How to check ground fault?
Steps on How to Test a GFCI Breaker with a Multimeter
- Test and Reset Buttons. Your GFCI has two buttons in between the two plug connections, labeled as TEST and RESET. ...
- Insert multimeter in the slots. While your outlet remains off, check if there’s still a presence of power left by inserting the plugs of the multimeter’s probes inside ...
- Measure the outlet’s voltage. ...
- Check the outlet’s wiring. ...
How do I troubleshoot a ground fault?
Troubleshooting Common Ground Fault Receptacle Problems
- Looking at the Ground Fault Receptacle. Take a look at the outside of the ground fault receptacle and look for the buttons marked reset and trip.
- Checking Outlets. Using your plug in electrical tester you should check that the ground fault receptacle outlets are receiving outlets. ...
- Checking Power. ...
- Detective Work. ...
What is the difference between short circuit and ground fault?
- A Short Circuit is a break down in insulation causing contact between live/line conductors
- A short circuit occurs when a “hot” wire and a “neutral” wire actually touch each other. ...
- when short occurs, a large current flow through a fuse or circuit breaker will open the circuit, blowing the fuse or tripping the breaker
Can you hook up a GFCI without a ground wire?
Using a GFCI without ground wire is OK as long as you label it as such. This one needs a sticker. GFCI outlets come with a supply of them. Safety first: Turn off the power at the breaker box.

At what current does a ground fault interrupter trip?
around 6 mAGFCI uses and maintenance The actuating energy for standard breakers and fuses far exceeds the lethal amount, but most GFCIs trip at around 6 mA. A GFCI uses a current transformer to detect the difference between the line current supplied to the load and the neutral current returning from the load.
Does a GFCI limit current?
It does not limit the magnitude of ground fault current. It does limit the length of time that a ground fault will flow. In other words, you will still receive a severe shock during the time it takes the GFCI device to trip “off.” See Figure 3.
What causes a GFCI to stop the flow of electrical current?
If the GFCI's internal current transformer senses more than a 4-5 milliamp loss, it instantly shuts down the outlet and any outlets it feeds to prevent accidental electrocution.
Does a GFCI trip the circuit or cut off electricity first?
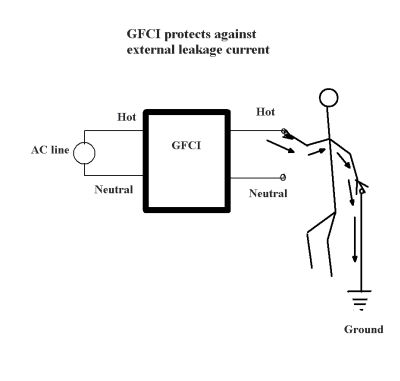
The GFCI can sense the current flowing through you because not all of the current is flowing from hot to neutral as it expects -- some of it is flowing through you to the ground. As soon as the GFCI senses this "leakage" of power, it trips the circuit and cuts off the electricity.
Does GFCI trip overcurrent?
So a GFCI receptacle outlet does not trip due to an overloaded circuit. A GFCI breaker in a panel will trip, however, because it combines both overcurrent and GFCI protection in one device—and the overcurrent protection part will cause it to trip.
How does a GFCI sense current?
How does a GFCI work? The GFCI will “sense” the difference in the amount of electricity flowing into the circuit to that flowing out, even in amounts of current as small as 4 or 5 milliamps. The GFCI reacts quickly (less than one-tenth of a second) to trip or shut off the circuit.
What is the common effect of a ground fault?
Effects of Ground Fault When a ground fault occurs in a single-phase system it increases the chances of electrical shock to humans. As the grounding is done for balancing the voltages of all three phases so if a ground fault occurs in a three-phase system the voltage unbalance will occur which may disturb all loads.
Why would a GFCI trip with no load on it?
If your insulation is worn out, old, or damaged, it could cause your GFCI to trip. The insulation is in the wall is meant to help prevent such leaks from occurring. So if your insulation is worn, this can cause more leaks. Sometimes having too much equipment or appliances plugged in can also cause your GFCI to trip.
Can a GFCI work without a ground?
In short, yes. If your circuit doesn't have a ground wire, you can still install a GFCI outlet for protection. GFCI outlets without a ground wire are legal and work; however, choosing to install GFCI outlets without a ground wire does come with some disadvantages.
Will a ground fault trip a breaker?
Short circuits AND ground faults both cause breakers to trip and the flow of power to be interrupted. Both are dangerous and lead to shock or fire hazards!
Can you use a GFCI breaker as a regular breaker?
The main difference is that normal circuit breakers do not have neutral wires to attach to the breaker's main buss bar. With the proper planning and attention to safety, nearly anyone can replace a GFI breaker with a normal one.
What does a ground fault circuit interrupter not do?
What a ground fault circuit interrupter does not? It does not protect against electrical shock when a person touches both circuit conductors at the same time (two “hot” wires, or one “hot” wire and one grounded neutral conductor) because the current flowing in both conductors is the same. Thus, there is no unbalance of current for ...
What is a GFCI circuit?
What a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) does? A ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) monitors the current balance between the ungrounded “hot” conductor and the grounded conductor. As soon as the current flowing through the “hot” conductor is in the range of 4 to 6 milli-amperes more than the current flowing in ...
Why is there a small amount of current in a coil?
When small current is induced in the coil. A small amount of current is induced in the coil because of the unbalance of current in the conductors. This current difference is amplified sufficiently by the ground fault interrupter to cause it to trip the circuit off before the person touching the faulty appliance is injured or killed. Note!!
Why is there no current in a coil?
No current is induced in the coil because both wires are carrying the same current. The ground fault circuit interrupter does not trip the circuit off. Figure 1a – No current is induced in the coil because both wires are carrying the same current.
What is a branch circuit breaker?
The branch circuit fuse or circuit breaker provides this protection. It does not sense solid short circuits between two “hot” conductors. The branch circuit fuse or circuit breaker provides this protection. It does not sense and protect against the damaging effects of arcing faults, such as would occur with frayed extension cords.
Does a GFCI have to be unbalanced?
Thus, there is no unbalance of current for the GFCI to sense and trip. It does not limit the magnitude of ground fault current. It does limit the length of time that a ground fault will flow. In other words, you will still receive a severe shock during the time it takes the GFCI device to trip “off.”. See Figure 3.
How does a GFCI sense a circuit?
The GFCI will “sense” the difference in the amount of electricity flowing into the circuit to that flowing out, even in amounts of current as small as 4 or 5 milliamps. The GFCI reacts quickly (less than one-tenth of a second) to trip or shut off the circuit.
What is a GFCI?
A ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) can help prevent electrocution. If a person’s body starts to receive a shock, the GFCI senses this and cuts off the power before he/she can get injured. GFCIs are generally installed where electrical circuits may accidentally come into contact with water.
How often should a GFCI be checked?
GFCIs should be checked monthly to determine if they are operating properly. A portable GFCI should be used out-of-doors with various electrical power tools (i.e., drills, mowers, trimmers) and should be tested before each use!
Why is GFCI protection used?
Because of this potential for shock, GFCI protection is used to protect human life.
How many types of GFCI are there?
There are three types of GFCIs. The most often used “receptacle-type” GFCI, similar to a common wall outlet, is the type with which most consumers are familiar.
What is a ground fault?
According to the National Electrical Code, a “ground fault” is a conducting connection (whether intentional or accidental) between any electric conductor and any conducting material that is grounded or that may become grounded. Electricity always wants to find a path to the ground. In a ground fault, electricity has found a path to ground, ...
Can a GFCI circuit be replaced?
If this is the case, have a qualified electrician replace it as soon as possible. GFCIs should be tested monthly to ensure they are in working condition.
This short series will touch on the basics and the differences between GFCIs and AFCIs. This article will focus on ground-fault circuit interrupters
GFCIs are designed to protect a person from being shocked or electrocuted when they come in contact with a device that is accidentally touching a circuit. AFCIs, on the other hand, are designed to protect a home from catching fire due to arcing in defective conductors or appliances (see Figure 1 ).
Electrical Shock
An electrical shock is a shock that results anytime a body becomes part of an electrical circuit. Electrical shock kills over 1000 people a year in the United States, according to the National Safety Council (NSC).
GFCIs
A ground-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is an electric device that protects personnel by detecting ground faults and quickly disconnecting power from the circuit (see Figure 3 ). GFCIs were created due to the limitations of commonly used circuit breakers, which were designed to trip only when large currents are present (short or overload).
GFCI Operation
A sequence of events takes place when a fault current is detected by a GFCI. Typically, a load (for example, an electric shaver, drill, or garden tool) has the same amount of current flowing to it through the black or red (hot) wire as flowing away from it through the white (neutral) wire.
GFCI Required Locations
The National Electric Code® requires ground-fault circuit interrupters for protection in many areas. It is always a good idea to check the NEC requirements as well as local building codes.
GFCI Installation
GFCIs are installed in standard receptacle boxes indoors and in weatherproof boxes outdoors. GFCI receptacles are typically installed individually. GFCIs may also be installed to protect several standard receptacles in one continuous circuit.
Plug-in GFCIs
Plug-in GFCIs are the most convenient type of GFCI device to use. Through the simple use of a plug-in GFCI in any grounded receptacle, any tool plugged into the GFCI device and its operator are protected (see Figure 4 ).
How Does a GFCI Work?
The GFCI is meant to be a lifesaving device that continually senses imbalances in an electrical circuit. When it senses a ground fault, or current leaking to ground, it is designed to open the circuit within as little as 1/40th of a second.
What are the Types of GFCI?
There are three common types of ground fault circuit interrupters available:
Where Should GFCIs be Installed?
The National Electrical Code® (NEC) requires GFCI protection to be used for most outdoor residential receptacles (since 1973), bathroom receptacles (since 1975), garage wall outlets (since 1978), kitchen receptacles (since 1987) and all receptacles in crawl spaces and unfinished basements (since 1990).
How Should I Test a GFCI?
All GFCIs should be tested upon installation and at least once a month to make sure they are working properly. To test a GFCI receptacle:
What is a GFCI circuit?
Ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) — a device that functions to interrupt a circuit or portion of a circuit, within a predetermined time, when a current to ground exceeds some predetermined value that is less than that required to operate the overcurrent protective device of the supply circuit. Ground fault circuit interrupter, Class A (Class ...
What is a GFCI?
In general, a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is a device that detects dangerous ground faults and automatically turns off the power to prevent electric shocks. The electrical industry practitioners are well aware that there is a Class A GFCI, which provides personnel protection and operates when a fault current to ground (leakage current) ...
What type of circuit interrupter is used for 125V?
Each 125 V, single-phase receptacle installed in machine rooms, control rooms, machine spaces, control spaces, and counterweight enclosures shall be protected with a ground fault circuit interrupter of the Class A type.
What is ground fault protection?
Ground fault protection — a means of detecting and interrupting a ground fault current at a level less than the current required to operate the circuit overcurrent device (see Appendix B).
What is a class A GFCI?
A Class A ground fault circuit interrupter (Class A GFCI) is an interrupter that will interrupt the circuit to the load when the ground fault current is 6 mA or more, but not when the ground fault current is 4 mA* or less in a time
What is the purpose of a Class A GFCI?
The prime function of a Class A GFCI is to provide protection against hazardous electric shocks from leakage current flowing to ground from defective circuits or equipment. It does not provide protection against shock if a person makes contact with two of the circuit conductors on the load side of the GFCI.
Does a ground fault alarm interrupt current?
It is interesting to note that although a ground fault detection does not interrupt the ground fault current, it automatically initiates a visual and audible alarm to indicate the presence of the ground fault to qualified persons. So, it could be considered as a part of ground fault protection.
How does a GFCI work?
The GFCI works by measuring the current leaving the hot side of the power source and comparing it to the current returning to the neutral side. If they are not equal, this means that some of the current is flowing along an unintended path possibly through water or through a person.
What is a GFCI?
A GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) is an automatic device that offers personal protection against lethal electrical shock or electrocution. It is a special electrical receptacle or outlet that can stop electrical power within milliseconds as a safety precaution. Let’s see how?
What is the purpose of making electrical devices shock free?
For making electrical devices “shock free” and eliminating chances of fires, electrocutions and injuries to users , all one needs to do is eliminate electrical hazards with affordable devices .
What are the causes of electrical hazards?
Causes of Electrical Hazards. Apart from ever–increasing use of electrical power and outdated home electrical systems lacking capacity to handle modern electrical appliances and devices, wiring hazards are a major cause of electrocutions and home fires. Misuse of surge suppressors, power strips and extension cords is also a cause ...
What is the slot in a GFCI?
The larger “left slot” corresponds to “neutral and “right slot” is called “hot”. The third, round hole is the “ground”. Normally, electricity flows from hot to neutral in the outlet. The GFCI works by measuring the current leaving the hot side of the power source and comparing it to the current returning to the neutral side.
How many lives have been saved by GFCIs?
Thousands of lives saved: Since the 1970s, GFCIs have saved thousands of lives and have helped cut the number of home electrocutions in half. If GFCIs were installed in older homes, experts suggest 70 per cent of the electrocutions that occur each year in the home could be prevented.
When a person's body starts to receive a shock, the GFCI senses this and cuts off
So when a person’s body starts to receive a shock, the GFCI senses this and cuts off the power before he or she can get injured. In general, GFCIs are installed wherever there is the potential for contact between a person and an electrical appliance in or near moisture, water, or water pipes.