". The Old English castel, Occitan castel or chastel, French château, Spanish castillo, Portuguese castelo, Italian castello, and a number of words in other languages also derive from castellum. The word castle was introduced into English shortly before the Norman Conquest to deno…
Common features
A motte was an earthen mound with a flat top. It was often artificial, although sometimes it incorporated a pre-existing feature of the landscape. The excavation of earth to make the mound left a ditch around the motte, called a moat (which could be either wet or dry). Although the motte is commonly associated with the bailey to form a motte-and-bailey castle, this was not alway…
History
Historian Charles Coulson states that the accumulation of wealth and resources, such as food, led to the need for defensive structures. The earliest fortifications originated in the Fertile Crescent, the Indus Valley, Europe, Egypt, and China where settlements were protected by large walls. In Northern Europe hill forts were first developed in the Bronze Age, which then proliferated across Europe …
Construction
Once the site of a castle had been selected – whether a strategic position or one intended to dominate the landscape as a mark of power – the building material had to be selected. An earth and timber castle was cheaper and easier to erect than one built from stone. The costs involved in construction are not well-recorded, and most surviving records relate to royal castles. A castle with eart…
Social centre
Due to the lord's presence in a castle, it was a centre of administration from where he controlled his lands. He relied on the support of those below him, as without the support of his more powerful tenants a lord could expect his power to be undermined. Successful lords regularly held court with those immediately below them on the social scale, but absentees could expect to find their influen…
Locations and landscapes
The positioning of castles was influenced by the available terrain. Whereas hill castles such as Marksburg were common in Germany, where 66 per cent of all known medieval were highland area while 34 per cent were on low-lying land, they formed a minority of sites in England. Because of the range of functions they had to fulfil, castles were built in a variety of locations. Multiple factors we…
Warfare
As a static structure, castles could often be avoided. Their immediate area of influence was about 400 metres (1,300 ft) and their weapons had a short range even early in the age of artillery. However, leaving an enemy behind would allow them to interfere with communications and make raids. Garrisons were expensive and as a result often small unless the castle was important. Cost al…