When the axes are perpendicular, no light is passed by the second filter. The effect of rotating two polarizing filters, where the first polarizes the light. (a) All of the polarized light is passed by the second polarizing filter, because its axis is parallel to the first.
How is the transmitted light polarized along the axis of polarizer?
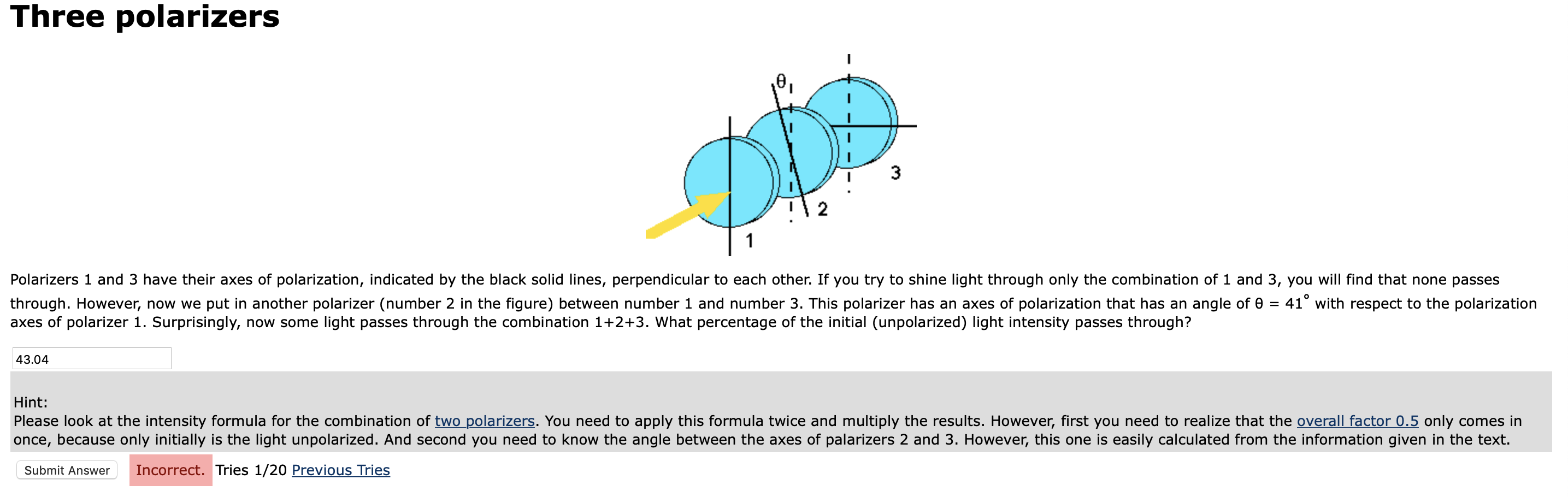
The transmitted light is polarized along the axis of the polarizer. Details of the calculation: In this problem we have 3 polarizing filters. For the second polarizer θ = 30obetween the polarization direction of the light incident of the filter and the axis of the filter.
What is the angle between the plane of polarisation and transmission plane?
Polarized light of intensity I0 is incident on a polarising filter. The angle between the plane of polarisation of the incident light and the transmission plane of the polariser is θ. Which graph shows how the intensity I of the light transmitted through the polariser varies with θ?
How to calculate the transmitted intensity of a polarized light?
When polarized light of intensity I0is incident on a polarizer, the transmitted intensity is given by I = I0cos2θ, where θ is the angle between the polarization direction of the incident light and the axis of the filter. The transmitted light is polarized along the axis of the polarizer. Details of the calculation:
What is the direction of light transmission?
Light transmitted is linearly polarized perpendicular to the direction of the chains. The transmission axis is perpendicular to the chains. A polarizer produces linearly polarized light.
Is plane of polarization perpendicular to plane of vibration?
In plane polarised light, the plane containing the direction of vibration and propagation of light is called plane of vibration. Plane which is perpendicular to the plane of vibration is called plane of polarisation.
What happens when polarizers are perpendicular?
If the light is polarized in the same direction as the polarizer, it will all go through. If the light is polarized perpendicular to the polarizer, all of the light will be stopped.
Is polarized light perpendicular?
In linearly polarized light, the electric vector is vibrating in a plane that is perpendicular to the direction of propagation, as discussed above.
What happens when two polarizing filters are placed so that their axes of polarization are perpendicular to each other?
If the second polarizing filter is rotated, only the component of the light parallel to the second filter's axis is passed. When the axes are perpendicular, no light is passed by the second.
What is the transmission axis of a polarizer?
The transmission axis of a polarizer is the axis such that light with its electric field oriented parallel to this axis will be transmitted. If the light is not already linearly polarized parallel to the transmission axis, only that component of the light parallel to the axis will pass through the polarizer unhindered.
In which of the following polarization the electric field components are perpendicular to each other and have equal magnitude?
Circular polarization has electric field components are perpendicular to each other and have equal magnitude.
What angle is needed between the direction of unpolarized light and the axis of a polarizing filter to reduce its intensity by 90.0 %?
18.4 degrees5: At the end of Example 1, it was stated that the intensity of polarized light is reduced to 90.0% of its original value by passing through a polarizing filter with its axis at an angle of 18.4 degrees to the direction of polarization.
What is the direction when light is polarized the electric field?
Explanation: The polarization of an electromagnetic wave (made up of electric and magnetic fields) is defined as the direction along which the electric field vector (E) points. In polarized light, the electric field is oriented in a single direction. Unpolarized light is "polarized" in all directions.
What angle is needed between the direction of polarized light and the axis of a polarizing filter to cut its intensity in half?
45.0ºWhat angle is needed between the direction of polarized light and the axis of a polarizing filter to cut its intensity in half? The angle between the axes of two polarizing filters is 45.0º.
How does the direction of polarization of light compare with the direction of vibration of the electrons that produced it?
How does the direction of the polarization of light compare with the direction of vibration of the electron that produces it? The direction of polarization is parallel to the direction of electron vibration.
What angle is needed between the direction of polarized light and the axis of a polarizing filter to reduce its intensity by 50 %?
45°A fairly large angle between the direction of polarization and the filter axis is needed to reduce the intensity to 10.0% of its original value. This seems reasonable based on experimenting with polarizing films. It is interesting that at an angle of 45°, the intensity is reduced to 50% of its original value.
What happens when polarized light passes through a polarizer?
If we polarize white light and pass it through sugar syrup, the direction of polarization of the light emerging from the syrup will be different for the different color components. If the light then passes through a second polarizer, its color changes with the orientation of the transmission axis of this polarizer.
What is the direction of polarization?
Waves having such a direction are said to be polarized. For an EM wave, we define the direction of polarization to be the direction parallel to the electric field. Thus we can think of the electric field arrows as showing the direction of polarization, as in (Figure). An EM wave, such as light, is a transverse wave.
What is polarization in physics?
Polarization is the attribute that a wave’s oscillations have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave. (This is not the same type of polarization as that discussed for the separation of charges.) Waves having such a direction are said to be polarized.
What is the effect of rotating two polarizing filters?
The effect of rotating two polarizing filters, where the first polarizes the light. (a) All of the polarized light is passed by the second polarizing filter, because its axis is parallel to the first. (b) As the second is rotated, only part of the light is passed.
What is the direction of EM waves?
For EM waves, the direction of the electric field is analogous to the disturbances on the ropes. The transverse oscillations in one rope are in a vertical plane, and those in the other rope are in a horizontal plane. The first is said to be vertically polarized, and the other is said to be horizontally polarized.
What is horizontally polarized?
Those in the other rope are in a horizontal plane and are horizontally polarized. If a vertical slit is placed on the first rope, the waves pass through. However, a vertical slit blocks the horizontally polarized waves. For EM waves, the direction of the electric field is analogous to the disturbances on the ropes.
How to tell if a Polaroid is polarized?
If you hold your Polaroid sunglasses in front of you and rotate them while looking at blue sky, you will see the sky get bright and dim. This is a clear indication that light scattered by air is partially polarized. (Figure) helps illustrate how this happens. Since light is a transverse EM wave, it vibrates the electrons of air molecules perpendicular to the direction it is traveling. The electrons then radiate like small antennae. Since they are oscillating perpendicular to the direction of the light ray, they produce EM radiation that is polarized perpendicular to the direction of the ray. When viewing the light along a line perpendicular to the original ray, as in (Figure), there can be no polarization in the scattered light parallel to the original ray, because that would require the original ray to be a longitudinal wave. Along other directions, a component of the other polarization can be projected along the line of sight, and the scattered light will only be partially polarized. Furthermore, multiple scattering can bring light to your eyes from other directions and can contain different polarizations.
Why do polaroids cut glare?
Polaroids have this ability because of a wave characteristic of light called polarization.
What happens if the second polarizer is oriented at an angle not perpendicular to the first
However, if the second polarizer is oriented at an angle not perpendicular to the axis of the first polarizer, there will be some component of the electric field of the polarized light that lies in the same direction as the axis of the second polarizer, and thus some light will be transmitted through the second polarizer.
What is polarization in waves?
Polarization is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations, In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves (shear waves) in solids.
What is a polarizer filter?
A polarizer is an optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization pass through while blocking light waves of other polarizations. A polarizer only allows light which is vibrating in a particular plane to pass through it. This plane forms the “ axis ” of polarization. Unpolarized light vibrates in all planes perpendicular to ...
Which wave has polarization?
Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves (shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating electric field and magnetic field which are always perpendicular; by convention, ...
What is circular polarization?
In circular or elliptical polarization, the fields rotate at a constant rate in a plane as the wave travels. The rotation can have two possible directions; if the fields rotate in a right hand sense with respect to the direction of wave travel, it is called right circular polarization, while if the fields rotate in a left hand sense, ...
Is light polarized in one plane?
The transmitted light is polarized in one plane. If this polarized light is incident upon a second polarizer, the axis of which is oriented such that it is perpendicular to the plane of polarization of the incident light, no light will be transmitted through the second polarizer.
Polarisation of Light
The waves that are formed when an interaction takes place between the magnetic field and electric field are known as electromagnetic waves. A phenomenon that is caused due to the wave nature of electromagnetic radiation is called the polarization of light. There are two types of waves that exist - transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
Types of Polarisation
Depending on the motion of transverse and longitudinal waves, there are three types of polarisation:
Methods used in Polarisation of Light
Most of the light in the refracted ray is unpolarised, having just one or two polarised components. The refracted ray is polarised partially.
Things to Remember
Polarisation is a property of light that can be seen in transverse waves. Light waves travelling only in a single plane are called polarized light waves.
Sample Questions Based on Polarisation
Ans. Polarisation is known as the process that transforms the unpolarized light into polarized one. Through a filter when unpolarized light is passed, the oscillations are restricted along only one line. Hence, the light becomes polarised.
Previous Year Questions
Q 1. (a) Using the phenomenon of polarization, show how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated? (b) Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1.
What is polarization in physics?
Polarization is the attribute that a wave’s oscillations do have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave. (This is not the same type of polarization as that discussed for the separation of charges.) Waves having such a direction are said to be polarized.
What is horizontally polarized?
Those in the other rope are in a horizontal plane and are horizontally polarized. If a vertical slit is placed on the first rope, the waves pass through. However, a vertical slit blocks the horizontally polarized waves. For EM waves, the direction of the electric field is analogous to the disturbances on the ropes.
What is polarizing filter?
Polarizing filters have a polarization axis that acts as a slit. This slit passes EM waves (often visible light) that have an electric field parallel to the axis. This is accomplished with long molecules aligned perpendicular to the axis, as shown in (Figure).
How to tell if sunglasses are polarized?
You can check this for yourself by holding polarizing sunglasses in front of you and rotating them while looking at light reflected from water or glass. As you rotate the sunglasses, you will notice the light gets bright and dim, but not completely black. This implies the reflected light is partially polarized and cannot be completely blocked by a polarizing filter.
What happens when a second polarizing filter is rotated?
If the second polarizing filter is rotated, only the component of the light parallel to the second filter’s axis is passed. When the axes are perpendicular, no light is passed by the second filter. The effect of rotating two polarizing filters, where the first polarizes the light.
Why are polarizing sunglasses used?
Polarizing sunglasses are familiar to most of us. They have a special ability to cut the glare of light reflected from water or glass ( (Figure) ). They have this ability because of a wave characteristic of light called polarization.
What is the transverse oscillation?
The transverse oscillations in one rope (a) are in a vertical plane, and those in the other rope (b) are in a horizontal plane. The first is said to be vertically polarized, and the other is said to be horizontally polarized. Vertical slits pass vertically polarized waves and block horizontally polarized waves.

Is Plane of Polarization Perpendicular to Plane of Vibration?
- The plane of polarization is defined as the plane containing the direction of propagation of a polarized wave. The plane of vibration is the plane which contains vibrations and which is along the optic axis of the wave. It is always perpendicular to the plane of polarization.
What Is The Plane of Vibration of This Light?
- Hence, polarisation is the phenomenon of producing plane polarised light from unpolarised light. In plane polarised light, the plane containing the direction of vibration and propagation of light is called plane of vibration.
What Is Polarization by Transmission?
- Polarization is a phenomenon peculiar to transverse waves. Longitudinal waves such as sound cannot be polarized. An ideal polarizer is a material that passes only EM waves for which the electric field vector is parallel to its transmission axis. …
Polarization by Use of A Polaroid Filter
Polarization by Reflection
- Unpolarized light can also undergo polarization by reflection off of nonmetallic surfaces. The extent to which polarization occurs is dependent upon the angle at which the light approaches the surface and upon the material that the surface is made of. Metallic surfaces reflect light with a variety of vibrational directions; such reflected light is unpolarized. However, nonmetallic surfac…
Polarization by Refraction
- Polarization can also occur by the refraction of light. Refraction occurs when a beam of light passes from one material into another material. At the surface of the two materials, the path of the beam changes its direction. The refracted beam acquires some degree of polarization. Most often, the polarization occurs in a plane perpendicular to the s...
Polarization by Scattering
- Polarization also occurs when light is scattered while traveling through a medium. When light strikes the atoms of a material, it will often set the electrons of those atoms into vibration. The vibrating electrons then produce their own electromagnetic wave that is radiated outward in all directions. This newly generated wave strikes neighboring atoms, forcing their electrons into vib…
Applications of Polarization
- Polarization has a wealth of other applications besides their use in glare-reducing sunglasses. In industry, Polaroid filters are used to perform stress analysis tests on transparent plastics. As light passes through a plastic, each color of visible light is polarized with its own orientation. If such a plastic is placed between two polarizing plates, a colorful pattern is revealed. As the top plate is …