
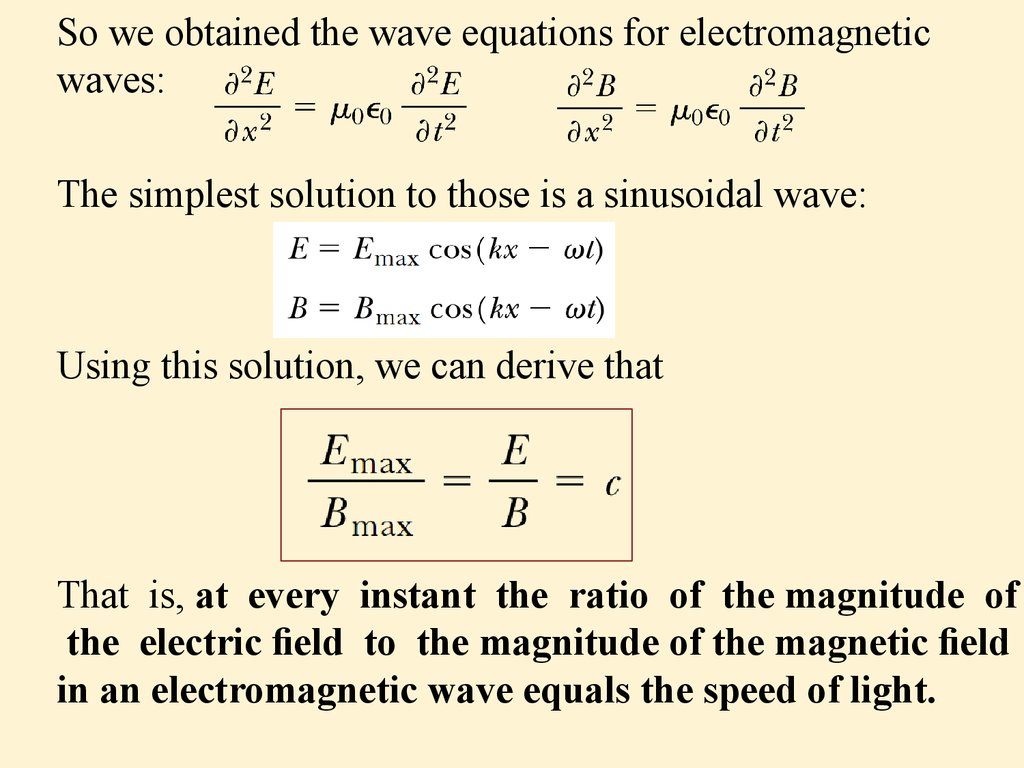
‘Wave’ is a common term for a number of different ways in which energy is transferred:
- In electromagnetic waves, energy is transferred through vibrations of electric and magnetic fields.
- In sound waves, energy is transferred through vibration of air particles or particles of a solid through which the sound travels.
- In water waves, energy is transferred through the vibration of the water particles.
Where do mechanical waves transfer energy?
Types of Mechanical Waves and How Does Energy Travel in a Mechanical Wave?
- Longitudinal Waves. Longitudinal waves are mechanical waves in which particles within the medium oscillate back and forth in a direction parallel to that of the wave propagation.
- Transverse Mechanical Waves. Another kind of mechanical wave is a transverse wave. ...
- Surface Waves. ...
Where is energy stored in electromagnetic waves?
Section Summary
- The energy carried by any wave is proportional to its amplitude squared. ...
- This can also be expressed in terms of the maximum magnetic field strength B0 as I ave = cB2 0 2μ0 I ave = cB 0 2 2 μ 0 ...
- The three expressions for Iave are all equivalent.
Where do waves get their energy from?
Waves get their energy from the wind. Wind comes from solar energy. Waves gather, store, and transmit this energy thousands of miles with little loss. As long as the sun shines, wave energy will never be depleted. It varies in intensity, but it is available twenty-four hours a day, 365 days a year.
How do you generate electricity from waves?
Wave energy can be harnessed out at sea or by the shoreline. For example, waves reaching the shore can be used like a piston to push air up and down a large pipe. The force of the air being pushed is used to turn a turbine. This turbine is attached to a generator that creates the electricity.
Where do electromagnetic waves not transfer energy?
An EM wave can travel without a material medium—that is, in a vacuum or space empty of matter—and does not lose energy as it moves.
How do electromagnetic waves carry energy?
Electromagnetic waves bring energy into a system by virtue of their electric and magnetic fields. These fields can exert forces and move charges in the system and, thus, do work on them. However, there is energy in an electromagnetic wave itself, whether it is absorbed or not.
Can electromagnetic waves transport energy?
Electromagnetic waves transport energy and momentum across space.
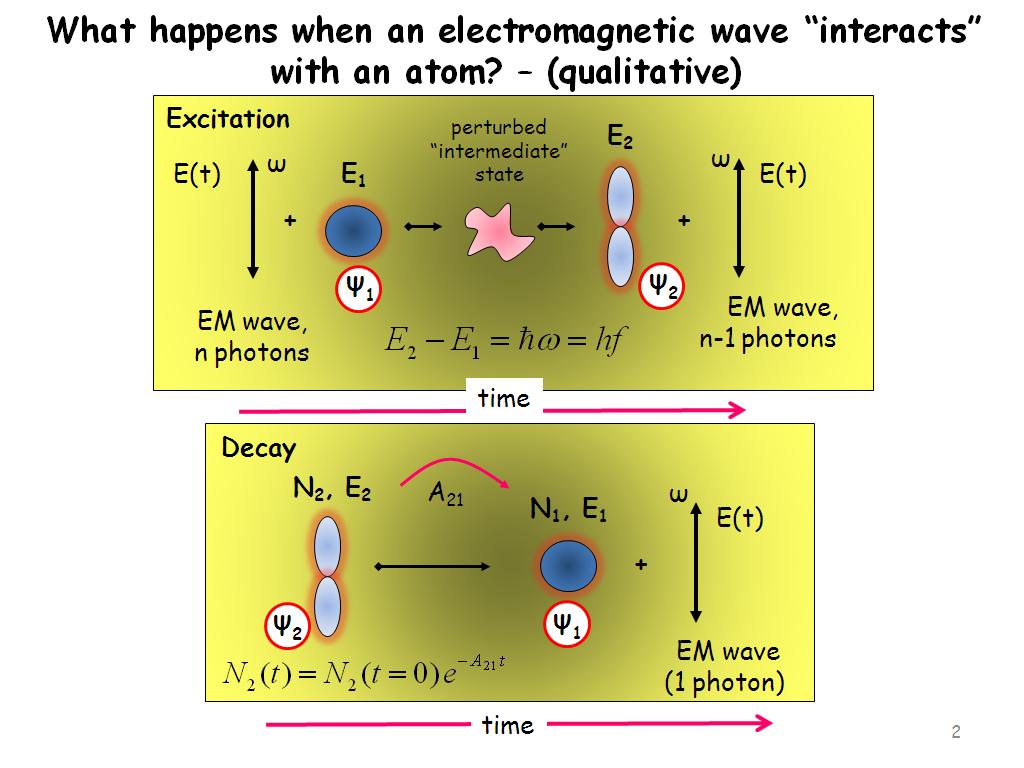
How electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum?
Solution : The EM waves are produced by the accelerated charge. The electron jumping from outer to inner orbit of the electron radiates EM waves. EM waves are propagated as electric & magnetic fields oscillation in mutually perpendicular directions which shows that EM waves carry momentum & energy.
What is transferred by electromagnetic waves quizlet?
The energy that is transferred by electromagnetic waves is called called electromagnetic radiation Because electromagnetic radiation does not need a medium can travel through the vacuum of outer space.
Which electromagnetic wave transfers the most energy?
1 AnswerGamma( γ ) radiation has the greatest energy.This is because γ -radiation has the highest frequency.Energy α frequency.
What Is Electromagnetic Energy?
Electromagnetic energy is radiant energy that travels in waves at the speed of light. It can also be described as radiant energy, electromagnetic r...
How Do Electromagnetic Waves Work?
Electromagnetic energy consists of changing magnetic and electric fields that transfer electromagnetic energy. Positive charges create electric fie...
What Is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is a span of the range of frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. Each type of wave and frequency co...
Is Electromagnetic Energy Safe?
The dangers associated with electromagnetic waves beg the question of whether or not electromagnetic energy is safe. Electromagnetic radiation depe...
Why Is Electromagnetic Energy Important?
As the environmental state of the planet becomes a growing concern, so does our need to understand electromagnetic radiation. Scientists will need...
What Is Electromagnetic Energy?
Electromagnetic energy is radiant energy that travels in waves at the speed of light.
How Do Electromagnetic Waves Work?
Electromagnetic energy consists of changing magnetic and electric fields that transfer electromagnetic energy. Positive charges create electric fields, or a charged space surrounds it that radiates outward. When that charged particle is manipulated — for example, by moving it up and down — you change the electric field.
What Is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is a span of the range of frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. Each type of wave and frequency combination creates different forms of energy.
Electromagnetic Radiation Across the Spectrum
At the start of the electromagnetic spectrum are low-frequency radio waves.
Is Electromagnetic Energy Safe?
The dangers associated with electromagnetic waves beg the question of whether or not electromagnetic energy is safe.
Why Is Electromagnetic Energy Important?
As the environmental state of the planet becomes a growing concern, so does our need to understand electromagnetic radiation. Scientists will need to continue their research on radiation and electromagnetic energy while the need for renewable and sustainable power grows.
What is electromagnetic wave?
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves. Their vibrations or oscillations are changes in electrical and magnetic fields at right angles to the direction of wave travel. All electromagnetic waves: transfer energy as radiation from the source of the waves to an absorber. can travel through a vacuum such as in space.
How are radio waves transmitted?
Radio waves are transmitted easily through air. They do not cause damage if absorbed by the human body, and they can be reflected to change their direction. These properties make them ideal for communications. Radio waves can be produced by oscillations in electrical circuits.
What are the effects of ultraviolet radiation?
Ionisation can have hazardous effects on the body, such as: ultraviolet waves can cause skin to age prematurely and increase the risk of skin cancer.
What are the effects of gamma rays?
Ultraviolet waves, x-rays and gamma rays are types of ionising radiation. They can add or remove electrons from molecules, producing electrically charged ions. Ionisation can have hazardous effects on the body, such as: 1 ultraviolet waves can cause skin to age prematurely and increase the risk of skin cancer 2 x-rays and gamma rays can cause the mutation of genes, which can lead to cancer
How do gamma rays get absorbed?
Changes in atoms and their nuclei can cause electromagnetic waves to be generated or absorbed. Gamma rays are produced by changes in the nucleus of an atom. They are a form of nuclear radiation. High energy waves such as x-rays and gamma rays are transmitted through body tissues with very little absorption.
How many groups of electromagnetic waves are there?
This causes electromagnetic waves to be separated into seven distinct groups in the spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum. Each group contains a range of frequencies. For example, visible light contains all the frequencies that can be detected by the human eye: red light has the lowest frequencies of visible light.
How fast can electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum?
can travel through a vacuum such as in space. travel at the same speed through a vacuum or the air. Electromagnetic waves travel at 300 million metres per second (m/s) through a vacuum.
Electromagnetic Waves
Waves Or particles? Yes!
- Light is made of discrete packets of energy called photons. Photons carry momentum, have no mass, and travel at the speed of light. All light has both particle-like and wave-like properties. How an instrument is designed to sense the light influences which of these properties are observed. An instrument that diffracts light into a spectrum for analysis is an example of observing the wave-l…
Polarization
- One of the physical properties of light is that it can be polarized. Polarization is a measurement of the electromagnetic field's alignment. In the figure above, the electric field (in red) is vertically polarized. Think of a throwing a Frisbee at a picket fence. In one orientation it will pass through, in another it will be rejected. This is similar to how sunglasses are able to eliminate glare by absor…
Describing Electromagnetic Energy
- The terms light, electromagnetic waves, and radiation all refer to the same physical phenomenon: electromagnetic energy. This energy can be described by frequency, wavelength, or energy. All three are related mathematically such that if you know one, you can calculate the other two. Radio and microwaves are usually described in terms of frequency (Hertz), infrared and visible light in t…
Frequency
- The number of crests that pass a given point within one second is described as the frequency of the wave. One wave—or cycle—per second is called a Hertz (Hz), after Heinrich Hertz who established the existence of radio waves. A wave with two cycles that pass a point in one second has a frequency of 2 Hz.
Wavelength
- Electromagnetic waves have crests and troughs similar to those of ocean waves. The distance between crests is the wavelength. The shortest wavelengths are just fractions of the size of an atom, while the longest wavelengths scientists currently study can be larger than the diameter of our planet!
Energy
- An electromagnetic wave can also be described in terms of its energy—in units of measure called electron volts (eV). An electron volt is the amount of kinetic energy needed to move an electron through one volt potential. Moving along the spectrum from long to short wavelengths, energy increases as the wavelength shortens. Consider a jump rope with its ends being pulled up and d…