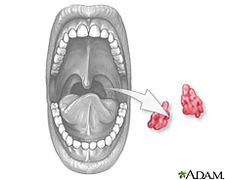
- Anterior tonsil pillar This is the fold of tissue just in front of the tonsils. ...
- Posterior tonsil pillar This is the fold of tissue just behind the tonsils. ...
- Glossotonsillar sulcus This is the bottom part of the tonsils where they blend into the lingual tonsil tissue on the back of the tongue. ...
- Tonsillar fossa This is the “pocket” in which the tonsils sit. ...
Where are the tonsils located?
What are the tonsils in the throat?
What is the pink mucosa of the tonsils?
Why is it important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading?
Why is tonsil grading important?
What is the BMI of a person with a palate position of 3 and 4?
Why do tonsils swell?
See 4 more
About this website
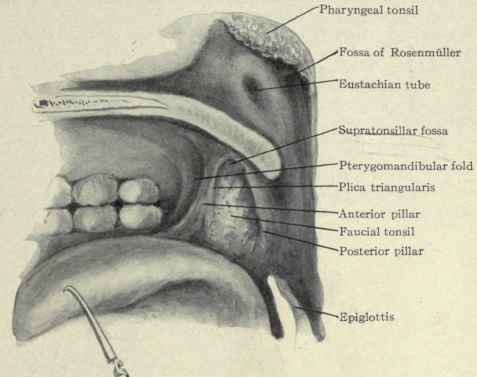
What muscles consist the tonsillar pillars?
The anterior tonsillar pillar is formed by the palatoglossus muscle, and the posterior pillar is formed by the palatopharyngeus muscle.
What are the pillars of the throat?
The anterior pillar is the palatoglossal arch formed of the palatoglossus muscle. The posterior pillar is the palatopharyngeal arch formed of the palatopharyngeus muscle. Between these two arches on the lateral walls of the oropharynx is the tonsillar fossa which is the location of the palatine tonsil.
What muscle forms the posterior pillar of the tonsillar fossa?
palatopharyngeal muscleThe palatopharyngeal muscle, with its overlying mucosa, forms the posterior tonsillar pillar. The two pillars connect laterally and inferiorly with the lateral oropharyngeal wall. The inferior aspect of the soft palate, which forms the upper portion of the oropharynx, is the site of the majority of soft palate tumors.
Where is the tonsillar tissue located in the oral cavity?
The palatine (or faucial) tonsils, commonly referred to as tonsils, are bundles of lymphatic tissue located in the lateral oropharynx. They sit in the isthmus of the fauces, bordered anteriorly by the palatoglossal arch and posteriorly by the palatopharyngeal arch.
How far back do tonsils go?
Your tonsils are near the back of your throat, just behind your soft palate. There are two of them — one on each side.
Are tonsils behind uvula?
The tonsils can be seen on either side of the throat at the back of the mouth. The adenoids are higher in the throat and usually cannot be seen. The uvula is the small, finger-shaped piece of tissue that hangs down from the soft palate in the back of the throat.
What is behind posterior tonsil pillar?
Posterior tonsil pillar This is the fold of tissue just behind the tonsils. It is created by the palatopharyngeus muscle which extends from the soft palate to the lateral wall of the pharynx.
What lies between anterior and posterior pillars?
What makes up the anterior and posterior pillars, and what lies between them? the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal muscles make up the anterior and posterior pillars, and the palatine tonsil lies between them.
What is the skin behind your tonsils?
Each tonsil is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes, covered by pink mucosa (like on the adjacent mouth lining). Running through the mucosa of each tonsil are pits, called crypts. The tonsils are part of the lymphatic system, which helps to fight infections.
What are the 5 tonsils?
The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system.
What is the tonsillar lymph node?
The tonsils are lymph nodes in the back of the mouth and top of the throat. They help to filter out bacteria and other germs to prevent infection in the body. A bacterial or viral infection can cause tonsillitis. Strep throat is a common cause.
Can you live without tonsils?
For some, the tonsils harbor bacteria that foster chronic infection. “The good news is, having your tonsils removed has proven to significantly reduce the rate of infection for chronic sufferers. And you don't need your tonsils, so there are no long-term consequences for having them removed,” Dr. Ingley says.
What makes up the anterior and posterior pillars?
What makes up the anterior and posterior pillars, and what lies between them? the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal muscles make up the anterior and posterior pillars, and the palatine tonsil lies between them.
Why is my uvula swollen?
Uvulitis is inflammation of your uvula, the fleshy, teardrop-shaped piece of tissue in the back of your throat. The condition can be caused by infection, allergies or trauma. Depending on the cause, uvulitis treatments may include antibiotics, antihistamines or, in some cases, surgery.
How many tubes are in your throat?
Sometimes you may swallow and cough because something “went down the wrong pipe.” The body has two “pipes” – the trachea (windpipe), which connects the throat to the lungs; and the esophagus, which connects the throat to the stomach.
What does a normal throat look like?
A healthy throat is usually consistently pink and shiny. Some people may have noticeable pink tissue on either side of the back of their throat, which is usually the tonsils.
What does size 3+ tonsils mean? and what are the effects of ... - HealthTap
Tonsil size: Tonsils are graded in size from 1 to 4, depending on how they look when your doctor examines you. A size 1+ is barely visible, and a 4+ means the tonsils are so large they touch in the middle. Tonsil size itself doesn't really mean anything, the important thing is whether they cause problems - such as recurrent infections or interfere with your breathing at night, causing sleep apnea.
Brodsky scale most reliable for tonsil size evaluation in kids
By Rob Goodier. NEW YORK (Reuters Health) - The Brodsky scale for evaluating the size of children's tonsils may give the most consistent results compared to two other tools - the Friedman scale and a new modified three-grade scale, a new study has found.
Tonsillar Hypertrophy Grading Scale - FPnotebook.com
FPnotebook.com is a rapid access, point-of-care medical reference for primary care and emergency clinicians. Started in 1995, this collection now contains 7137 interlinked topic pages divided into a tree of 31 specialty books and 738 chapters.
Where are the tonsils located?
Adenoid and nasopharyngeal tonsils - they are located at the back of the nose. They are partially surrounded by the Eustachian tubes. They can cause conditions such as difficulty in nasal breathing, ear infections, and sinusitis.
What are the tonsils in the throat?
In the back of the throat, there is a lymphoid group of tissues known as the tonsils. In the throat, there are four groups of tonsillar tissues, including palatine, lingual, adenoid, and nasopharyngeal. Each tonsil is covered by pink mucosa and is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. Pits running through the mucosa ...
What is the pink mucosa of the tonsils?
Each tonsil is covered by pink mucosa and is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. Pits running through the mucosa of each tonsil are called crypts. Tonsils help to fight infections and are a part of the lymphatic system. Removal of tonsils does not seem to increase the chances of infections.
Why is it important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading?
In clinical settings, it is important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading, as well as perform reliable monitoring. The grading scale of tonsils helps the clinicians to record the change in the tonsil size and communicate accordingly.
Why is tonsil grading important?
In clinical settings, it is important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading, as well as perform reliable monitoring. The grading scale of tonsils helps the clinicians to record the change in the tonsil size and communicate accordingly. Various grading systems may provide results that may be interpreted differently by the users. This makes the assessment of tonsil size by using tonsil grading system unreliable. Due to the variability in tonsil grading systems, there can be confusion in communicating the tonsil size. Hence, it is necessary to compare the existing tonsillar grading scales and to check the reliability and reproducibility. However, the reliability of this needs to be studied. Due to recurrent infection or as a part of generalized lymphoid hypertrophy, tonsils undergo hypertrophy. There is a good correlation between clinical tonsil grade and tonsil volume in snorers and obstructive sleep apnea.
What is the BMI of a person with a palate position of 3 and 4?
If the palate position is 3 and 4, then the tonsil size is 3 or 4. The BMI of the person is less than 40 kg/ m 2. Stage III: defined by palate position of 3 or 4 and the tonsil score is 0, 1, or 2. BMI of the person is more than 40 kg/ m 2. Brodsky developed a grading system.
Why do tonsils swell?
In response to infections, the tonsils swell and may vary in size. Tonsils can get affected by abscesses around the tonsils, infections of small pockets within the tonsils, and chronic tonsillitis. If there are symptoms of enlarged or infected tonsils, then you should see a doctor.
How to make tonsils normal?
One of the best ways to do it is by consuming a few spoons of honey daily. Thus gradually, you can see your tonsils recover and becoming normal.
Why are my tonsils enlarged?
Bacterial and Viral effect: One of the most common reasons of enlarged tonsils is the impact of bacteria, virus or any other microbes on tonsil glands. As I told, tonsils are present to stop many harmful microbes from entering your body. So when any such microbes attack your tonsils (causing an inflammation), then it results in the enlargement of your tonsils. The most common problems include tonsillitis, strep throat, peritonsillar abscess which can make your tonsils seem swollen.
What is a tonsil grade 0?
Tonsil Grade 0 – Your Tonsils are perfectly in the Tonsillar fossa and are not enlarged.
How to heal tonsils from viral infection?
You can either take antibiotics or natural remedies and make the microbes to die. Once you kill the microbes, you need to slowly heal your tonsils, so that the swelling and inflammation reduces.
What are the symptoms of tonsillar hypertrophy?
Thus the complications/symptoms of Tonsillar hypertrophy varies from simple symptoms like swelling, pain to serious troubles like difficulty breathing, unable to sleep and many more.
Does tonsil hypertrophy work?
For Tonsillar hypertrophy, general treatments that are suggested by many websites, people won’t actually work. Unlike other diseases, Tonsillar hypertrophy requires a special treatment which is varied according to the real cause causing your Enlarged tonsils.
Can tonsillar hypertrophy go away?
Yes, it was even medically approved that, Tonsillar hypertrophy can go away on its own in children, once they grow bigger and become adults.
Where is the lingual tonsil tissue?
Glossotonsillar sulcus. This is the bottom part of the tonsils where they blend into the lingual tonsil tissue on the back of the tongue. It is basically the area between the tonsils and the base of tongue. Tonsillar fossa. This is the “pocket” in which the tonsils sit.
Why do tonsils swell up?
They are made up of lymphoid tissue, which contains infection-fighting immune cells, and they tend to swell up when someone is sick. The tonsils can cause problems such as recurrent infections (e.g. Strep throat), snoring, or a sleeping disorder known as obstructive sleep apnea, and often have to be removed.
What is the bottom part of the ring called?
The bottom portion of the ring at the base of tongue is called the lingual tonsils (see below). As mentioned above, the palatine tonsils make up the sides of the ring, and the pharyngeal tonsils, also known as the adenoids, form the top of the ring, located near the roof of the nasopharynx.
What is the soft palate?
The soft palate is the part of the roof of the mouth behind the hard palate . The uvula is a muscular appendage that hangs from the middle of the soft palate. The soft palate is made up of many muscles which move as someone breathes, eats, and speaks. The nasopharynx is above and behind the soft palate.
What is the muscle that protects the airway?
Underneath the tonsil tissue lies the muscle that is responsible for the movement of the tongue base. The base of tongue is very important for swallowing and protecting the airway by preventing aspiration. Other anatomical structures related to the base of tongue include: Vallecula.
What is the base of the tongue called?
It also helps to manipulate food during chewing and to prepare the food to be moved to the oropharynx. The base of tongue is part of the oropharynx, and usually not visible when the mouth is open. The surface of this part of the tongue is lined with lymphoid tissue similar to the palatine tonsils, which are called the lingual tonsils.
What is the nasopharynx?
The naso pharynx is above and behind the soft palate. When the soft palate moves up, or elevates, while eating or drinking, it closes the connection between the nasopharynx and the oropharynx, preventing food and liquids from going up into the nose.
What muscle is the tonsillar bed?
The tonsillar bed is bounded laterally by the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle, superiorly by the soft palate, and inferiorly by the base of the tongue. Fig. 1.1 (a) Transoral view of the oropharynx.
Which plexus joins the glossopharyngeal and tonsillar plexus?
Tonsillar plexus: the middle and posterior palatine nerves (branches of the Meckel′s ganglion) join with the tonsillar branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve to form a plexus around the tonsils (this is known as “circulus tonsillaris”) Maxillary nerve. Passes through (not synapses) sphenopalatine ganglion.
What muscles are involved in lateral tongue resection?
With proper preoperative planning, the tongue base resection should not exceed 50% of the tongue base to help prevent poor functional outcomes. 2 The base of tongue resection should extend to the vallecula posteriorly. The extrinsic muscles of the tongue that are encountered in the lateral tongue base include the palatoglossus and styloglossus muscles . If a larger dissection of the tongue base is required due to tumor involvement, the lingual artery, the lingual nerve, and possibly the hypoglossal nerve may be encountered in the lateral tongue base. The lingual artery is depicted in Fig. 1.5 .
What is visualized in a pharyngeal dissection?
Visualized is the ascending pharyngeal with its inferior, middle, and superior pharyngeal branches. Additionally, the tonsillar venous plexus can be seen lateral and deep to the arterial structures. Along the cephalad portion (bottom) of the dissection, the stylopharyngeus and stylohyoid are splayed.
What are the contraindications for a TORS radical tonsillectomy?
The main indication for TORS is primary resection of squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsillar fossa, specifically T1 and T2 tumors with selected T3 and T4a neoplasms. 2 Contraindications for TORS radical tonsillectomy include stage IVC cancer (with exception for curable, solitary, distant metastasis), T4a cancer (with exception of those involving only the extrinsic muscles of the tongue or minimal involvement of the medial pterygoid muscle), radiologic evidence of tumor adjacent to the common or internal carotid artery, any T-stage tumor with fixed invasion of tissues lateral to the pharyngeal constrictor muscles or posteriorly of the prevertebral fascia, unresectable node involvement, and dermal metastasis. 2 Other non–tumor-related contraindications include trismus that prevents adequate exposure, a retropharyngeal internal carotid artery, and any medical comorbidities precluding the patient from general anesthesia or surgery. 2
What is a TORS procedure?
Transoral robotic surgery (TORS) radical tonsillectomy, first described by Weinstein et al in 2007, is a modified variation of the transoral lateral oropharyngectomy described by Holsinger in 2005. 1 Preoperative evaluation and planning with crosssectional imaging for this procedure is paramount in order to ensure the safety of nearby important vascular structures, such as the carotid arterial system, and also to help preserve functional outcomes. As will be shown, the anatomical relationships in the tonsillar region with its many vital structures require a strong knowledge of the anatomy of this region as well as familiarity with the TORS perspective. The dissection will involve the parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal spaces, the lateral base of the tongue, and the soft palate.
Where does the glossopharyngeal nerve go?
Inferiorly in the parapharyngeal space, following the styloglossus and stylopharyngeus muscles as they diverge to their respective insertions, the lingual branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve runs anteriorly toward the lateral tongue base. The glossopharyngeal nerve exits the jugular foramen and traverses inferiorly with the carotid sheath posterior to the stylopharyngeus muscle. When the glossopharyngeal nerve turns anteriorly toward the lateral tongue base, it can be identified medial to the stylohyoid ligament between the superior and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscles en route to the base of the tongue. There is some variation in the course of the glossopharyngeal nerve noted in some cadaveric studies. In the majority of cases, the glossopharyngeal nerve is separated from the tonsillar bed by either the superior pharyngeal constrictor, the styloglossus, or the stylopharyngeus muscle; however, in about 20% of cases the glossopharyngeal nerve was adherent to the tonsillar capsule as it traveled to the base of the tongue. 4 Due to this variation, careful dissection of the inferior portion of the tonsillar bed should be performed in attempt to prevent injury to the lingual branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Where are the tonsils located?
Adenoid and nasopharyngeal tonsils - they are located at the back of the nose. They are partially surrounded by the Eustachian tubes. They can cause conditions such as difficulty in nasal breathing, ear infections, and sinusitis.
What are the tonsils in the throat?
In the back of the throat, there is a lymphoid group of tissues known as the tonsils. In the throat, there are four groups of tonsillar tissues, including palatine, lingual, adenoid, and nasopharyngeal. Each tonsil is covered by pink mucosa and is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. Pits running through the mucosa ...
What is the pink mucosa of the tonsils?
Each tonsil is covered by pink mucosa and is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. Pits running through the mucosa of each tonsil are called crypts. Tonsils help to fight infections and are a part of the lymphatic system. Removal of tonsils does not seem to increase the chances of infections.
Why is it important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading?
In clinical settings, it is important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading, as well as perform reliable monitoring. The grading scale of tonsils helps the clinicians to record the change in the tonsil size and communicate accordingly.
Why is tonsil grading important?
In clinical settings, it is important to document tonsil size and tonsil grading, as well as perform reliable monitoring. The grading scale of tonsils helps the clinicians to record the change in the tonsil size and communicate accordingly. Various grading systems may provide results that may be interpreted differently by the users. This makes the assessment of tonsil size by using tonsil grading system unreliable. Due to the variability in tonsil grading systems, there can be confusion in communicating the tonsil size. Hence, it is necessary to compare the existing tonsillar grading scales and to check the reliability and reproducibility. However, the reliability of this needs to be studied. Due to recurrent infection or as a part of generalized lymphoid hypertrophy, tonsils undergo hypertrophy. There is a good correlation between clinical tonsil grade and tonsil volume in snorers and obstructive sleep apnea.
What is the BMI of a person with a palate position of 3 and 4?
If the palate position is 3 and 4, then the tonsil size is 3 or 4. The BMI of the person is less than 40 kg/ m 2. Stage III: defined by palate position of 3 or 4 and the tonsil score is 0, 1, or 2. BMI of the person is more than 40 kg/ m 2. Brodsky developed a grading system.
Why do tonsils swell?
In response to infections, the tonsils swell and may vary in size. Tonsils can get affected by abscesses around the tonsils, infections of small pockets within the tonsils, and chronic tonsillitis. If there are symptoms of enlarged or infected tonsils, then you should see a doctor.
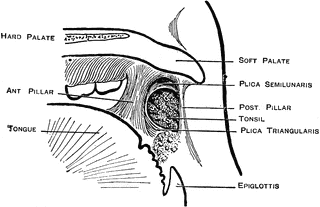
Pathophysiology
- In the back of the throat, there is a lymphoid group of tissues known as the tonsils. In the throat, there are four groups of tonsillar tissues, including palatine, lingual, adenoid, and nasopharyngeal. Each tonsil is covered by pink mucosa and is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. Pits running through the mucosa of each tonsil are called crypts. Tonsils help to fight infections and …
Diagnosis
- Tonsils can get affected by abscesses around the tonsils, infections of small pockets within the tonsils, and chronic tonsillitis. If there are symptoms of enlarged or infected tonsils, then you should see a doctor. The various methods to check tonsils are medical history, physical examination of the patient, throat cultures/strep tests, which help in determining infections, bloo…
Classification
- The size of the tonsils is graded on a scale from one to four. Four is the largest size. The tongue should be rested comfortably in the mouth for best judgment of the tonsil. Palatine tonsils are graded based on how much the airway is obstructed due to the tonsil protruding from either side of the oropharynx.
Clinical significance
- Along the back wall of the throat are scattered blebs of tonsils known as Waldeyers ring. In a person, even after tonsillectomy, Waldeyers ring play a vital role in causing pharyngeal strep tonsillitis. The tonsils are assessed by making the patient open his mouth and depressing the tongue. A tongue blade is used, while a penlight is used for inspe...
Assessment
- The primary difference in both the assessments is that in the Friedman system the tongue is not protruded out. This scale is also referred to as the Modified Mallampati Scale. By combining the palate grade, tonsil size, and BMI, Friedman created a staging system. This would help to determine the surgical practices for obstructive sleep apnea. Lower staging would predict succe…
Variations
- Grade 0 is when the tonsils are in the tonsillar fossa. The tonsils in this grade do not extend medially to the anterior tonsillar fossa.
Signs and symptoms
- Enlargement of tonsils causes difficulty in swallowing, limits the airflow, causes pain or discomfort and obstructive sleep apnea. If the obstructive sleep apnea is long term, then it can cause delay in the growth and development of a person, behavioral problems, and also cardiopulmonary problems. To check the airway muscle tone in children, clinicians look for the s…
Example
- The Brodsky grading scale and Friedman grading scale are the two most widely used grading scales. In the Brodsky grading scale, the tonsils are graded from 1 to 4, which depend on the percentage of oropharyngeal airway that is occupied by the tonsil. In the Friedman grading scale, the tonsil size is classified on the basis of the location of the tonsil in relation to its surrounding …
Results
- In this study, it was found that the most consistent results can be obtained by the Brodsky scale in comparison to the Friedman scale and a three-grade scale. In clinical and research work, it is recommended to use the Brodsky scale to grade tonsil size. The most reliable measurements both between the observers and between different measurements by the same observer can be …