
Why did Virginia eventually become a royal colony?
Why did Virginia eventually become a royal colony? After almost two decades as a private enterprise, Virginia became a royal colony, the first in English history. Partly because the English kings were occupied with affairs at home, the Virginia house of burgesses was able to continue its functions and won formal recognition in the late 1630s.
Why did the Virginia Colony become a success?
Virginia has had agricultural success with tobacco and the colony’s economy has benefited from it substantially, the colony also has great geographical features such as bays and plenty of rivers as well as a mild climate. The Virginia Colony had many natural resources including forests,fish,and agricultural land.
Why did people settle in Virginia Colony?
Why did they settle Virginia? purpose of Virginia: Virginia was founded primarily for the purpose of profit by the joint-stock owned Virginia Company of London. It was also important in giving England territorial claims in America to match Spanish and French expansion, and to also give England markets and resources in the New World.
Why did the Virginia Company establish the colony?
The Virginia Company of London was a joint-stock company chartered by King James I in 1606 to establish a colony in North America. Such a venture allowed the Crown to reap the benefits of colonization—natural resources, new markets for English goods, leverage against the Spanish—without bearing the costs.
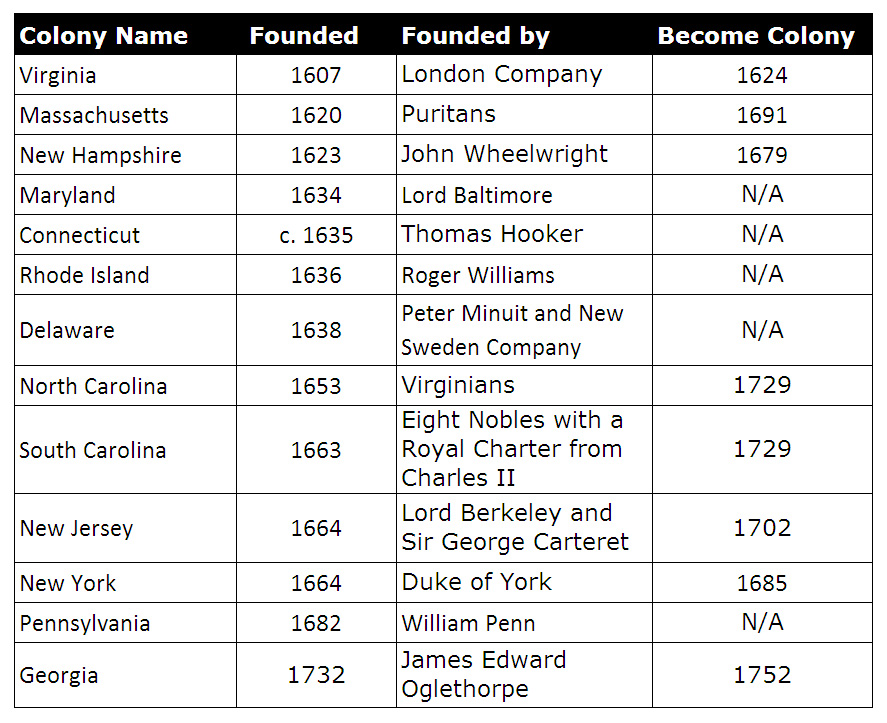
What was the name of the Virginia colony?
The colony 's formal name was the Colony and Dominion of Virginia.
What was Virginia involved in?
Virginia and the American Revolution. Virginia was involved in fighting against what they saw as British tyranny from the end of the French and Indian War. The Virginia General Assembly fought against the Sugar Act which had been passed in 1764. They argued that it was taxation without representation.
What was the name of the colony in the winter?
The winter became known as "The Starving Time," and the colony became known as a deathtrap. During the early period of the colony, Jamestown was primarily a military outpost, populated by men, either gentlemen or indentured servants.
How many ships did England send to the colonies?
England continued to send supplies and colonists and in late Spring 1609, after the colony had been reorganized into a joint stock venture, London sent nine ships and 500 colonists. The ship bearing the deputy governor Thomas Gates wrecked off the Bermuda coast.
What was the first colony in North America?
In 1607, Jamestown became Great Britain's first settlement in North America, the first foothold of the Virginia Colony. Its permanency came after three failed attempts by Sir Walter Raleigh beginning in 1586 to attempt to establish a stronghold in the land he called Virginia after his queen, Elizabeth I. And its continued survival was very much in ...
Why did Jamestown have a high mortality rate?
Jamestown had a high mortality rate due to disease, colonial mismanagement, and raids from Indigenous peoples. The presence of women and family units encouraged some growth and stability, but factionalism and fiscal insolvency continued to plague Virginia.
Why was Jamestown chosen?
The location of Jamestown was chosen because it would be easily defended since it was surrounded by water on three sides; the water was deep enough for the colonists' ships, and Indigenous tribes did not inhabi t the land. Unfortunately, there were reasons Indigenous peoples did not inhabit the land; there was no potable water source, and the marshy landscape emitted great clouds of mosquitoes and flies. Disease, heat, and skirmishes with Indigenous peoples consumed both colonists and their supplies, and by the time the first supply ship arrived in September, only 37 of the original 104 colonists were living.
Why was the Virginia colony called the Old Dominion?
After the English Civil War in the 1640s and 50s, the Virginia colony was nicknamed "The Old Dominion" by King Charles II for its perceived loyalty to the English monarchy during the era of the Protectorate and Commonwealth of England.
What states were created by the colony of Virginia?
The entire modern states of West Virginia, Kentucky, Indiana and Illinois, and portions of Ohio and Western Pennsylvania were later created from the territory encompassed, or claimed by, the colony of Virginia at the time of further American independence in July 1776.
How many colonists died in the Powhatan War?
After twelve years of peace following the Indian Wars of 1622–1632, another Anglo–Powhatan War began on March 18, 1644, as a last effort by the remnants of the Powhatan Confederacy, still under Opechancanough, to dislodge the English settlers of the Virginia Colony. Around 500 colonists were killed, but that number represented a relatively low percent of the overall population, as opposed to the earlier massacre (the 1622 attack had wiped out a third; that of 1644 barely a tenth). However, Opechancanough, still preferring to use Powhatan tactics, did not make any major follow-up to this attack.
Why did the Popham colony fail?
The Popham colony quickly failed due to a famine, disease, and conflicts with local Native American tribes in the first two years . Jamestown occupied land belonging to the Powhatan Confederacy, and was also at the brink of failure before the arrival of a new group of settlers and supplies by ship in 1610.
What was the capital of the Virginia colony in 1699?
Jamestown on the James River remained the capital of the Virginia colony until 1699; from 1699 until its dissolution the capital was in Williamsburg. The colony experienced its first major political turmoil with Bacon's Rebellion of 1676.
What was the first profitable export in Virginia?
Tobacco became Virginia's first profitable export, the production of which had a significant impact on the society and settlement patterns. In 1624, the Virginia Company's charter was revoked by King James I, and the Virginia colony was transferred to royal authority as a crown colony.
Which colony sided with the Crown?
While the newer, Puritan colonies, most notably Massachusetts, were dominated by Parliamentarians, the older colonies sided with the Crown. The Virginia Company's two settlements, Virginia and Bermuda (Bermuda's Independent Puritans were expelled as the Eleutheran Adventurers, settling the Bahamas under William Sayle ), Antigua and Barbados were conspicuous in their loyalty to the Crown, and were singled out by the Rump Parliament in An Act for prohibiting Trade with the Barbadoes, Virginia, Bermuda and Antego in October 1650. This dictated that:
Who founded the Virginia colony?
The Virginia Colony was founded in 1607 by John Smith and other colonists including John Rolfe backed by the London Company, at Jamestown. Named after Queen Elizabeth I of England - the "Virgin Queen".
Why was Virginia founded?
purpose of Virginia: Virginia was founded primarily for the purpose of profit by the joint- stock owned Virginia Company of London. It was also important in giving England territorial claims in America to match Spanish and French expansion, and to also give England markets and resources in the New World.
What were the natural resources of the Virginia colony?
The Virginia Colony had many natural resources including forests, fish, and agricultural land. The Virginia Colony's trade and export included tobacco, cotton, livestock, fruit, grain, and vegetables. Plantations were common in the Virginia Colony, where cotton and tobacco were often grown in large quantities.
Why was Virginia founded?
One of the New England colonies and chartered by James I in 1606, Virginia was founded to give the English territorial claims to America as well as to offer a colonial market for trade.
What was the purpose of the Virginia Company?
purpose of Virginia: Virginia was founded primarily for the purpose of profit by the joint-stock owned Virginia Company of London. It was also important in giving England territorial claims in America to match Spanish and French expansion, and to also give England markets and resources in the New World. indentured servants: People who promised ...
What was Rolfe's purpose in the colony?
Rolfe is credited with introducing tobacco as a crop for export, which ensured the colony of profits as well as bringing eight years of peace between Indians and colonists through his marriage to Pocahontas. purpose of Virginia: Virginia was founded primarily for the purpose of profit by the joint-stock owned Virginia Company of London.
What were the successes of Virginia?
successes of Virginia: Virginia succeeded politically in terms of creating the House of Burgesses as a semi-democratic assembly and forcing governors to cooperate with the legislature. They did this through the power of the purse as governors did not control money, and therefore depended on the legislature for they salaries.
What is the term for the period early in any settlements development when food and supplies are scarce?
starving time : The period early in any settlements development when food and supplies are scarce due to lack of preparation, unfamiliarity with the surroundings, weather, and inability to successfully grow crops. The starving time usually cost a large percentage of the settlers lives and lasted for the first few years.
What was the name of the group of supporters of Charles I during the English Civil War?
Cavalier: The group of supporters of Charles I in the English Civil War which lasted from 1642-1648. The term Cavalier continued to be used to mean any supporter of the British crown, especially Americans who were British sympathizers during the American Revolution.
When was Jamestown founded?
Jamestown: The first successful settlement in the Virginia colony founded in May, 1607. Harsh conditions nearly destroyed the colony but in 1610 supplies arrived with a new wave of settlers. The settlement became part of the Virginia Company of London in 1620.
Who was the founder of the Virginia colony?
Sir Walter Raleigh. The Virginia colony was founded and, at first, run by the Virginia Company of London. Sir Walter Raleigh had paid for his colonial ventures himself, and so assumed nearly all of the risk.
What was the colonial period in Virginia?
The colonial period in Virginia began in 1607 with the landing of the first English settlers at Jamestown and ended in 1776 with the establishment of the Commonwealth of Virginia. Although a thriving Indian society had existed for thousands of years before the English arrived, war with the European settlers and the introduction of new diseases for which the Indians had no resistance spelled disaster for it. The English colonists, meanwhile, just barely survived, suffering through summer droughts and winter starvation. Salvation came to the colony in the form of smoking tobacco, or what King James I called a “vile and stinking custom,” when John Rolfe cultivated a variety of tobacco that sold well in England. In 1619, a General Assembly convened, bringing limited self-government to America. That same year brought the first slaves to Virginia. For most of the 1600s, white indentured servants worked the colony’s tobacco fields, but by 1705 the Virginia colony had become a slave society. Nearly all power was in the hands of white male landowners, who ran the government and, by law, belonged to the Church of England. Women who married and worked at home were considered “good wives”; those who refused such “proper” roles were considered troublesome. And while Virginia’s ruling men did not encourage women to be independent, they nevertheless fought for their own independence, taking full part in the American Revolution (1775–1783).
What was the labor force in Virginia in the 1600s?
During most of the 1600s, Virginia’s labor force consisted primari ly of white indentured servants and a handful of convict laborers, who in many cases were treated no better than slaves. Some Virginia Indians also worked as servants or, more often, were enslaved.
How did religion and politics relate to colonial Virginia?
Religion and politics were intimately linked in colonial Virginia. The Church of England practiced a form of Protestant Christianity that in some ways resembled Catholicism. Because the Church of England was the established church, colonists were legally required to attend its services and, through taxes, to financially support its ministers. The parish, meanwhile, served as the basic unit of both religious and civil authority. It provided social welfare and delivered moral offenders to the courts. Attending church became another important means for people to make social, political, and economic connections. As the authors of Old Dominion, New Commonwealth (2007) have written, when colonists gathered for church each Sunday, they “came together not only to worship but to exchange business documents, discuss tobacco prices, argue over the quality of horses, catch up on local gossip, and share news of the wider world.”
What did Indians do to their young?
Like people everywhere, Indians married and divorced, cooked, played games, named their children, and educated their young. Boys were initiated into manhood through a frightening process called the huskanaw, which involved a ritual death and rebirth. And although there were no written laws, Virginia Indians punished wrongdoers according to their own traditions and customs.
How did the number of slaves in Virginia grow?
Over time, especially as the African slave population included more women, the number of slaves in Virginia began to grow naturally through childbirth. By 1770, 91 percent of Virginia’s slaves were born in America. As a group, they began to develop distinctive modes of language, storytelling, and music.
How did tobacco help Virginia?
Tobacco, in other words, helped bring self-government to Virginia. Before long, however, it also brought slavery.

Overview
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed proprietary attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey Gilbert in 1583, and the subsequent farther south Roanoke Island (modern eastern North Carolina) by Sir Walter Raleigh in the late 1580s.
Names and etymology
The name "Virginia" is the oldest designation for English claims in North America. In 1584, Sir Walter Raleigh sent Philip Amadas and Arthur Barlowe to explore what is now the North Carolina coast, and they returned with word of a regional king (weroance) named Wingina, who ruled a land supposedly called Wingandacoa.
The name Virginia for a region in North America may have been originally suggested by Sir Walte…
History
Although Spain, France, Sweden, and the Netherlands all had competing claims to the region, none of these prevented the English from becoming the first European power to colonize successfully the Mid-Atlantic coastline. Earlier attempts had been made by the Spanish in what is now Georgia (San Miguel de Gualdape, 1526–27; several Spanish missions in Georgia between 1568 and 16…
Relations with the Natives
As the English expanded out from Jamestown, encroachment of the new arrivals and their ever-growing numbers on what had been Indian lands resulted in several conflicts with the Virginia Indians. For much of the 17th century, English contact and conflict were mostly with the Algonquian peoples that populated the coastal regions, primarily the Powhatan Confederacy. Following …
Geography
The cultural geography of colonial Virginia gradually evolved, with a variety of settlement and jurisdiction models experimented with. By the late 17th century and into the 18th century, the primary settlement pattern was based on plantations (to grow tobacco), farms, and some towns (mostly ports or courthouse villages).
Government and law
In the initial years under the Virginia Company, the colony was governed by a council, headed by a council President. From 1611 to 1618, under the orders of Sir Thomas Dale, the settlers of the colony were under a regime of civil law that became known as Dale's Code.
Under a charter from the company in 1618, a new model of governance was put in place in 1619, which created a new House of Burgesses. On July 30, 1619, burgesses met at Jamestown Church as …
Economy
The entrepreneurs of the Virginia Company experimented with a number of means of making the colony profitable. The orders sent with the first colonists instructed that they search for precious metals (specifically gold). While no gold was found, various products were sent back, including pitch and clapboard. In 1608, early attempts were made at breaking the Continental hold on glassmaking through the creation of a glassworks. In 1619, the colonist built the first ironworks i…
Culture
England supplied the great majority of colonists. In 1608, the first Poles and Slovaks arrived as part of a group of skilled craftsmen. In 1619, the first Africans arrived. Many more Africans were imported as slaves, such as Angela. In the early 17th century, French Huguenots arrived in the colony as refugees from religious warfare.