
Timeline of the Crusades: Second Crusade 1144 - 1150
- December 24, 1144. —Muslim forces under the command of Imad ad-Din Zengi re-capture Edessa, originally taken by Crusaders under Baldwin of Boulogne in 1098.
- December 01, 1145. ...
- March 13, 1146. ...
- March 31, 1146. ...
- June 01, 1146. ...
- September 15, 1146. ...
- December 1146. ...
- April 13, 1147. ...
- October 1147. ...
- October 25, 1147. ...
What are facts about the Second Crusade?
The Second Crusade
- The Second Crusade - 1147 - 1149
- The Second Crusade and the Origin of the Religious Orders of Knighthood
- The Cause of the Second Crusade - The Fall and Massacre at Edessa
- The Preaching of St. Bernard
- The Second Crusade & King Louis VII of France and Conrad III of Germany
- The Failure of the Second Crusade
What really happened in the Crusades?
What really happened during the Crusades? Crusades against Muslims. By the ninth century, Muslims controlled much of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine) and... The first Crusade. The first Crusade was not one army, but four different contingents recruited to fight the Muslims. Second and subsequent ...
Who ended the Second Crusade?
The Second Crusade was led by two European kings—Louis VII of France and Conrad III of Germany. The German and French armies took separate routes to Anatolia, fighting skirmishes along the way, and both were defeated separately by the Seljuq Turks.
What ended Second Crusade?
promote the cause of a Second Crusade (1147–49) to quell the prospect of a great Muslim surge engulfing both Latin and Greek Orthodox Christians. The Crusade ended in failure because of Bernard’s inability to account for the quarrelsome nature of politics, peoples, dynasties, and adventurers.
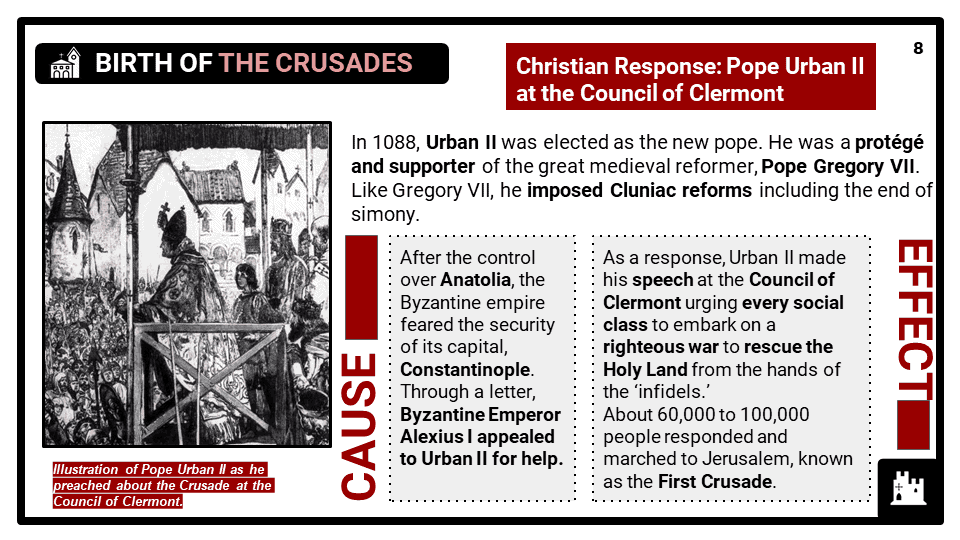
What major events happened in the Second Crusade?
Almeria in northern Spain is captured from the Moors during the Second Crusade. The capture of Lisbon by the Second Crusaders. At Dorylaion a force of Muslim Seljuk Turks attacks an army led by Conrad III during the Second Crusade. An army led by Louis VII defeats a Seljuk army in Asia Minor during the Second Crusade.
What were the key events of the crusade?
The First Crusade, called in response to a request for help from the Byzantine emperor Alexius Comnenus, was astonishingly successful. The Crusaders conquered Nicaea (in Turkey) and Antioch and then went on to seize Jerusalem, and they established a string of Crusader-ruled states.
What happened in the Second Crusade quizlet?
A German army was defeated in Anatolia. A French army, of 50,000 Crusaders, arrived in Jerusalem and attacked Damascus on their way to Edessa. Muslims from Edessa helped Damascus and beat back the Crusaders. The French army went home, ending the second Crusade.
What were the major events of the Third Crusades?
The Crusade captures Cyprus and the Kingdom of Cyprus is established. The Levantine coast from Tyre to Jaffa returned to Crusader control. The Crusaders recapture Tiberias and some inland territories from the Muslims....Levantine Crusader states:Kingdom of Jerusalem.County of Tripoli.Principality of Antioch.
When was the Second Crusade?
1147 – 1149Second Crusade / Period
What led to the creation of the Second Crusade?
The fall of the crusader city of Edessa to the Muslims was the spark that ignited the Second Crusade. The victory entrenched Zengi as leader of the Muslims in the Holy Land, a mantle that would be taken up by his son Nur ad-Din and then by Saladin.
What did the Second Crusade accomplish?
The Second Crusade (1147-1149 CE) was a military campaign organised by the Pope and European nobles to recapture the city of Edessa in Mesopotamia which had fallen in 1144 CE to the Muslim Seljuk Turks.
What was the outcome of the 2nd Crusade?
In the end, the crusade in the east was a failure for the crusaders and a victory for the Muslims.
When did the Second Crusade take place quizlet?
When did the second crusade happen? Second crusade was between 1146-1148.
Who won the Second Crusade?
Unlike the First Crusade, however, the Second Crusade was led by two of Europe's greatest rulers, King Louis VII of France and Emperor Conrad III of Germany. Louis enthusiastically supported the Crusade, but Conrad was reluctant at first and was won over only by the eloquence of St. Bernard.
What happened in the Third Crusade quizlet?
The third crusade happened in 1180 Salah al-Din formed the largest Muslim empire since the Seljuks. In 1187 Salah al-Din's armies captured Jerusalem. In 1191 King Richard I's army forced the surrender of the Palestine town of Acre.In 1192 KIng Richard I and Salah al-Din signed a peace treaty.
What was the result of the Third Crusade quizlet?
What were the results of the third Crusade? A peace treaty was signed: achieved the safety of Christian pilgrimages to Jerusalem, Muslims restored some territory, and Muslims strengthened their military position.
What was the outcome of the Fourth Crusade quizlet?
Outcome of the Fourth Crusade. > Constantinople was nearly destroyed, and all the valuable things were plundered and taken to Venice. A noble who was given a fief by his lord in exchange for loyalty.
When did the Second Crusade take place?
The capture of Lisbon by the Second Crusaders. 25 Oct 1147. At Dorylaion a force of Muslim Seljuk Turks attacks an army led by Conrad III during the Second Crusade . Dec 1147.
Who sacked Edessa?
Joscelin II's attempt to retake Edessa fails and the city is sacked by Nur ad-Din. The Second Crusade is launched to recapture Edessa for Christendom. It is not successful. Campaigns against pagans in the Baltic are led by Germanic and Danish nobles during the Second Crusade .
What was the significance of the Second Crusade?
They are seen as pivotal battles of the wider Reconquista, which would be completed in 1492. In the East the situation was much darker for the Christians.
Why was the Second Crusade started?
The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade (1096–1099) by King Baldwin I of Jerusalem in 1098. While it was the first Crusader state to be founded, it was also the first to fall.
What was the military system in the Middle East during the Second Crusade?
The basis of the military system in the Islamic Middle East was the iqta' system of fiefs, which supported a certain number of troops in every district.
What was the Pope's plan for the Second Crusade?
In the spring of 1147, the Pope authorized the expansion of the crusade into the Iberian peninsula, in the context of the Reconquista. He also authorized Alfonso VII of León and Castile to equate his campaigns against the Moors with the rest of the Second Crusade. In May 1147, the first contingents of crusaders left from Dartmouth in England for the Holy Land. Bad weather forced the ships to stop on the Portuguese coast, at the northern city of Porto on 16 June 1147. There they were convinced to meet with King Afonso I of Portugal.
What was the name of the monk who attacked Jews in the First Crusade?
As in the First Crusade, the preaching inadvertently led to attacks on Jews; a fanatical French monk named Rudolf was apparently inspiring massacres of Jews in the Rhineland, Cologne, Mainz, Worms and Speyer, with Rudolf claiming Jews were not contributing financially to the rescue of the Holy Land.
What were the three Crusader states?
After the First Crusade and the minor Crusade of 1101, there were three crusader states established in the east: the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the Principality of Antioch and the County of Edessa. A fourth, the County of Tripoli, was established in 1109.
When did the fall of Edessa happen?
The news of the fall of Edessa was brought back to Europe first by pilgrims early in 1145, and then by embassies from Antioch, Jerusalem and Armenia. Bishop Hugh of Jabala reported the news to Pope Eugene III, who issued the bull Quantum praedecessores on 1 December of that year, calling for a second crusade.
When did the Second Crusade take place?
The Second Crusade occurred from 1147 until 1149 CE and was carried out in response to the fall of the County of Edessa to Turkish forces. As stated above, the crusaders of the First Crusade had established several ‘ Crusader States ’ during the timeframe of the First Crusade, including the County of Edessa.
What was the second Crusade?
SECOND CRUSADE. The Crusades are one of the most significant events in the history of Europe and the Middle East. They were a series of religious wars carried out by Christian crusaders from Europe during the timeframe of the Middle Ages. Beginning in 1095 CE, the Crusades saw European knights and noblemen travel to the Middle East in an attempt ...
What was the significance of the Battle of Damascus?
This battle was vitally important to the Second Crusade, as they crusaders were defeated in the battle and suffered heavy losses.
Why did the Crusaders wear crosses?
In fact, many of the crusaders wore crosses on their clothing and armor as they made their pilgrimage to the Holy Land. This article details the events of the Second Crusade. Click here to read more information about the other major Crusades. The Second Crusade occurred from 1147 until 1149 CE and was carried out in response to the fall ...
Why did Pope Eugene III call for a crusade?
The fall of Edessa in 1144 caused Pope Eugene III to call for another crusade in order to recapture the territory, but also as a general call to protect Christian lands in the Middle East. Pope Eugene III called for the crusade on December 1st of 1145 and wanted it to be led by some of most power kings in Europe at the time.
Why did the Crusades begin?
Beginning in 1095 CE, the Crusades saw European knights and noblemen travel to the Middle East in an attempt to capture the Holy Land away from Muslim people that had controlled the region for the previous centuries. The term crusade means ‘cross’.
What was the name of the city that the Turkish invaded in response to the arrival of the European crusader
The Siege of Damascus. In response to the arrival of the European crusaders in the Holy Land, the Turks amassed a large amount of forces at the city of Damascus. Damascus was a Turkish controlled city north of Jerusalem. Both the French and German crusaders headed north from Jerusalem and attacked the Turkish forces in the Siege of Damascus.
What was the result of the failure of the Second Crusade?
Europe suffered greatly in terms of its economy and lack of recruits as a result of the failure of the Second Crusade, which was seen as marking the first sign of the fall of the Crusaders States in the Middle East.
What was the second crusade?
The Second Crusade took place between 1147 and 1149 and was instigated by Pope Eugene (Eugenius) III in a bid to defeat the Muslims who were still threatening to retake control of the Holy Lands. A second crusade was considered necessary due to the capture of the County of Edessa in 1144, which meant ...
Why was the second Crusade necessary?
A second crusade was considered necessary due to the capture of the County of Edessa in 1144, which meant that the crusader states were vulnerable to attack.
What happened to Jerusalem after the Second Crusade?
Following the failure of the Second Crusade, Jerusalem was also left without adequate protection, something which ultimately led to the demand for the Third Crusade. See also: The Third Crusade.
Who defeated the Turks in the Second Crusade?
However, upon the arrival of Nur al-Din and his armies, both Louis VII of France and Conrad III of Germany were defeated by the Turks and abandoned their siege, ending the Second Crusade.
What was Conrad's first attack on the Seljuk Turks?
Conrad launched an initial attack on the Seljuk Turks capital, Iconium, while the French attacked another target in Anatolia. This splitting up gave the Turks a chance to march at speed from one location to the next without being outnumbered by the crusade and overwhelmed.
Why did the Second Crusade fail?
…promote the cause of a Second Crusade (1147–49) to quell the prospect of a great Muslim surge engulfing both Latin and Greek Orthodox Christians. The Crusade ended in failure because of Bernard’s inability to account for the quarrelsome nature of politics, peoples, dynasties, and adventurers.
What was the significance of the Siege of Damascus?
In Siege of Damascus. The defeat of the Second Crusade at Damascus ensured that the Christian crusader states in the Holy Land would remain on the defensive for the foreseeable future.
What were the major events of the Crusades?
Timeline of Major Events of the Crusades. Turks migrate from central Asia to southwest Asia, conquer Persia, and invade Armenia and Iraq, finally capturing Baghdad, the Abbasid capital city. Turks invade Byzantine territory in Asia Minor (today’s Turkey); Turkic forces take Jerusalem from the Fatimid dynasty of North Africa.
Where did the Second Crusade take place?
1147-1149. The Second Crusade begins, which includes Crusades in parts of Muslim-ruled Spain, Eastern Germany and the East (Outremer in French) 1147. Spanish Crusaders take Lisbon from Muslim rule.
When did the Crusaders arrive in Jerusalem?
June 7, 1099. Main body of Crusaders arrives at Jerusalem. July 15, 1099. Crusaders seize and sack the city of Jerusalem and massacre Muslims, Eastern Christians, and Jews; Godfrey elected ruler of the city.
Who led the Fifth Crusade?
Fifth Crusade begins; Invasion of Egypt under the rule of al-Malik al-Kamil is led by Cardinal Pelagius; Crusaders besiege Damietta and try to Crusaders try take Cairo; Al-Kamil's forces and rising Nile isolates and defeats Crusader army; Al-Kamil provides bread and supplies to save Crusader army from starvation. 1219.
Which city was captured by the Christian forces under Alfonso VI. 1096?
1085. Antioch in northern Syria conquered by Turks; in Spain, the Muslim city of Toledo is captured by Christian forces under Alfonso VI. 1096.
Who took Aleppo and Damascus?
Mongols under Hülegü take Aleppo and Damascus; Mongol ruler dies and Hulegu returns to Asia, relieving invasion threat to Europe. September 3, 1260. Mamluk armies defeat Mongols at the Battle of 'Ayn Jalut (Goliath Spring), and take city of Damascus; Baybars becomes ruler of Egypt. July 25, 1261.
Who took Jerusalem's ruler?
Kings Richard and Philip take the city of Acre and name Jerusalem's ruler; Philip leaves for home, while Richard takes Arsuf and Jaffa and fortifies Ascalon. September 2, 1192. Richard and Saladin end their fighting with a treaty, and Richard leaves for home in England. 1193.

Overview
The Second Crusade (1147–1150) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade (1096–1099) by King Baldwin I of Jerusalem in 1098. While it was the first Crusader state to be founded, it was also the first to fall.
Background: the fall of Edessa, preparations
After the First Crusade and the minor Crusade of 1101, there were three crusader states established in the east: the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the Principality of Antioch and the County of Edessa. A fourth, the County of Tripoli, was established in 1109. Edessa was the most northerly of these, and also the weakest and least populated; as such, it was subject to frequent attacks from the surrounding M…
Related European crusades
When the Second Crusade was called, many south Germans volunteered to crusade in the Holy Land. The north German Saxons were reluctant. They told St Bernard of their desire to campaign against pagan Slavs at an Imperial Diet meeting in Frankfurt on 13 March 1147. Approving of the Saxons' plan, Eugenius issued a papal bull known as the Divina dispensatione on 13 April. This bull stat…
Forces
The professional soldiers of the Muslim states, who were usually ethnic Turks, tended to be very well-trained and equipped. The basis of the military system in the Islamic Middle East was the iqta' system of fiefs, which supported a certain number of troops in every district. In the event of war, the ahdath militias, based in the cities under the command of the ra’is (chief), and who were usually ethnic
Crusade in the East
Joscelin II retook the town of Edessa and besieged the citadel following Zengi's murder, but Nur ad-Din defeated him in November 1146. On 16 February 1147, the French crusaders met at Étampes to discuss their route. The Germans had already decided to travel overland through Hungary; they regarded the sea route as politically impractical because Roger II of Sicily was an enemy of Conrad. M…
Aftermath
Each of the Christian forces felt betrayed by the other. A new plan was made to attack Ascalon and Conrad took his troops there, but no further help arrived, due to the lack of trust that had resulted from the failed siege. This mutual distrust would linger for a generation due to the defeat, to the ruin of the Christian kingdoms in the Holy Land. After quitting Ascalon, Conrad returned to Constan…
Notes
1. ^ Norwich 1995, pp. 94–95.
2. ^ Magdalino 1993, p. 52.
3. ^ Riley-Smith 2005, pp. 50–53.
4. ^ Tyerman 2006, pp. 185–189.
Further reading
• Osbernus. De expugniatione Lyxbonensi. The Conquest of Lisbon. Edited and translated by Charles Wendell David. Columbia University Press, 1936.
• Odo of Deuil. De profectione Ludovici VII in orientem. Edited and translated by Virginia Gingerick Berry. Columbia University Press, 1948.
• Otto of Freising. Gesta Friderici I Imperatoris. The Deeds of Frederick Barbarossa. Edited and translated by Charles Christopher Mierow. Columbia University Press, 19…
• Osbernus. De expugniatione Lyxbonensi. The Conquest of Lisbon. Edited and translated by Charles Wendell David. Columbia University Press, 1936.
• Odo of Deuil. De profectione Ludovici VII in orientem. Edited and translated by Virginia Gingerick Berry. Columbia University Press, 1948.
• Otto of Freising. Gesta Friderici I Imperatoris. The Deeds of Frederick Barbarossa. Edited and translated by Charles Christopher Mierow. Columbia University Press, 1953.