How long did El Niño last in the 1990s?
However, El Niño did emerge later in the year, and it persisted for 7 months. The bigger surprise was 1992, which was the coldest year of the 1990s despite being an El Niño year. The 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo was likely to blame.
What is El Nino and La Niña?
What is El Niño? What is La Niña? An El Niño condition occurs when surface water in the equatorial Pacific becomes warmer than average and east winds blow weaker than normal. The opposite condition is called La Niña. During this phase of ENSO, the water is cooler than normal and the east winds are stronger.
What are the best books about El Niño?
Caviedes, César N. (2001). El Niño in History: Storming Through the Ages. Gainesville: University Press of Florida. ISBN 978-0-8130-2099-0. Fagan, Brian M. (1999). Floods, Famines, and Emperors: El Niño and the Fate of Civilizations.
What is El Niño and why is it dangerous?
As El Niño brings rain to South America, it brings droughts to Indonesia and Australia. These droughts threaten the region’s water supplies, as reservoirs dry and rivers carry less water. Agriculture, which depends on water for irrigation, is threatened.

What year was El Niño the strongest?
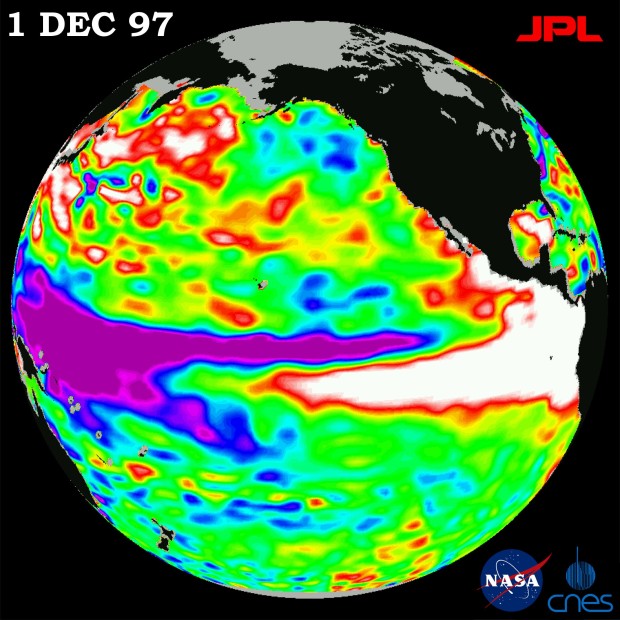
1997-98El Niño Frequency The strongest El Niño event was in the winter of 1997-98, where the ONI peaked at 2.3. Oceanic Niño Index since 1950.
In which year was the impact of El Niño most felt?
In 1992, El Niño caused the region's worst drought in a century, affecting around 86 million people, 72 percent of the population.
What decade had the most El Niño years?
There are three factors though that made reporting of the 1997-98 El Niño different from other recent El Niño events. The 1997-98 El Niño was the strongest on record at that time, and it developed more rapidly than any El Niño of the past 40 years.
Which El Niño event was considered the most powerful one?
The 1997–1998 El Niño was regarded as one of the most powerful El Niño–Southern Oscillation events in recorded history, resulting in widespread droughts, flooding and other natural disasters across the globe.
Is 2021 an El Niño year?
(WSFA) - It's back again! La Niña conditions have officially developed and are expected to remain in place through the entirety of winter 2021-2022. So what exactly does that mean? La Niña means we're in the negative phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation, or ENSO for short.
Is 2022 an El Niño year?
Most current climate model predictions expect the negative Niño-3.4 anomaly will weaken over the summer and strengthen in the fall. The range of forecasts for departures from average temperatures in the Niño-3.4 region of the tropical Pacific in 2022 from the North American Multi-Model Ensemble (NMME).
Is El Niño becoming more frequent?
Summary: Global weather fluctuations called El Niño events are likely to become more frequent by 2040, a new study shows. Global weather fluctuations called El Niño events are likely to become more frequent by 2040, a new study shows.
Is 2020 El Niño year?
Previous La Ninas occurred during the winter of 2020-2021 and 2017-2018, and an El Nino developed in 2018-2019. When neither climate pattern is present, ENSO is neutral and does not influence global climate patterns. Learn more: Meet a NOAA scientist behind the La Nina forecast.
Is 2011 an El Niño year?
Ranked El Niño Events by 3-Month SeasonRankDJFFMA8192619589195819191018972010112010197321 more rows
When was the strongest La Niña?
The 2010–2012 La Niña event was one of the strongest on record. It caused Australia to experience its wettest September on record in 2010, and its second-wettest year on record in 2010....2010–2012 La Niña event.DissipatedApril 2012DamageSignificantAreas affectedThe Pacific Ocean and surrounding areas7 more rows
Was 2015 an El Niño?
The 2015-16 event possessed most of the classic defining features of an El Niño event. Water temperatures in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean were more than 2° C (3.6° F) above average, as they had been during previous strong El Niño events in 1982-83 and 1997-98.
What year was El Niño in California?
El Niño events in 1982-1983 and 1997-1998 drenched the West Coast with record rain. The last El Nino, a weak one, occurred in 2018-2019.
What was the most severe climate oscillation in the world in 1997?
The 1997–1998 El Niño , the most-recent severe climate oscillation, fueled the formation of 18 tropical systems in the South Pacific, but only Susan and Ron reached the category 4 or 5 levels ( Hoarau et al. 2008 ).
When was the largest storm in the Pacific Northwest?
The largest storm developed on 2–4 March 1999, generating a 46-foot (14.1-m) wave. Hence, as stated by Allan and Komar ( 2002 ), “the Pacific Northwest received a ‘one-two punch’ from the successive El Niño and La Niña winters.”. NASA, Jacques Descloitres.
What is the name of the Atlantic nio?
His name is Atlantic Niño, and he has an uncanny resemblance to his big brother: Like El Niño, Atlantic Niño is characterized by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the eastern equatorial basin and weaker-than-average trade winds throughout the east-central equatorial Atlantic.
What are some of ENSO's impacts?
Ecosystems and human communities can be positively or negatively affected. For example, in the Southern United States, during the fall through spring, El Niño usually causes increased rainfall and sometimes destructive flooding. La Niña, however, usually causes drier weather in the South, but the Northwest tends to be colder and wetter than average. Even though El Niño occurs in the Pacific Ocean, it often reduces the number of hurricanes that form in the Atlantic Ocean. Conversely, La Niña events tend to be related to an increase in the number of Atlantic hurricanes.
How does ENSO help students?
ENSO provides teachers with the opportunity to have students discover ways that the oceanic and atmospheric systems interact and how those interactions can impact ecosystems and human society. The resources in this collection can be used to help learn about the basics of ENSO, the inter-relationship of Earth systems, the consequences of these interactions, and how to use and analyze data. These resources can be used to teach students how scientists study the complexity of the Earth’s systems and why better El Niño/La Niña forecasts can benefit agriculture, natural resource managers and human communities.
How does ENSO affect humans?
How ENSO impacts humans. El Niño, La Niña, and the neutral condition all produce important consequences for people and ecosystems across the globe. The interactions between the ocean and atmosphere alters weather around the world and can result in severe storms or mild weather, drought or flooding. Beyond “just” influencing ...
What Is ENSO
El Niño and La Niña are the warm and cool phases of a recurring climate pattern across the tropical Pacific—the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, or “ENSO” for short. The pattern shifts back and forth irregularly every two to seven years, and each phase triggers predictable disruptions of temperature, precipitation.
U.S. Impacts
El Niño is anchored in the tropical Pacific, but it affects climate "downstream" in the United States. In the summer, El Niño's primary influence on U.S. climate is on the hurricane season in both the eastern Pacific and the Atlantic. In winter, it influences the jet stream and the path of storms that move from the Pacific over the United States.
Global Impacts
El Niño and La Niña have their strongest influence on global climate during the Northern Hemisphere winter. During La Niña winters, the southern tier of the United States is often drier than normal. Northern Australia, Indonesia, and the Philippines are often wetter than normal.
Understanding the ENSO Alert System
On the second Thursday of each month, scientists with NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center in collaboration with forecasters at the International Research Institute for Climate and Society (IRI) release an official update on the status of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Here is a description of the categories and criteria they use.
Overview
Occurrences
El Niño events are thought to have been occurring for thousands of years. For example, it is thought that El Niño affected the Moche in modern-day Peru, who sacrificed humans in order to try to prevent the rains.
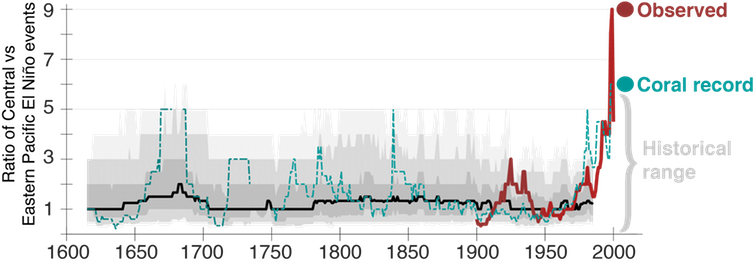
It is thought that there have been at least 30 El Niño events since 1900, with the 1982–83, 1997–98 and 2014–16 events among the strongest on record. Since 2000, El Niño events have …
Concept
Originally, the term El Niño applied to an annual weak warm ocean current that ran southwards along the coast of Peru and Ecuador at about Christmas time. However, over time the term has evolved and now refers to the warm and negative phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation and is the warming of the ocean surface or above-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. This warming causes a shift in the atmospheric circulation with r…
Cultural history and prehistoric information
ENSO conditions have occurred at two- to seven-year intervals for at least the past 300 years, but most of them have been weak. Evidence is also strong for El Niño events during the early Holocene epoch 10,000 years ago.
El Niño may have led to the demise of the Moche and other pre-Columbian Peruvian cultures. A recent study suggests a strong El Niño effect between 1789 and 1793 caused poor crop yields i…
Diversity
It is thought that there are several different types of El Niño events, with the canonical eastern Pacific and the Modoki central Pacific types being the two that receive the most attention. These different types of El Niño events are classified by where the tropical Pacific sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies are the largest. For example, the strongest sea surface temperature …
Effects on the global climate
El Niño affects the global climate and disrupts normal weather patterns, which as a result can lead to intense storms in some places and droughts in others.
Most tropical cyclones form on the side of the subtropical ridge closer to the equator, then move poleward past the ridge axis before recurving into the main belt of the Westerlies. Areas west of Japan and Korea tend to experience many f…
Regional impacts
Observations of El Niño events since 1950 show that impacts associated with El Niño events depend on the time of year. However, while certain events and impacts are expected to occur during events, it is not certain or guaranteed that they will occur. The impacts that generally do occur during most El Niño events include below-average rainfall over Indonesia and northern South America, whi…
Socio-ecological effects for humanity and nature
When El Niño conditions last for many months, extensive ocean warming and the reduction in easterly trade winds limits upwelling of cold nutrient-rich deep water, and its economic effect on local fishing for an international market can be serious.
More generally, El Niño can affect commodity prices and the macroeconomy of different countries. It can constrain the supply of rain-driven agricultural commodities; reduce agricultura…