
When light is shone into right eye the pupil constricts?
When light is shone into right eye, right pupil constricts. Direct reflex of the right pupil is unaffected, The right afferent limb, right CN II, and the right efferent limb, right CN III, are both intact. The left consensual reflex is lost. When the right eye is stimulated by light, left pupil does not constrict consensually.
What happens when light is shone into one eye?
Light shone into one eye will cause both pupils to constrict. The pupil is the dark circular opening in the center of the iris and is where light enters the eye. By analogy with a camera, the pupil is equivalent to aperture, whereas the iris is equivalent to the diaphragm.
How does the pupillary light reflex regulate the intensity of light?
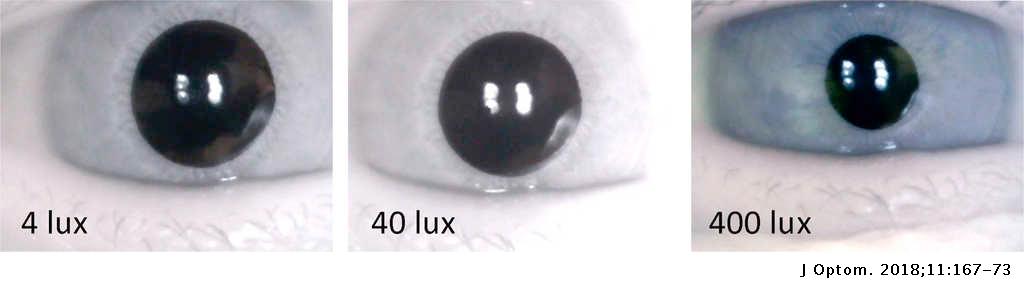
A greater intensity of light causes the pupil to constrict (miosis/myosis; thereby allowing less light in), whereas a lower intensity of light causes the pupil to dilate (mydriasis, expansion; thereby allowing more light in). Thus, the pupillary light reflex regulates the intensity of light entering the eye.
What muscle constricts the pupil in response to light?
The pupillary light reflex constricts the pupil in response to light, and pupillary constriction is achieved through the innervation of the iris sphincter muscle. NCBI

What happens to the pupil when there is bright light?
In dim light, your pupil expands to allow more light to enter your eye. In bright light, it contracts. Your pupil can range in diameter from 1/16 inch (1.5 mm) to more than 1/3 inch (8 mm).
Why do pupils constrict in light?
The pupil is the part of your eye that controls how much light gets in. In bright light, your pupils get smaller (constrict) to limit the amount of light that enters. In the dark, your pupils get bigger (dilate). That allows more light in, which improves night vision.
How does the pupil reflex work?
The pupillary light reflex is an autonomic reflex that constricts the pupil in response to light, thereby adjusting the amount of light that reaches the retina. Pupillary constriction occurs via innervation of the iris sphincter muscle, which is controlled by the parasympathetic system.
When a penlight is shined into one eye the opposite eye should?
To perform this test, shine a penlight into one eye to attain maximum pupil constriction, then quickly switch the light source to the other eye and back again. Normally, the second eye should respond with the same pupillary constriction as the first eye as a result of a consensual response.
Why do pupils dilate and constrict?
Muscles in the colored part of your eye, called the iris, control your pupil size. Your pupils get bigger or smaller, depending on the amount of light around you. In low light, your pupils open up, or dilate, to let in more light. When it's bright, they get smaller, or constrict, to let in less light.
How does the pupil constrict?
a) When the iris sphincter muscle (green) contracts, it tightens the inner side of the iris, thus causing the pupil to constrict. b) When the iris dilator muscle (yellow) contracts, it pulls the inner side of the iris outward, thus causing the pupil to dilate.
What is the pupillary response of the right eye when a light was shone into the pupil?
The right consensual reflex is intact. When the left eye is stimulated by light, the right pupil constricts, because the afferent limb on the left and the efferent limb on the right are both intact. The right direct reflex is intact. When light is shone into right eye, right pupil constricts.
What does pupil reaction indicate?
Any changes in the patient's pupil reaction, size or shape, together with other neurological signs, are an indication of raised intracranial pressure (ICP) and compression of the optic nerve.
What was the response of the pupil in the opposite eye?
The consensual response is the change in pupil size in the eye opposite to the eye to which the light is directed (e.g., if the light is shone in the right eye, the left pupil also constricts consensually).
Why does the pupil constrict when looking at a near object?
The pupil constricts in order to prevent strongly diverging light rays hitting the periphery of the cornea and the lens from entering the eye and creating a blurred image.
What does it mean if pupils are not reactive to light?
Pupils that do not respond to light or other stimuli are called fixed pupils. Often, fixed pupils are also dilated pupils. Abnormally shaped pupils can occur as a result of abnormalities of prenatal development or injury.
Why does the pupil constrict in bright light conditions quizlet?
Why must the pupil constrict in high light levels? To avoid damage to the retina.
What is consensual pupillary reflex?
A consensual pupillary reflex is response of a pupil to light that enters the contralateral (opposite) eye. Thus there are four types of pupillary light reflexes, based on this terminology of absolute (left versus right) and relative (same side versus opposite side) laterality: Left direct pupillary reflex is the left pupil's response ...
How does the pupillary reflex work?
The pupillary response to light is not purely reflexive, but is modulated by cognitive factors, such as attention, awareness, and the way visual input is interpreted. For example, if a bright stimulus is presented to one eye, and a dark stimulus to the other eye, perception alternates between the two eyes (i.e., binocular rivalry ): Sometimes the dark stimulus is perceived, sometimes the bright stimulus, but never both at the same time. Using this technique, it has been shown the pupil is smaller when a bright stimulus dominates awareness, relative to when a dark stimulus dominates awareness. This shows that the pupillary light reflex is modulated by visual awareness. Similarly, it has been shown that the pupil constricts when you covertly (i.e., without looking at) pay attention to a bright stimulus, compared to a dark stimulus, even when visual input is identical. Moreover, the magnitude of the pupillary light reflex following a distracting probe is strongly correlated with the extent to which the probe captures visual attention and interferes with task performance. This shows that the pupillary light reflex is modulated by visual attention and trial-by-trial variation in visual attention. Finally, a picture that is subjectively perceived as bright (e.g. a picture of the sun), elicits a stronger pupillary constriction than an image that is perceived as less bright (e.g. a picture of an indoor scene), even when the objective brightness of both images is equal. This shows that the pupillary light reflex is modulated by subjective (as opposed to objective) brightness.
What is the pupillary reflex?
Pupillary reflex is synonymous with pupillary response, which may be pupillary constriction or dilation. Pupillary reflex is conceptually linked to the side (left or right) of the reacting pupil, and not to the side from which light stimulation originates. Left pupillary reflex refers to the response of the left pupil to light, ...
How many segments are there in the pupillary light reflex?
Referring to the neural pathway schematic diagram, the entire pupillary light reflex system can be visualized as having eight neural segments, numbered 1 through 8. Odd-numbered segments 1, 3, 5, and 7 are on the left. Even-numbered segments 2, 4, 6, and 8 are on the right. Segments 1 and 2 each includes both the retina and the optic nerve (cranial Nerve #2). Segments 3 and 4 are nerve fibers that cross from the pretectal nucleus on one side to the Edinger-Westphal nucleus on the contralateral side. Segments 5 and 6 are fibers that connect the pretectal nucleus on one side to the Edinger-Westphal nucleus on the same side. Segments 3, 4, 5, and 6 are all located within a compact region within the midbrain. Segments 7 and 8 each contains parasympathetic fibers that courses from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus, through the ciliary ganglion, along the oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve #3), to the ciliary sphincter, the muscular structure within the iris.
How many efferent limbs are there in the afferent limb?
Each afferent limb has two efferent limbs, one ipsilateral and one contralateral. The ipsilateral efferent limb transmits nerve signals for direct light reflex of the ipsilateral pupil. The contralateral efferent limb causes consensual light reflex of the contralateral pupil.
What is the PLR in the eye?
The pupillary light reflex ( PLR) or photopupillary reflex is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity ( luminance) of light that falls on the retinal ganglion cells of the retina in the back of the eye, thereby assisting in adaptation of vision to various levels of lightness/darkness.
What is the difference between left and right pupillary reflex?
Left pupillary reflex refers to the response of the left pupil to light, regardless of which eye is exposed to a light source . Right pupillary reflex means reaction of the right pupil, whether light is shone into the left eye, right eye, or both eyes. When light is shone into only one eye and not the other, it is normal for both pupils ...
Overview
The pupillary light reflex (PLR) or photopupillary reflex is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity (luminance) of light that falls on the retinal ganglion cells of the retina in the back of the eye, thereby assisting in adaptation of vision to various levels of lightness/darkness. A greater intensity of light causes the pupil to constrict (miosis/myosis; thereby allowing less light in), whereas a lower intensity of light causes the pupil to dilate (mydri…
Terminology
The pupil is the dark circular opening in the center of the iris and is where light enters the eye. By analogy with a camera, the pupil is equivalent to aperture, whereas the iris is equivalent to the diaphragm. It may be helpful to consider the Pupillary reflex as an 'Iris' reflex, as the iris sphincter and dilator muscles are what can be seen responding to ambient light. Whereas, the pupil is the passive opening formed by the active iris. Pupillary reflex is synonymous with pupillary response…
Neural pathway anatomy
The pupillary light reflex neural pathway on each side has an afferent limb and two efferent limbs. The afferent limb has nerve fibers running within the optic nerve (CN II). Each efferent limb has nerve fibers running along the oculomotor nerve (CN III). The afferent limb carries sensory input. Anatomically, the afferent limb consists of the retina, the optic nerve, and the pretectal nucleus in the mid…
Clinical significance
Pupillary light reflex provides a useful diagnostic tool for testing the integrity of the sensory and motor functions of the eye. Emergency physicians routinely test pupillary light reflex to assess brain stem function. Abnormal pupillary reflex can be found in optic nerve injury, oculomotor nerve damage, brain stem lesion (including brain stem death), and depressant drugs, such as barbiturates. Exam…
Cognitive influences
The pupillary response to light is not purely reflexive, but is modulated by cognitive factors, such as attention, awareness, and the way visual input is interpreted. For example, if a bright stimulus is presented to one eye, and a dark stimulus to the other eye, perception alternates between the two eyes (i.e., binocular rivalry): Sometimes the dark stimulus is perceived, sometimes the bright stimulus, but never both at the same time. Using this technique, it has been shown the pupil is s…
Mathematical model
Pupillary light reflex is modeled as a physiologically-based non-linear delay differential equation that describes the changes in the pupil diameter as a function of the environment lighting:
where is the pupil diameter measured in millimeters and is the luminous intensity reaching the retina in a time , which can be described as : luminance reaching the eye in lumens/mm times the pupil area in mm . is the pupillary latency, a time delay between the instant in which the light puls…
See also
• Pupil
• Pupillary response
• Slit lamp
External links
• Animation of pupillary light reflex
• Reflex,+Pupillary at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
• A pupil examination simulator, demonstrating the changes in pupil reactions for various nerve lesions.