Where are convergent plate boundaries found? In the ocean basins convergent plate margins are marked by deep trenches in the sea floor. The convergent plate boundaries that occur on continents are the collisional mountain belts .
What are the 3 types of convergent plate boundaries?
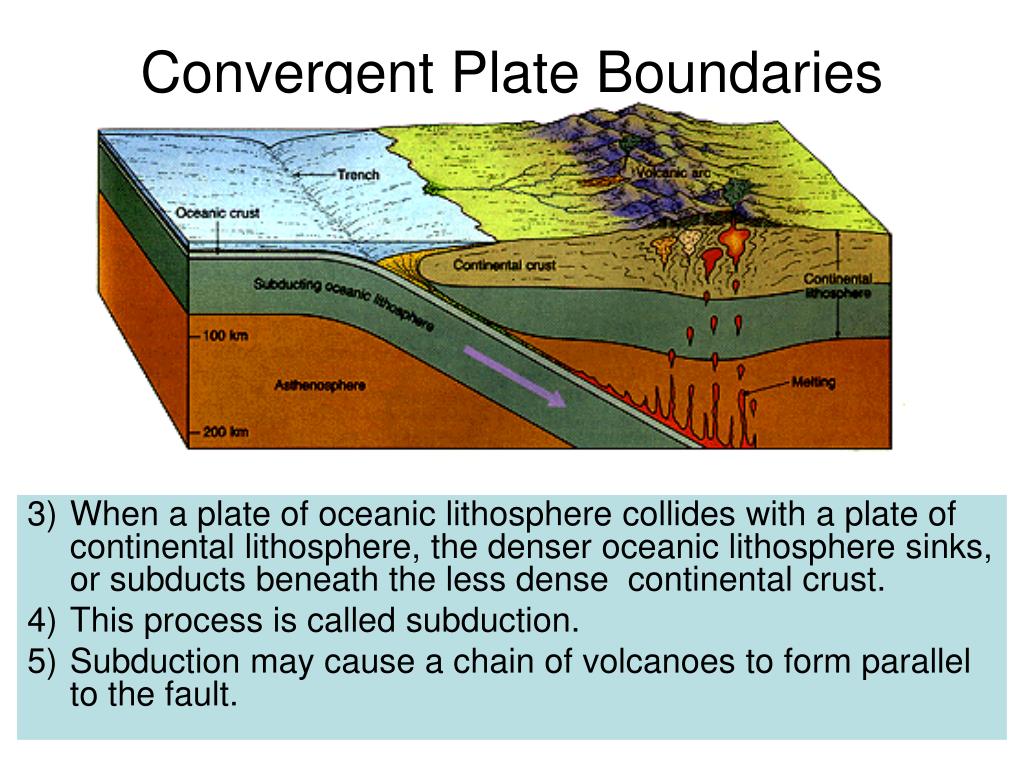
• There are three types of convergent plate boundaries: oceanic-oceanic boundaries, oceanic-continental boundaries, and continental-continental boundaries. Each one is unique because of the density of the plates involved.
What are the 4 types of convergent boundaries?
Convergent boundaries , where two plates are moving toward each other, are of three types, depending on the type of crust present on either side of the boundary — oceanic or continental . The types are ocean-ocean, ocean-continent, and continent-continent.
What is a real life example of a convergent boundary?
The Himalayas are an example of convergent boundaries. The Andes mountains formed at the convergence of the Nazca Plate and the South American Plate. The Nazca Plate is less dense than the South American Plate and subducts underneath.
What happens at a convergent plate boundary?
A convergent plate boundary is a location where two tectonic plates are moving toward each other, often causing one plate to slide below the other (in a process known as subduction). The collision of tectonic plates can result in earthquakes, volcanoes, the formation of mountains, and other geological events.
How do continents grow outward?
What is the name of the region where the continental crust lifts up a broad region known as a collisional?
What is the process of convergent plate boundary?
Where are the two mountain ranges formed during plate convergence?
Where are accreted terranes found?
Where do tectonic plates converge?
See 3 more
About this website

Where are convergent boundaries most common?
It's common to see convergent plates along the edge of continents. Likewise, you'll see large chains of mountains and volcanoes. For example, the Pacific Ring of Fire has had some of the most violent earthquakes in history. Most of the Pacific Ring of Fire is convergent plate boundaries.
What are 3 examples of convergent boundaries?
Three types of convergent boundaries are recognized: continent‐continent, ocean‐continent, and ocean‐ocean.
Where is a divergent plate found?
mid-ocean oceanic ridgesMost divergent boundaries are located along mid-ocean oceanic ridges (although some are on land). The mid-ocean ridge system is a giant undersea mountain range, and is the largest geological feature on Earth; at 65,000 km long and about 1000 km wide, it covers 23% of Earth's surface (Figure 4.5.
What is the best example of convergent?
The best example of convergent tectonic plates is Washington -Oregon and the best example if divergent tectonic plates Is Mid-Atlantic ridge..
What are 2 real world examples of convergent boundaries?
The Cascadia Subduction Zone and Southern Alaska Subduction Zone reveal two mountain ranges formed during plate convergence: an accretionary wedge near the coast and a volcanic arc farther inland. Rocks in California's Sierra Nevada are cooled magma chambers that fed volcanoes of an ancient subduction zone.
What are the convergent boundaries?
Convergent boundaries, also called destructive boundaries, are places where two or more plates move toward each other. Convergent boundary movement is divided into two types, subduction and collision, depending on the density of the involved plates.
In which two places do divergent boundaries occur?
There are two types of divergent boundaries, categorized by where they occur: continental rift zones and mid-ocean ridges. Continental rift zones occur in weak spots in the continental lithospheric plate.
What are 3 examples of divergent boundaries?
ExamplesMid-Atlantic Ridge.Red Sea Rift.Baikal Rift Zone - incipient plate boundary.East African Rift - incipient plate boundary.East Pacific Rise.Gakkel Ridge.Galapagos Rise.Explorer Ridge.More items...
What are 2 convergent boundaries?
Convergent boundary movement is divided into two types, subduction and collision, depending on the density of the involved plates.
What are the 3 types of divergent boundaries?
False, because the correct statement is: There are three types of divergent plate boundaries, namely continental-continental, oceanic-continental, and oceanic-oceanic.
What are the 3 types of boundary?
Divergent boundaries -- where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each other. Convergent boundaries -- where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another. Transform boundaries -- where crust is neither produced nor destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other.
Convergent boundary - Wikipedia
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction.The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and ...
What are the three types of convergent plate boundaries?
• There are three types of convergent plate boundaries: oceanic-oceanic boundaries, oceanic-continental boundaries, and continental-continental boundaries. Each one is unique because of the density of the ...
What happens when two oceanic plates collide?
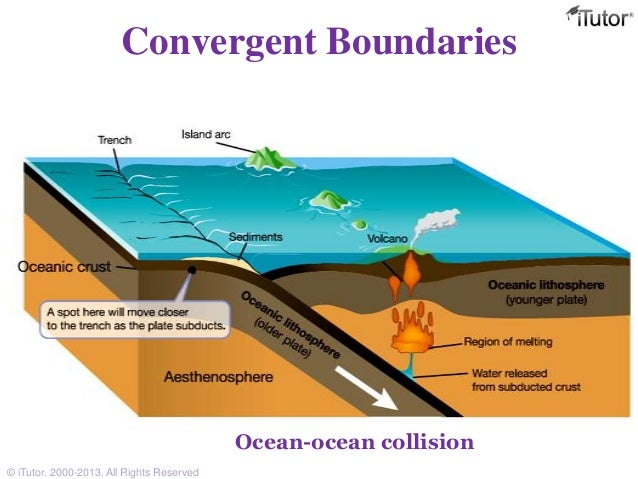
When two oceanic plates collide, the denser plate sinks below the lighter plate and eventually forms dark, heavy, basaltic volcanic islands. The western half of the Pacific Ring of Fire is full of these volcanic island arcs, including the Aleutian, Japanese, Ryukyu, Philippine, Mariana, Solomon, and Tonga-Kermadec.
What is convergent boundary?
A convergent plate boundary is a location where two tectonic plates are moving toward each other, often causing one plate to slide below the other (in a process known as subduction). The collision of tectonic plates can result in earthquakes, volcanoes, the formation of mountains, and other geological events.
Why are continental plates unique?
Each one is unique because of the density of the plates involved. • Convergent plate boundaries are often the sites of earthquakes, volcanoes, and other significant geological activity. Earth's surface is made up of two types of lithospheric plates: continental and oceanic. The crust that makes up continental plates is thicker yet less dense ...
What are oceanic plates made of?
Oceanic plates are made up of heavier basalt, the result of magma flows from mid-ocean ridges . When plates converge, they do so in one of three settings: oceanic plates collide with each other (forming oceanic-oceanic boundaries), oceanic plates collide with continental plates (forming oceanic-continental boundaries), ...
Why do tectonic plates move?
Because of thermal changes in the mantle, tectonic plates are always moving—through the fastest-moving plate, the Nazca, only travels about 160 millimeters per year. Where plates meet, they form a variety of different boundaries depending on the direction of their motion. Transform boundaries, for example, are formed where two plates grind ...
Where are divergent boundaries formed?
Divergent boundaries are formed where two plates pull apart from each other (the most famous example is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where the North American and Eurasian plates diverge). Convergent boundaries are formed wherever two plates move toward each other. In the collision, the denser plate is typically subducted, ...
How is magma produced?
Magma chambers are produced as a result of this melting, and the magma is lower in density than the surrounding rock material. It begins ascending by melting and fracturing its way through the overlying rock material. Magma chambers that reach the surface break through to form a volcanic eruption cone.
What is the effect of partial melting on the oceanic plate?
This partial melting produces magma chambers above the subducting oceanic plate. These magma chambers are less dense than the surrounding mantle materials and are buoyant. The buoyant magma chambers begin a slow ascent through the overlying materials, melting and fracturing their way upwards.
How deep does the oceanic plate go?
As the oceanic plate descends, it is forced into higher temperature environments. At a depth of about 100 miles (160 km), materials in the subducting plate begin to approach their melting temperatures and a process of partial melting begins. ADVERTISEMENT.
What happens when continental plates collide?
When continental and oceanic plates collide, the thinner and more dense oceanic plate is overridden by the thicker and less dense continental plate. The oceanic plate is forced down into the mantle in a process known as "subduction.". As the oceanic plate descends, it is forced into higher temperature environments.
What are the effects of plate boundary?
Effects that are found at this type of plate boundary include: a zone of progressively deeper earthquakes; an oceanic trench; a chain of volcanic islands; the destruction of oceanic lithosphere.
How does a convergent boundary occur?
When a convergent boundary occurs between two oceanic plates, one of those plates will subduct beneath the other. Normally the older plate will subduct because of its higher density. The subducting plate is heated as it is forced deeper into the mantle, and at a depth of about 100 miles (150 km) the plate begins to melt. Magma chambers are produced as a result of this melting, and the magma is lower in density than the surrounding rock material. It begins ascending by melting and fracturing its way through the overlying rock material. Magma chambers that reach the surface break through to form a volcanic eruption cone. In the early stages of this type of boundary, the cones will be deep beneath the ocean surface but later grow to be higher than sea level. This produces an island chain. With continued development the islands grow larger, merge, and an elongate landmass is created.
What happens if a magma chamber rises to the surface without solidifying?
If a magma chamber rises to the surface without solidifying, the magma will break through in the form of a volcanic eruption. The Washington-Oregon coastline of the United States is an example of this type of convergent plate boundary.
What are the sites of subduction?
The Cascadia Subduction Zone and Southern Alaska are the sites of ongoing subduction as the Pacific and Juan de Fuca plates slide beneath the North American Plate. Some parks in the Sierra Nevada Mountains reveal igneous magma chamber rocks that represent the eroded remnants of an ancient subduction zone, when volcanoes similar to those found in the modern Cascade Mountains extended southward all the way through California.
What is the result of the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate?
Subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate results in the formation of the Coastal Ranges and Cascade Volcanoes, as well as a variety of earthquakes, in the Pacific Northwest. Olympic and Mt. Rainier national parks showcase the contrasting landscapes of the two parallel mountain ranges.
What type of crust forms when a plate with thinner (less buoyant) oceanic crust descends beneath a?
Subduction zones form where a plate with thinner (less-buoyant) oceanic crust descends beneath a plate with thicker (more-buoyant) continental crust. Two parallel mountain ranges commonly develop above such a subduction zone – a coastal range consisting of sedimentary strata and hard rock lifted out of the sea ( accretionary wedge ), and a volcanic range farther inland ( volcanic arc ). Ancient magma chamber rocks can be exposed if subduction stops and the volcanoes erode away.
What are the two mountain ranges in the Cascadia subduction zone?
Parks in the Cascadia Subduction Zone dramatically display the two distinct mountain ranges – the Coast Range just above where the Juan de Fuca Plate begins to subduct, and the volcanic Cascade Range farther inland, where the top of the plate is deeper.
What is the wedge formed between the converging plates?
An accretionary wedge forms between the converging plates as material is scraped off the subducting plate.
How deep are volcanoes?
The volcanoes are forming above the region where the top of the subducting Juan de Fuca Plate reaches about 50 miles (80 kilometers) depth. Increased temperature and pressure at that depth cause the rocks to metamorphose and dehydrate (”sweat”).
How tall is Mount Rainier?
Mount Rainier is a 14,000 foot (4,300 meter) volcano in the Cascade Range developed above the place where the subducting Juan de Fuca Plate reaches sufficient depth to release hot fluids into the overriding North American Plate.#N#Photo courtesy of Robert J. Lillie.
How do continents grow outward?
Continents grow outward as volcanic islands and continental fragments enter a subduction zone and attach to the edge of the continent. Examples of such accreted terranes are found in NPS sites in southern Alaska and northern Washington State. Sometimes plate convergence closes an entire ocean. The crusts of the continents are too thick and buoyant to subduct, forming a collisional mountain range, such as the Appalachian/Ouachita/Marathon chain in the eastern United States and the Brooks Range in northern Alaska.
What is the name of the region where the continental crust lifts up a broad region known as a collisional?
Continents collide where subduction completely closes an ocean. The buoyant continental crust lifts up a broad region known as a collisional mountain range.
What is the process of convergent plate boundary?
Where tectonic plates converge, a plate capped by thin oceanic crust descends (subducts) beneath a plate with much thicker continental crust. The landscapes of many National Park Service sites show convergent plate boundary processes that result in a variety of mountain ranges and complex geological structures characteristic of subduction zones, accreted terranes and collisional mountain ranges.
Where are the two mountain ranges formed during plate convergence?
The Cascadia Subduction Zone and Southern Alaska Subduction Zone reveal two mountain ranges formed during plate convergence: an accretionary wedge near the coast and a volcanic arc farther inland. Rocks in California’s Sierra Nevada are cooled magma chambers that fed volcanoes of an ancient subduction zone. Examples of accreted terranes are found in southeast Alaska and northern Washington state. The Appalachian, Ouachita, and Marathon mountains comprise a collisional mountain range formed 500 to 300 million years ago, whereas the Brooks Range is the result of a more recent continental collision.
Where do tectonic plates converge?
Where tectonic plates converge, the one with thin oceanic crust subducts beneath the one capped by thick continental crust. A subduction zone consists of material scraped off the ocean floor near the coast (accretionary wedge) and a chain of volcanoes farther inland (volcanic arc).
How does a collisional mountain range form?
A collisional mountain range forms as an entire ocean closes and blocks of thick continental crust collide.
Why did the Ouachita Mountains never grow high?
Soft Continental Collision. The Ouachita Mountains never grew very high because continental collision stopped before the two thick continental crusts ever over lapped. A very thick pile of sediments was deposited and deformed above the relatively thin crust of the ancient passive continental margin.
How tall are Ouachita mountains?
In their prime, Ouachita peaks probably rose to no more than the modest height (~9,000 feet; 2,750 meters) of the Carpathian Mountains in central Europe. The low buoyancy of thin crust allowed the accumulation of thick sedimentary layers as the ancient ocean closed about 280 million years ago.
Where are the NPS sites?
The Appalachian Mountains are part of a collisional mountain range that includes the Ouachita Mountains of Arkansas and Oklahoma, and the Marathon Mountains in west Texas.
Which ocean closes as the continents collide?
Iapetus Ocean Closes. Pangea forms as the continents collide. The Appalachians are part of a larger zone of continental collision that includes the Marathon and Ouachita mountains in the southern United States, the Atlas Mountains in Africa, and the Caledonide Mountains in Greenland, the British Isles, and Scandinavia.
Where is the Brooks Range?
Northern Alaska was the site of continental collision that progressed to a stage somewhere between the soft collision seen in the Ouachita and Marathon mountains, and the hard collision observed in the Appalachians and Himalayas. In its prime, about 100 million years ago, the Brooks Range probably had mountains as high as the Alps of Europe. Gates of the Arctic National Park and Preserve reveals mountains much higher than those seen in the Appalachians, because the Brooks Range is still young—erosion has not worn the landscape down quite as much. Other NPS sites farther west in the Brooks Range include Cape Krusenstern National Monument, Kobuk Valley National Park, and Noatak National Preserve.
What is the history of the Appalachian Mountains?
The tectonic history of the Appalachian Mountains involves opening an ancient ocean along a divergent plate boundary, closing the ocean during plate convergence, and then more divergence that opened the Atlantic Ocean. Tracing this large-scale development helps us understand the place of origin of the various geologic provinces of the Southern Appalachian Mountains, as well as the rocks and structures observed along the Blue Ridge Parkway, the C&O Canal National Historical Park, and other NPS sites in the region.
What happens to the continental plate at an ocean-continent boundary?
At an ocean-continent convergent boundary, the denser oceanic plate is pushed under the less dense continental plate in the same manner as at an ocean-ocean boundary. Sediment that has accumulated on the seafloor is thrust up into an accretionary wedge, and compression leads to thrusting within the continental plate (Figure 4.6.2). The magma produced adjacent to the subduction zone rises to the base of the continental crust and leads to partial melting of the crustal rock. The resulting magma ascends through the crust, producing a mountain chain with many volcanoes. As with an ocean-ocean boundary, the subducting crust can produce a deep trench running parallel to the coastline.
What is the crust of the Earth?
the Earth’s crust underlying the continents (as opposed to ocean crust) (3.2) when part of a plate is forced beneath another plate along a subduction zone (4.3) the rigid outer part of the Earth, including the crust and the mantle down to a depth of about 100 km (3.2) long chains of volcanic islands found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries ...
What happens when a continent and a continent collide?
There is tremendous deformation of the pre-existing continental rocks, forcing the material upwards and creating mountains.
What are some examples of ocean-continent convergent boundaries?
Examples of ocean-continent convergent boundaries are subduction of the Nazca Plate under South America (which has created the Andes Mountains and the Peru Trench) and subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate under North America (creating the Cascade Range).
What is the trench and volcanic island formed from?
Figure 4.6.1 A trench and volcanic island formed from an ocean-ocean convergent zone (Steven Earle, “Physical Geology”). Examples of ocean-ocean convergent zones are subduction of the Pacific Plate south of Alaska (creating the Aleutian Islands) and under the Philippine Plate, where it creates the Marianas Trench, the deepest part of the ocean.
What happens when water is added to the hot mantle?
It mixes with the overlying mantle, and the addition of water to the hot mantle lowers the crust’s melting point and leads to the formation of magma (flux melting).
What are the three types of convergent boundaries?
The types are ocean-ocean, ocean-continent, and continent-continent.
Types of Convergent Boundaries
Convergent boundaries are of 3 types. These are determined by the area or location on the earth’s crust where the boundaries are formed.
1. Pacific Ring of Fire
This is the most famous boundary because it’s the most active seismic area in the world.
3. African Eurasian boundary (featuring the Alps)
The Alps are some of the most majestic mountains around. It features sedimentary rocks which is evidence that it originally emerged from the sea.
4. Nazca and South American boundary (featuring the Andes ranges)
These mountain ranges are located in South America. They formed from the collision of the Nazca and South America plates.
5. South American and Caribbean plate
This is an ocean-ocean boundary in which the South American plate meets the Caribbean plate.
Conclusion
Boundaries may restrict or confine. But convergent boundaries are of a different order.
How do continents grow outward?
Continents grow outward as volcanic islands and continental fragments enter a subduction zone and attach to the edge of the continent. Examples of such accreted terranes are found in NPS sites in southern Alaska and northern Washington State. Sometimes plate convergence closes an entire ocean. The crusts of the continents are too thick and buoyant to subduct, forming a collisional mountain range, such as the Appalachian/Ouachita/Marathon chain in the eastern United States and the Brooks Range in northern Alaska.
What is the name of the region where the continental crust lifts up a broad region known as a collisional?
Continents collide where subduction completely closes an ocean. The buoyant continental crust lifts up a broad region known as a collisional mountain range.
What is the process of convergent plate boundary?
Where tectonic plates converge, a plate capped by thin oceanic crust descends (subducts) beneath a plate with much thicker continental crust. The landscapes of many National Park Service sites show convergent plate boundary processes that result in a variety of mountain ranges and complex geological structures characteristic of subduction zones, accreted terranes and collisional mountain ranges.
Where are the two mountain ranges formed during plate convergence?
The Cascadia Subduction Zone and Southern Alaska Subduction Zone reveal two mountain ranges formed during plate convergence: an accretionary wedge near the coast and a volcanic arc farther inland. Rocks in California’s Sierra Nevada are cooled magma chambers that fed volcanoes of an ancient subduction zone. Examples of accreted terranes are found in southeast Alaska and northern Washington state. The Appalachian, Ouachita, and Marathon mountains comprise a collisional mountain range formed 500 to 300 million years ago, whereas the Brooks Range is the result of a more recent continental collision.
Where are accreted terranes found?
Examples of accreted terranes are found in southeast Alaska and northern Washington state. The Appalachian, Ouachita, and Marathon mountains comprise a collisional mountain range formed 500 to 300 million years ago, whereas the Brooks Range is the result of a more recent continental collision.
Where do tectonic plates converge?
Where tectonic plates converge, the one with thin oceanic crust subducts beneath the one capped by thick continental crust. A subduction zone consists of material scraped off the ocean floor near the coast (accretionary wedge) and a chain of volcanoes farther inland (volcanic arc).