
| Babylonia 𒆳𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠 (Akkadian) māt Akkadī | |
|---|---|
| 1895 BC–539 BC | |
| The extent of the Babylonian Empire at the start and end of Hammurabi's reign, located in what today is modern day Iraq | |
| Capital | Babylon |
| Official languages | Akkadian Sumerian Aramaic |
When did the Babylonian Empire begin and end?
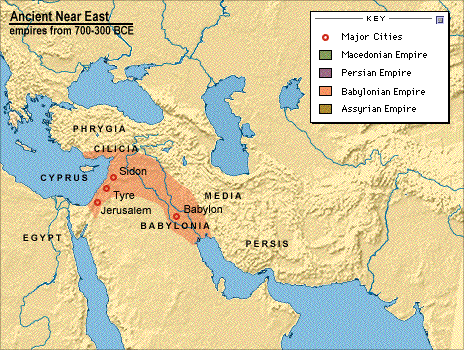
The first Babylonian Empire began in the 18th century BCE and lasted for about two centuries. The famous Code of Hammurabi was written during this time. The second Babylonian Empire took shape many centuries later, in the 7th century BCE. It was much larger than its predecessor but did not last as long. The Persians soon conquered the empire.
When did the fall of Babylon take place?
Print. The fall of Babylon is a historical event that occurred in 539 BC. This event saw the conquest of Babylon by the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great and marked the end of the Neo-Babylonian Empire.
When did the Babylonian captivity end?
Babylonian Captivity, also called Babylonian Exile, the forced detention of Jews in Babylonia following the latter’s conquest of the kingdom of Judah in 598/7 and 587/6 bce. The captivity formally ended in 538 bce, when the Persian conqueror of Babylonia, Cyrus the Great, gave the Jews permission to return...
What happened to Babylonia?
The Persians, under Cyrus the Great, captured Babylonia from Nebuchadrezzar’s last successor Nabonidus in 539 bce. Thereafter, Babylonia ceased to be independent, passing eventually in 331 bce to Alexander the Great, who planned to make Babylon the capital of his empire and who died in Nebuchadrezzar’s palace.
When did the Babylonian civilization begin?
It was founded around 2300 B.C. by the ancient Akkadian-speaking people of southern Mesopotamia.
How long did Babylon civilization last?
It lasted from roughly 1830 BC to 1531 BC. From 1770 to 1670 BC, its capital city, Babylon, was perhaps the largest city in the world. The last king, Samsu-Ditana was overthrown after a Hittite invasion. So, the First Babylonian Dynasty lasted roughly 300 years.
When was Babylon founded and destroyed?
After the Assyrians had destroyed and then rebuilt it, Babylon became the capital of the short-lived Neo-Babylonian Empire, a neo-Assyrian successor state, from 609 to 539 BC....Babylon.Part ofBabyloniaArea9 km2 (3.5 sq mi)HistoryFoundedc. 1894 BCAbandonedc. AD 100023 more rows
What caused the fall of Babylon?
In 539 BCE the empire fell to the Persians under Cyrus the Great at the Battle of Opis. Babylon's walls were impregnable and so the Persians cleverly devised a plan whereby they diverted the course of the Euphrates River so that it fell to a manageable depth.
What is Babylon now called today?
The ancient city lies within the modern-day city of Hillah, the center of Babel Governorate, Iraq, about 83 kilometers south of Baghdad, the Iraqi capital city.
What race were the Babylonians?
Henry Rawlinson supported Sayce's views and further asserted that the ancient Babylonians knew of two principle races, as found in their inscriptions: "the Adamu, or dark race and the Sarku, or light race". The Sarku (or Sarcu) Sayce and Rawlinson maintained were the Semitic colonists who were white skinned.
Is Babel and Babylon the same?
89) informs us that Babylon is “the Greek form of the Hebrew word 'babel,' which was closely allied to, and probably derived from, the Akkadian 'babilu' or 'gate of God,'” leaving out the “confusion” aspect altogether.
How did Babylon fall in the Bible?
Babylon was a gold cup in the LORD's hand; she made the whole earth drunk. The nations drank her wine; therefore they have now gone mad. Babylon will suddenly fall and be broken.
When did the Babylonian Empire end?
After Hammurabi's death, the Babylonian empire declined until 1595 bce, when the Hittite invader Mursil I unseated the Babylonian king Samsuditana, allowing the Kassites from the mountains east of Babylonia to assume power and establish a dynasty that lasted 400 years.
What country is Babylon today?
Where is Babylon? Babylon, one of the most famous cities from any ancient civilisation, was the capital of Babylonia in southern Mesopotamia. Today, that's about 60 miles south of Baghdad, Iraq.
What race were the Babylonians?
Henry Rawlinson supported Sayce's views and further asserted that the ancient Babylonians knew of two principle races, as found in their inscriptions: "the Adamu, or dark race and the Sarku, or light race". The Sarku (or Sarcu) Sayce and Rawlinson maintained were the Semitic colonists who were white skinned.
Which city is Babylon today?
The ruins of Babylon can be found in modern-day Iraq, about 52 miles (approximately 85 kilometers) to the southwest of the Iraqi capital, Baghdad.
The City Of Babylon
Map of the ancienty city of Babylon. Editorial credit: Focus and Blur / Shutterstock.com
The First Babylonian Empire
The extent of the Babylonian Empire at the start (yellow) and end (yellow-green) of Hammurabi's reign, located in what today is modern day Iraq.
Fall of the First Babylonian Empire
The first Babylonian Empire began to decline after Hammurabi's death. Towards the latter part of the 18th century BCE, the empire lost a large amount of its southern territory facing the Persian Gulf, where the ancient cities of Ur and Uruk were located. By the end of the 18th century, Assyria had freed itself from the Babylonians.
When did the Babylonian Empire decline?
After Hammurabi’s death, the Babylonian empire declined until 1595 bce, when the Hittite invader Mursil I unseated the Babylonian king Samsuditana, allowing the Kassites from the mountains east of Babylonia to assume power and establish a dynasty that lasted 400 years.
Who ruled over Babylonia during the 9th century?
From the 9th century to the fall of the Assyrian empire in the late 7th century bce, Assyrian kings most frequently ruled over Babylonia, often appointing sub-kings to administer the government. The last ruling Assyrian king was Ashurbanipal, who fought a civil war against his brother, the sub-king in Babylon, devastating the city and its population.
What was the name of the empire that ruled the Tigris Euphrates?
Under the rule of the Amorites, which lasted until about 1600 bce, Babylon became the political and commercial centre of the Tigris-Euphrates area, and Babylonia became a great empire, encompassing all of southern Mesopotamia and part of Assyria to the north.
Who was the ruler of Babylonia?
The ruler largely responsible for this rise to power was Hammurabi ( c. 1792–1750 bce ), the sixth king of the 1st dynasty of Babylon, who forged coalitions between the separate city-states, promoted science and scholarship, and promulgated his famous code of law.
Where did biology originate?
Much of the earliest recorded history of biology is derived from Assyrian and Babylonia n bas-reliefs showing cultivated plants and from carvings depicting veterinary medicine. Illustrations on certain seals reveal that the Babylonia ns had learned that the date palm reproduces sexually and that…
Where is Babylonia located?
Babylonia, ancient cultural region occupying southeastern Mesopotamia between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers (modern southern Iraq from around Baghdad to the Persian Gulf ).
Who conquered Palestine and Syria?
His son Nebuchadrezzar II (reigned 605–562 bce) conquered Syria and Palestine; he is best remembered for the destruction of Judah and Jerusalem in 587 bce and for the ensuing Babylonian captivity of the Jews.
Geographic location of the Babylonian civilization
The Babylonian civilization was located in the southeastern area of Mesopotamia, on the Asian continent , between the Euphrates and Tigris rivers . The Babylonians spread and formed an empire that came to occupy the territories of Sumeria and Arcad (ancient Mesopotamian regions).
The city of Babylon
Babylonian architecture was characterized by the construction of towers with a stepped shape.
Contributions of Babylonian culture
Babylon was characterized by being a great cultural and intellectual development center within Mesopotamia. Some of the disciplines in which the Babylonians excelled were:
Babylonian political and economic organization
The most important political figure in Babylon was the king , supreme leader of the empire and representative of God on Earth. He lived in the palace and was in charge of all the powers and the dictation of the rules.
When was the Babylonian dynasty?
Period of chaos, 1026–911 BC. The ruling Babylonian dynasty of Nabu-shum-libur was deposed by marauding Arameans in 1026 BC, and the heart of Babylonia, including the capital city itself descended into anarchic state, and no king was to rule Babylon for over 20 years.
Which dynasty was independent of Babylonia?
The Sealand Dynasty of southern Mesopotamia remained independent of Babylonia and in native Akkadian-speaking hands. Ulamburiash managed to attack it and conquered parts of the land from Ea-gamil, a king with a distinctly Sumerian name, around 1450 BC, whereupon Ea-Gamil fled to his allies in Elam.
What are the ancient Babylonian tablets?
Tablets dating back to the Old Babylonian period document the application of mathematics to the variation in the length of daylight over a solar year. Centuries of Babylonian observations of celestial phenomena are recorded in the series of cuneiform script tablets known as the 'Enūma Anu Enlil'. The oldest significant astronomical text that we possess is Tablet 63 of 'Enūma Anu Enlil', the Venus tablet of Ammi-Saduqa, which lists the first and last visible risings of Venus over a period of about 21 years and is the earliest evidence that the phenomena of a planet were recognized as periodic. The oldest rectangular astrolabe dates back to Babylonia c. 1100 BC. The MUL.APIN, contains catalogues of stars and constellations as well as schemes for predicting heliacal risings and the settings of the planets, lengths of daylight measured by a water clock, gnomon, shadows, and intercalations. The Babylonian GU text arranges stars in 'strings' that lie along declination circles and thus measure right-ascensions or time-intervals, and also employs the stars of the zenith, which are also separated by given right-ascensional differences.
What were the buildings built in Babylonia?
One such drain at Ur was made of lead. The use of brick led to the early development of the pilaster and column, and of frescoes and enameled tiles. The walls were brilliantly coloured, and sometimes plated with zinc or gold, as well as with tiles. Painted terracotta cones for torches were also embedded in the plaster. In Babylonia, in place of the relief, there was greater use of three-dimensional figures—the earliest examples being the Statues of Gudea, that are realistic if somewhat clumsy. The paucity of stone in Babylonia made every pebble precious, and led to a high perfection in the art of gem-cutting.
What happened after 1050 BC?
After 1050 BC the Middle Assyrian Empire descended into a period of civil war, followed by constant warfare with the Arameans, Phrygians, Neo-Hittite states and Hurrians, allowing Babylonia to once more largely free itself from the Assyrian yoke for a few decades.
What was Babylonia called?
During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was called "the country of Akkad" ( Māt Akkadī in Akkadian), a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older state of Assyria to the north and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran.
Why is Mesopotamia called Assyro Babylonian?
Bronze Age to Early Iron Age Mesopotamian culture is sometimes summarized as "Assyro-Babylonian", because of the close ethnic, linguistic and cultural interdependence of the two political centers. The term "Babylonia", especially in writings from around the early 20th century, was formerly used to also include Southern Mesopotamia's earliest pre-Babylonian history, and not only in reference to the later city-state of Babylon proper. This geographic usage of the name "Babylonia" has generally been replaced by the more accurate term Sumer or Sumero-Akkadian in more recent writing, referring to the pre-Assyro-Babylonian Mesopotamian civilization.
What is the Babylonian exile?
biblical literature: The Babylonian Exile and the restoration. The Babylonian Exile (586–538) marks an epochal dividing point in Old Testament history, standing between what were subsequently to be designated...
When did the Jews return to Palestine?
The captivity formally ended in 538 bce, when the Persian conqueror of Babylonia, Cyrus the Great, gave the Jews permission to return to Palestine.
When were the Jews exiled?
Many scholars cite 597 bceas the date of the first deportation, for in that year King Jehoiachinwas deposed and apparently sent into exilewith his family, his court, and thousands of workers. Others say the first deportation followed the destruction of Jerusalemby Nebuchadrezzarin 586; if so, the Jews were held in Babylonian captivity for 48 years. Among those who accept a tradition (Jeremiah 29:10) that the exile lasted 70 years, some choose the dates 608 to 538, others 586 to about 516 (the year when the rebuilt Templewas dedicated in Jerusalem).
How long did the exile last?
Among those who accept a tradition (Jeremiah 29:10) that the exile lasted 70 years, some choose the dates 608 to 538, others 586 to about 516 (the year when the rebuilt Temple was dedicated in Jerusalem).
What was the name of the exile of the Jews?
Alternative Title: Babylonian Exile. Babylonian Captivity, also called Babylonian Exile, the forced detention of Jews in Babylonia following the latter’s conquest of the kingdom of Judah in 598/7 and 587/6 bce.
When did the fall of Babylon happen?
The Fall of Babylon denotes the end of the Neo-Babylonian Empire after it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire in 539 B CE. Nabonidus (Nabû-na'id, 556–539 BCE), son of the Assyrian priestess Adda-Guppi, came to the throne in 556 BCE, ...
When did Babylon gain independence?
A few years later, in 514 BCE, Babylon again revolted and declared independence under the Armenian King Arakha; on this occasion, after its capture by the Persians, the walls were partly destroyed. Esagila, the great temple of Bel, however, still continued to be maintained and was a center of Babylonian patriotism.
What is the name of the empire that conquered Babylon?
Sardis. Invasion of Babylonia. Opis. Babylon. The Fall of Babylon denotes the end of the Neo-Babylonian Empire after it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire in 539 BCE. Nabonidus (Nabû-na'id, 556–539 BCE), son of the Assyrian priestess Adda-Guppi, came to the throne in 556 BCE, after overthrowing the young king Labashi-Marduk.
What is the surprise capture of Babylon?
This surprise capture of Babylon is consistent with the story recorded in Daniel 5. The timing of the attack may have contributed to the success of Ugbaru's strategy. Herodotus, Xenophon and Daniel 5 all record that Babylon was in the midst of a festival on the night it was taken.
When was Cyrus the Great revolted?
(March 2021) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message) It was in the sixth year of Nabonidus (550/549 BC) that Cyrus the Great, the Achaemenid Persian king of Anshan in Elam, revolted against his suzerain Astyages, king of the Manda or Medes, at Ecbatana.
What was the first act of Cyrus?
The Neo-Babylonian Empire had pursued a policy of population transfer but one of the first acts of Cyrus was to allow these exiles to return to their own homes, carrying with them the images of their gods and their sacred vessels. Permission to do so was embodied in a proclamation, whereby the conqueror endeavored to justify his claim to the Babylonian throne. According to the biblical account, Cyrus sent the Jewish exiles back to Israel from the Babylonian captivity. Although the Jews never rebelled against the Persian occupation, they were restive under the period of Darius I consolidating his rule, and under Artaxerxes I, without taking up arms, or reprisals being exacted from the Persian government.
When did Cyrus invade Babylon?
Invasion. In 539 BCE, Cyrus invaded Babylonia. Historical reconstruction of the fall of Babylon to Persia has been problematic due to the inconsistencies between the various source documents.
When did the Babylonian Empire end?
Finally, in 539 BC , the city of Babylon itself was taken by the Persians. The fall of Babylon marked the end of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The momentous event has been recorded by a number of ancient historians, though due to inconsistencies, it is difficult to reconstruct the actual events that took place.
When did the fall of Babylon happen?
The fall of Babylon is a historical event that occurred in 539 BC. This event saw the conquest of Babylon by the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great and marked the end of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The fall of Babylon is reported by a number of ancient sources, including the Cyrus Cylinder, the Greek historian Herodotus, ...
What did Nabopolassar do to the Assyrian Empire?
This coalition succeeded in destroying the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Having gained independence from the Assyrians, Nabopolassar established the Neo-Babylonian Empire, with Babylon as its capital. When he died, he left his son with immense stores of wealth and a strong Babylonian city.
Why did the Babylonian Empire fall short of its time?
This may be due to the lack of an effective bureaucracy, as his active participation on regional wars meant that he did not focus on establishing an administrative system that would ensure the continual running of his empire after his death. Thus, this First Babylonian Empire was short-lived and it soon fell under the dominion of foreigners , including the Hittites, the Kassites, and the Assyrians.
What was Nebuchadnezzar II's rule?
During Nebuchadnezzar II’s reign, which lasted until around 562 BC, the Neo-Babylonian Empire was in control of Babylonia, Assyria, parts of Asia Minor, Phoenicia, Israel, and northern Arabia. Nebuchadnezzar II is most remembered today for a handful of important acts. Firstly, he is documented for driving the Jews out of Babylon, ...
How long did Nabonidus reign?
Nabonidus reigned for a total of 17 years and is remembered for his restoration of the region’s ancient architectural and cultural traditions, hence earning him the nickname ‘the archaeologist king’ among modern day historians.
What happened to the Neo-Assyrian Empire?
Destruction of the Neo-Assyrian Empire and Birth of a New Babylon. Following the death of Ashurbanipal around 627 BC , civil war broke out in the Neo-Assyrian Empire, causing it to weaken. Many subjects of the Neo-Assyrian Empire seized this opportunity to revolt.

Geographic Location of The Babylonian Civilization
Birth and Development of The Babylonian Civilization
The City of Babylon
Babylonian Art and Culture
Contributions of Babylonian Culture
The Religion of Babylon
Babylonian Political and Economic Organization
Fall of Babylonian Civilization
- Babylon was taken by the Persian king Cyrus II. In 556 a. A. Babylonian king assumed the power Nabonido, who when acceding to the throne went to the Arab oasis Taima and left Babylon in the hands of his son Belshazzar. At the same time, in the Persian Empire (one of the strongest empires in the region), King Cyrus II (nicknamed the Great) had ascen...