
What did Woodrow Wilson's Fourteen Points do?
Fourteen Points, (Jan. 8, 1918), declaration by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson during World War I outlining his proposals for a postwar peace settlement.
What was the purpose of the Fourteen Points speech?
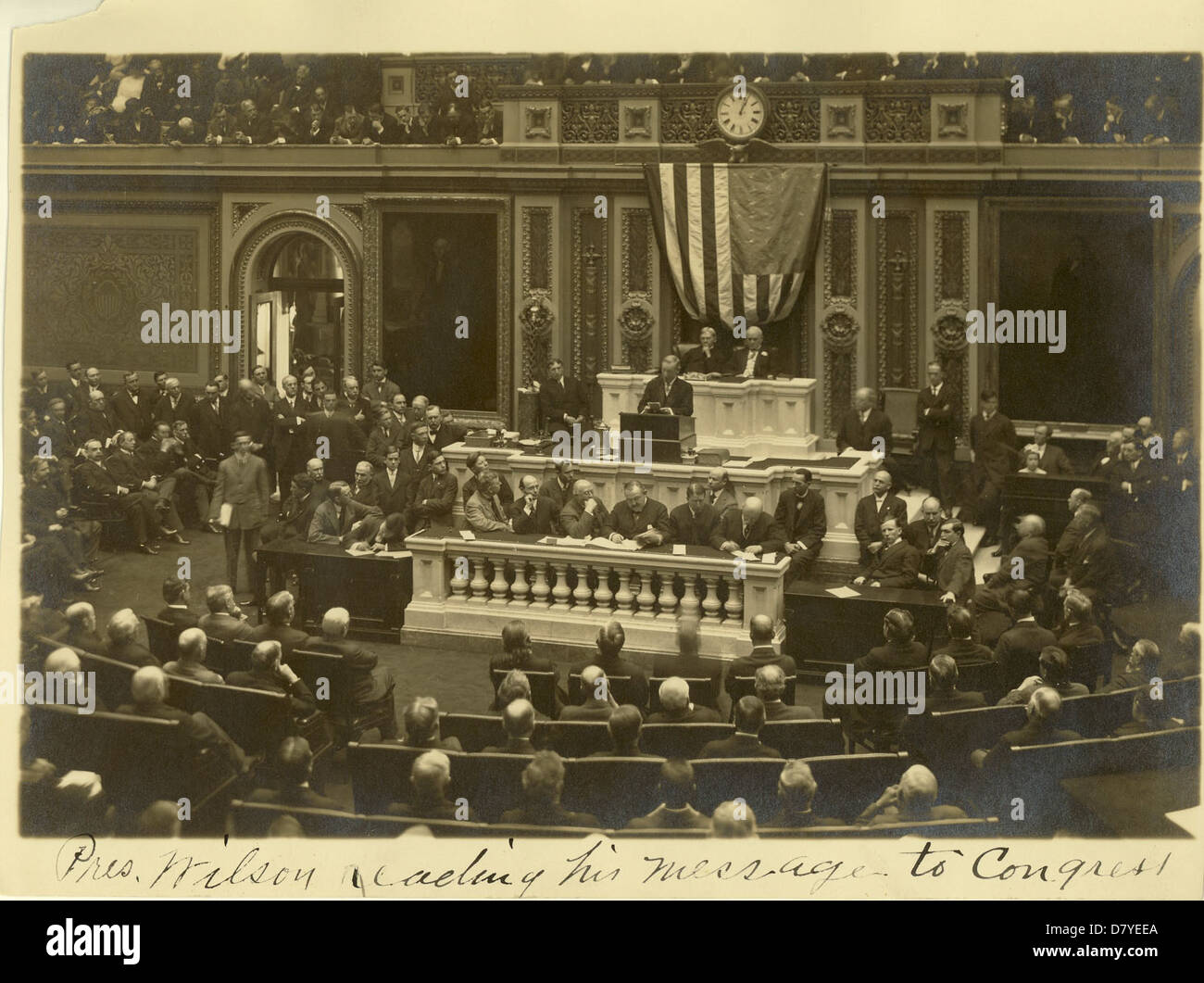
President Wilson delivers "Fourteen Points" speech The Fourteen Points speech of President Woodrow Wilson was an address delivered before a joint meeting of Congress on January 8, 1918, during which Wilson outlined his vision for a stable, long-lasting peace in Europe, the Americas and the rest of the world following World War I.
What were the 14 points in WW1?
What were the Fourteen Points? The Fourteen Points were a proposal made by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson in a speech before Congress on January 8, 1918, outlining his vision for ending World War I in a way that would prevent such a conflagration from occurring again.
What was the peace based on Wilson's 14 points?
As 1918 went on and the final German attacks failed, many in Germany became convinced they could no longer win the war, and a peace based on Wilson and his Fourteen Points seemed to be the best they would get; certainly, more than they could expect from France.
What was the 14 points?
What were the 14 points of the Fourteen Points?
Who sent the note to President Wilson?
What is the principle of free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial adjustment of all colonial claims?
See 1 more
About this website
What were Wilson's 14 points in simple terms?
What were the main points of Wilson's 14 points? Wilson's Fourteen Points primarily supported the idea of lasting peace. Many of the points focused on: trade equality, ending of secrete treaties, and alliances, freedom of the seas, and the establishment of the League of Nations.
What were Wilson's 14 points and what did they say?
The 14 points included proposals to ensure world peace in the future: open agreements, arms reductions, freedom of the seas, free trade, and self-determination for oppressed minorities.
What was Wilson's most important 14 points?
Point 14 was the most important on Woodrow Wilson's list; it advocated for an international organization to be established that would be responsible for helping to keep peace among the nations. This organization was later established and called the League of Nations.
What were the 14 points quizlet?
The 14 points included proposals to ensure world peace in the future: open agreements, arms reductions, freedom of the seas, free trade, and self-determination for oppressed minorities.
Was Wilson's 14 points successful?
Wilson subsequently used the Fourteen Points as the basis for negotiating the Treaty of Versailles that ended the war. Although the Treaty did not fully realize Wilson's unselfish vision, the Fourteen Points still stand as the most powerful expression of the idealist strain in United States diplomacy.
What point did Wilson think was the most important?
Wilson's final and, in his mind, most important point was the establishment of a “general association of nations” that would foster international cooperation, freedom, and peace.
Why did Wilson's 14 points fail?
As they began to debate the issues, the Allies could agree on little. Key elements of Wilson's Fourteen Points were dropped; reparations—the penalty that the losing countries must pay to the winners—could not be agreed upon; control of distant colonies was hotly contested.
What was Wilson's first point?
The Fourteen Points↑ Points one to four introduced general ideas that Wilson expected the nations of the world to adhere to in conducting foreign policy. The first point, open diplomacy, called for what today is referred to as transparency rather than secret alliances and partnerships for war.
Why did the 14 points Fail?
As they began to debate the issues, the Allies could agree on little. Key elements of Wilson's Fourteen Points were dropped; reparations—the penalty that the losing countries must pay to the winners—could not be agreed upon; control of distant colonies was hotly contested.
What were Woodrow Wilson's goals for peace?
From the outbreak of World War I, Woodrow Wilson pursued two goals: a non-punitive peace settlement to end the conflict and a reformation of world politics through an international peace-keeping organization to prevent such wars in the future.
What were the terms of the Treaty of Versailles?
Introduction. The Treaty of Versailles was signed by Germany and the Allied Nations on June 28, 1919, formally ending World War One. The terms of the treaty required that Germany pay financial reparations, disarm, lose territory, and give up all of its overseas colonies.
Which statement best explains the British and French response to the Fourteen Points plan?
Which statement best explains the British and French response to the “Fourteen Points” plan? France wanted revenge in the form of money and land, while Britain opposed the freedom of the seas.
What were the Fourteen Points?
The Fourteen Points were a proposal made by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson in a speech before Congress on January 8, 1918, outlining his vision for...
How did the Fourteen Points seek to change the world?
While half of the Fourteen Points addressed specific territorial issues between the combatant countries, the remainder were a vision for peace. The...
How important were the Fourteen Points?
In October 1918 Germany requested an armistice based on the Fourteen Points. Though the Armistice and Treaty of Versailles did not adhere to the id...
Why did the Fourteen Points fail?
In negotiating the Treaty of Versailles, the representatives of Britain, France, and Italy wanted to strengthen their own positions and felt it nec...
Why Did Woodrow Wilson's 14 Points Fail? - Reference.com
Woodrow Wilson's 14 points failed as France was seeking harsher punishments for Germany following WWI, the countries of Europe were interested in maintaining their imperial assets and he faced political opposition in the U.S. While not all of Wilson's points were implemented, they did result in the Treaty of Versailles being less harsh than it would have been without his input.
President Woodrow Wilson's 14 Points (1918) | National Archives
EnlargeDownload Link Citation: President Wilson's Message to Congress, January 8, 1918; Records of the United States Senate; Record Group 46; Records of the United States Senate; National Archives. View All Pages in the National Archives Catalog View Transcript In this January 8, 1918, address to Congress, President Woodrow Wilson proposed a 14-point program for world peace.
Fourteen Points summary | Britannica
Fourteen Points, Outline of proposals by Pres. Entertainment & Pop Culture; Geography & Travel; Health & Medicine; Lifestyles & Social Issues
What was the 14 points?
The Fourteen Points were a proposal made by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson in a speech before Congress on January 8, 1918, outlining his vision for ending World War I in a way that would prevent such a conflagration from occurring again.
What were the 14 points of the Fourteen Points?
The text of the Fourteen Points is as follows: 1. Open covenants of peace, open ly arrived at, after which there shall be no private ...
Who sent the note to President Wilson?
On October 3–4, 1918, Prince Maximilian of Baden, the German imperial chancellor, sent a note, via Switzerland, to President Wilson, requesting an immediate armistice and the opening of peace negotiations on the basis of the Fourteen Points.
What is the principle of free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial adjustment of all colonial claims?
A free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial adjustment of all colonial claims, based upon a strict observance of the principle that in determining all such questions of sovereignty the interests of the populations concerned must have equal weight with the equitable claims of the government whose title is to be determined.
What was the best peace based on Wilson's Fourteen Points?
As 1918 went on and the final German attacks failed, many in Germany became convinced they could no longer win the war, and a peace based on Wilson and his Fourteen Points seemed to be the best they would get ; certainly, more than they could expect from France.
What was the goal of the 14 points?
Wilson and the Germans hoped the Fourteen Points would be the framework for negotiations , but once again the competing claims of the other major nations – mainly Britain and France – undermined what Wilson had intended. However, Britain’s Lloyd George and France’s Clemenceau were keen to give in some areas and agreed to the League of Nations. Wilson was unhappy as the final agreements – including the Treaty of Versailles – differed markedly from his goals, and America refused to join the League. As the 1920s and 30s developed, and war returned worse than before, the Fourteen Points were widely considered to have failed.
What were the 14 points of the war?
The Fourteen Points Are Drafted. Once American had declared, a massive mobilization of troops and resources took place. In addition, Wilson decided America needed a firm set of war aims to help guide policy and, equally as importantly, begin to organize the peace in a manner which would be lasting.
What is absolute freedom of navigation?
Absolute freedom of navigation upon the seas, outside territorial waters, alike in peace and in war, except as the seas may be closed in whole or in part by international action for the enforcement of international covenants. III.
Who was unhappy with the League of Nations?
However, Britain’s Lloyd George and France’s Clemenceau were keen to give in some areas and agreed to the League of Nations. Wilson was unhappy as the final agreements – including the Treaty of Versailles – differed markedly from his goals, and America refused to join the League.
What is the purpose of the XIV covenant?
A general association of nations must be formed under specific covenants for the purpose of affording mutual guarantees of political independence and territorial integrity to great and small states alike.
What was the 14th point of the war?
In the 14th Point, Wilson envisioned a global organization to protect states and prevent future wars.
What is the 14 points of Woodrow Wilson's plan for peace?
November 11 is, of course, Veterans' Day.
Why did Wilson win the Nobel Peace Prize?
While Wilson won the 1919 Nobel Peace Prize for his Fourteen Points, he was disappointed by the punitive atmosphere of Versailles. He was also unable to convince Americans to join the League of Nations. Most Americans—in an isolationist mood after the war—did not want any part of a global organization which could lead them into another war.
What were the 14 points of the armistice?
The summarized Fourteen Points included: Open covenants of peace and transparent diplomacy. Absolute freedom of the seas.
What was the purpose of the Treaty of Versailles?
The Treaty of Versailles. The Fourteen Points served as the foundation for the Versailles Peace Conference that began outside of Paris in 1919. However, the Treaty of Versailles was markedly different than Wilson's proposal. France—which had been attacked by Germany in 1871 and was the site of most of the fighting in World War I—wanted ...
What is November 11?
Updated July 07, 2019. November 11 is, of course, Veterans' Day. Originally called "Armistice Day," it marked the ending of World War I in 1918. It also marked the beginning of an ambitious foreign policy plan by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson.
Did Wilson want to join the League of Nations?
Most Americans—in an isolationist mood after the war—did not want any part of a global organization which could lead them into another war. Wilson campaigned throughout the U.S. trying to convince Americans to accept the League of Nations. They never did, and the League limped toward World War II with U.S. support.
What was Wilson's 14 points?
In other ways, however, Wilson’s Fourteen Points played an essential role in world politics over the next several years. The speech was translated and distributed to the soldiers and citizens of Germany and Austria-Hungary and contributed to their decision to agree to an armistice in November 1918.
What was Wilson's purpose in his 14 points speech?
One of Wilson’s purposes in delivering the Fourteen Points speech was to present a practical alternative to the traditional notion of an international balance of power preserved by alliances among nations—belief in the viability of which had been shattered by World War I—and to the Bolshevik-inspired dreams of world revolution that at the time were gaining ground both within and outside of Russia.
What Were the Fourteen Points?
In his speech, Wilson itemized 14 strategies to ensure national security and world peace. Several points addressed specific territorial issues in Europe, but the most significant sections set the tone for postwar American diplomacy and the ideals that would form the backbone of U.S. foreign policy as the nation achieved superpower status in the early 20th century.
What was Wilson's proposal to the Allies?
Wilson’s proposal called for the victorious Allies to set unselfish peace terms with the vanquished Central Powers of World War I, including freedom of the seas, the restoration of territories conquered during the war and the right to national self-determination in such contentious regions as the Balkans. The devastation and carnage of the First ...
What did Wilson demand at the Paris Peace Conference?
At the Paris Peace Conference, Wilson had to contend with the leaders of the other victorious Allied nations, who disagreed with many of the Fourteen Points and demanded stiff penalties for Germany in the Treaty of Versailles.
What did Wilson advocate for?
He advocated equal trade conditions, arms reduction and national sovereignty for former colonies of Europe’s weakening empires.
What was the 14 points speech?
The Fourteen Points speech of President Woodrow Wilson was an address delivered before a joint meeting of Congress on January 8, 1918, during which Wilson outlined his vision for a stable, long-lasting peace in Europe, the Americas and the rest of the world following World War I.
What are the 14 points of peace?
The 14 points. 1. Open covenants of peace, openly arrived at. 2. Freedom of the seas. 3. The removal so far as possible of all economic barriers. 4. The reduction of national armaments to the lowest point consistent with domestic safety.
What was Wilson's dream?
Wilson’s dream of a new world order. Wilson wanted his 14 Points to lay the groundwork for the establishment of a new order based on democracy and self-determination for all people, including Germans. The proposals outlined in Wilson’s speech were the result of a secret series of studies he commissioned from a committee ...
Why did Clemenceau want to make sure Germany would be punished and weakened to the point that it would?
Clemenceau wanted to make sure Germany would be punished and weakened to the point that it would never be able to invade his country again.
What did Wilson promise when the war broke out?
When war broke out across Europe in 1914, Wilson pledged neutrality. He had initially hoped that America could be “impartial in thought as well as in action”.
When did Wilson declare war on Germany?
On 2 April 1917, Wilson appeared before Congress and called for a declaration of war against Germany, telling members:
Who was the German leader who sent a note to President Wilson requesting an immediate armistice and the opening of?
In early October 1918, Prince Maximilian of Baden, the German imperial chancellor, sent a note to President Wilson requesting an immediate armistice and the opening of peace negotiations on the basis of his 14 Points. The 1919 Paris Peace Conference saw the victorious Allied Powers meeting with the defeated Central Powers to officially declare ...
Who said the good Lord had only 10 points?
Upon hearing Wilson’s 14 Points, French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau was said to have remarked sarcastically, “The good Lord had only 10!” He believed Wilson’s peace terms were far too lenient to Germany.
What were Wilson's 14 points?
Almost a year later, this sentiment remained strong, articulated in a speech to Congress on January 8, 1918, where he introduced his Fourteen Points. Designed as guidelines for the rebuilding of the postwar world, the points included Wilson’s ideas regarding nations’ conduct of foreign policy, including freedom of the seas and free trade and ...
What was President Wilson's insistence on the inclusion of the League of Nations in the Treaty of Versailles?
President Wilson’s insistence on the inclusion of the League of Nations in the Treaty of Versailles (the settlement with Germany) forced him to compromise with Allied leaders on the other points.
What did Woodrow Wilson say about the Treaty of Versailles?
In his war address to Congress on April 2, 1917, President Woodrow Wilson spoke of the need for the United States to enter the war in part to “make the world safe for democracy.”.
What happened to Wilson when he was on tour?
Unfortunately, the president suffered a debilitating stroke while on tour.
Who inspects troops in London en route to Paris?
Woodrow Wilson inspecting troops in London en route to Paris.
What was Wilson's plan for the 14 points?from theworldwar.org
When Wilson left for Paris in December 1918, he was determined that the Fourteen Points, and his League of Nations (as the association of nations was known), be incorporated into the peace settlements.
What were the 14 points of the Fourteen Points?from britannica.com
The text of the Fourteen Points is as follows: 1. Open covenants of peace, open ly arrived at, after which there shall be no private ...
What was the purpose of the Fourteen Points speech?from theworldwar.org
In his war address to Congress on April 2, 1917, President Woodrow Wilson spoke of the need for the United States to enter the war in part to “make the world safe for democracy.”. Almost a year later, this sentiment remained strong, articulated in a speech to Congress on January 8, 1918, where he introduced his Fourteen Points.
What is the principle of free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial adjustment of all colonial claims?from britannica.com
A free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial adjustment of all colonial claims, based upon a strict observance of the principle that in determining all such questions of sovereignty the interests of the populations concerned must have equal weight with the equitable claims of the government whose title is to be determined.
Who sent the note to President Wilson?from britannica.com
On October 3–4, 1918, Prince Maximilian of Baden, the German imperial chancellor, sent a note, via Switzerland, to President Wilson, requesting an immediate armistice and the opening of peace negotiations on the basis of the Fourteen Points.
Who inspects troops in London en route to Paris?from theworldwar.org
Woodrow Wilson inspecting troops in London en route to Paris.
When did the 14 points come into force?
He declared these guidelines to the world in a message to Congress on January 8, 1918. When the war ended and the leaders of the victorious countries met to develop peace treaties and dole out punishments, the Fourteen Points were used as a basis for negotiations. The key features of the Fourteen Points include:
What Are the Fourteen Points?
As the leader of the free world, Wilson addressed a global audience as he outlined the characteristics of an everlasting peace. His words were echoed in the policies of every major Western power for the rest of the 20th century. But, how did Wilson find himself in the most influential position in the free world and how did he develop these characteristics of peace?
What are the 14 points of World War II?
Lesson Summary. The Fourteen Points are a list of moral guidelines that were developed by Woodrow Wilson as a response to the various causes of World War I .
How many points did Wilson have?
Learning Outcomes. Once you have completed the lesson, you should be able to: Summarize Wilson's Fourteen Points.
What did Wilson propose?
Wilson also proposed open trade between nations, national self-determination for oppressed peoples (the right for a group of people to determine their own governmental institutions because they view themselves as a distinct nation), and, finally, the development of the League of Nations.
What was the outcome of the 14 points?
The Outcome of the Fourteen Points. When the nations involved met to discuss the postwar world at the Paris Peace Conference, Britain, France, and Italy were mainly concerned with regaining their lost territories and establishing security on the borders with Germany.
What are the key features of the 14 points?
The key features of the Fourteen Points include: No secret agreements. Freedom of navigation on the seas. No economic barriers between nations. Disarmament of nations. Impartial decisions in regards to the colonies. The German Army was to leave Russia, and Russia would be able to develop its own political setup.
What was the 14 points?
The Fourteen Points were a proposal made by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson in a speech before Congress on January 8, 1918, outlining his vision for ending World War I in a way that would prevent such a conflagration from occurring again.
What were the 14 points of the Fourteen Points?
The text of the Fourteen Points is as follows: 1. Open covenants of peace, open ly arrived at, after which there shall be no private ...
Who sent the note to President Wilson?
On October 3–4, 1918, Prince Maximilian of Baden, the German imperial chancellor, sent a note, via Switzerland, to President Wilson, requesting an immediate armistice and the opening of peace negotiations on the basis of the Fourteen Points.
What is the principle of free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial adjustment of all colonial claims?
A free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial adjustment of all colonial claims, based upon a strict observance of the principle that in determining all such questions of sovereignty the interests of the populations concerned must have equal weight with the equitable claims of the government whose title is to be determined.
