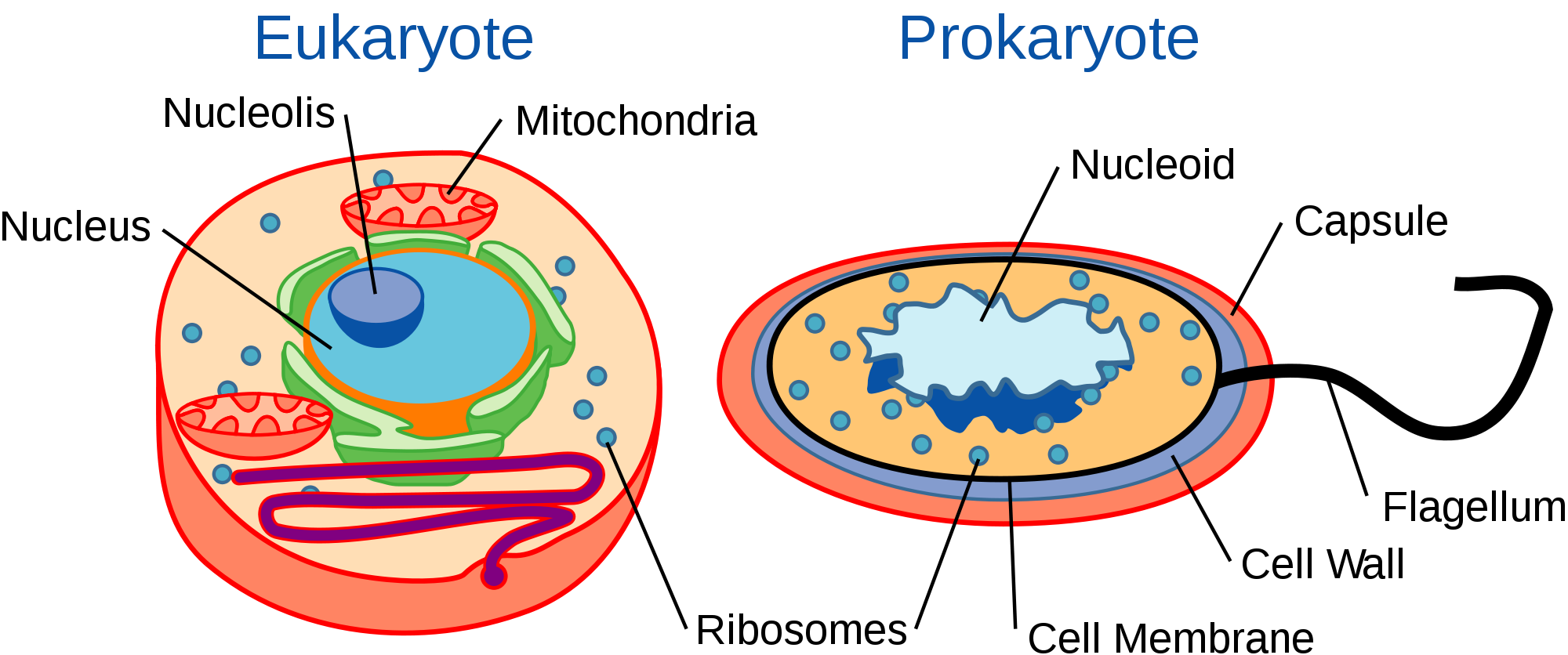
Where are tRNAs and rRNAs transcribed?
How do guide RNAs interact with pre-mRNA?
How are pre-mRNAs modified?
How much of a ribosome is RNA?
What are the exons of eukaryotic genes?
How many introns are present in mRNA?
How long does eukaryotic mRNA last?
See 2 more
Where does rRNA synthesis take place within an eukaryotic cell?
the nucleolusMolecules of rRNA are synthesized in a specialized region of the cell nucleus called the nucleolus, which appears as a dense area within the nucleus and contains the genes that encode rRNA.
Where does rRNA processing occur?
the nucleolusIn eukaryotes, the individual processes involved occur in defined regions of the cell: ribosomal proteins are synthesized in the cytosol, but most rRNAs are transcribed, processed and modified in the nucleolus, a distinct subnuclear compartment (Lafontaine and Tollervey, 2001; Boisvert et al., 2007).
What produces rRNA in eukaryotic cells?
In eukaryotes, the rRNA in ribosomes is organized into four strands, and in prokaryotes, three strands. Eukaryote ribosomes are produced and assembled in the nucleolus.
How are rRNA processed in eukaryotes?
In eukaryotes, three of the four ribosomal RNAs forming the 40S and 60S subunits are borne by a long polycistronic pre-ribosomal RNA. A complex sequence of processing steps is required to gradually release the mature RNAs from this precursor, concomitant with the assembly of the 79 ribosomal proteins.
Does RNA processing occur in eukaryotes?
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes process their ribosomal and transfer RNAs. The major difference in RNA processing, however, between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, is in the processing of messenger RNAs.
How is rRNA Synthesised?
rRNA Genes and Synthesis of rRNA In eukaryotic cells, rRNA is synthesized in the nucleolus and, once it is synthesized, it is assembled outside the nucleolus. rRNA is synthesized from mRNA within the nucleolus and its location, once assembled, can be found in the cytoplasm. In the nucleolus, there are encoded rRNAs.
How many rRNA is present in eukaryotes?
The eukaryotic SSU contains an 18S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) (1,800 nucleotides in yeast) and 33 different ribosomal proteins (r-proteins), which are organized into three distinct structural subdomains: the body, which contains the 5′ domain of 18S rRNA; the platform, which contains the central domain; and the head, which ...
What is the site of synthesis of rRNA and assembly of rRNA and proteins into ribosomal subunits?
Nucleoli are a prominent feature of an interphase nucleus (seeFig. 1.2). They are the site of most of the synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and assembly of ribosome subunits.
What is the function of rRNA in translation?
During translation of mRNA, rRNA functions to bind both mRNA and tRNA to facilitate the process of translating mRNA's codon sequence into amino acids. rRNA initiates the catalysis of protein synthesis when tRNA is sandwiched between the SSU and LSU.
Where does tRNA take place in the cell?
Although tRNAs participate in the essential function of protein translation in the cytoplasm, tRNA transcription and numerous processing steps occur in the nucleus.
What is the function of rRNA?
Within the ribosome, the rRNA molecules direct the catalytic steps of protein synthesis — the stitching together of amino acids to make a protein molecule. In fact, rRNA is sometimes called a ribozyme or catalytic RNA to reflect this function.
What does ribosomal RNA rRNA do?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules are the structural components of the ribosome. The rRNAs form extensive secondary structures and play an active role in recognizing conserved portions of mRNAs and tRNAs. They also assist with the catalysis of protein synthesis.
RNA Processing: Eukaryotic mRNA and tRNA Processing (With Diagram)
ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us make an in-depth study of the RNA processing. After reading this article you will learn about: 1. Processing of Eukaryotic mRNA 2. RNA Splicing and Mechanisms of Splicing and 3. Processing of tRNA. Almost all types of RNA molecules undergo post synthesis transformation which is called RNA processing. Prokaryotic mRNA is generally […]
15.4 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes - Biology 2e | OpenStax
Evolution Connection. RNA Editing in Trypanosomes The trypanosomes are a group of protozoa that include the pathogen Trypanosoma brucei, which causes nagana in cattle and sleeping sickness in humans throughout great areas of Africa (Figure 15.12).The trypanosome is carried by biting flies in the genus Glossina (commonly called tsetse flies). ). Trypanosomes, and virtually all other eukaryotes ...
Where are tRNAs and rRNAs transcribed?
The tRNAs and rRNAs are structural molecules that have roles in protein synthesis; however, these RNAs are not themselves translated. Pre-rRNAs are transcribed, processed, and assembled into ribosomes in the nucleolus. Pre-tRNAs are transcribed and processed in the nucleus and then released into the cytoplasm where they are linked to free amino acids for protein synthesis.
How do guide RNAs interact with pre-mRNA?
One or more of these molecules interacts by complementary base pairing with some of the nucleotides in the pre-mRNA transcript. However, the guide RNA has more A nucleotides than the pre-mRNA has U nucleotides to bind with. In these regions, the guide RNA loops out. The 3′ ends of guide RNAs have a long poly-U tail, and these U bases are inserted in regions of the pre-mRNA transcript at which the guide RNAs are looped. This process is entirely mediated by RNA molecules. That is, guide RNAs—rather than proteins—serve as the catalysts in RNA editing.
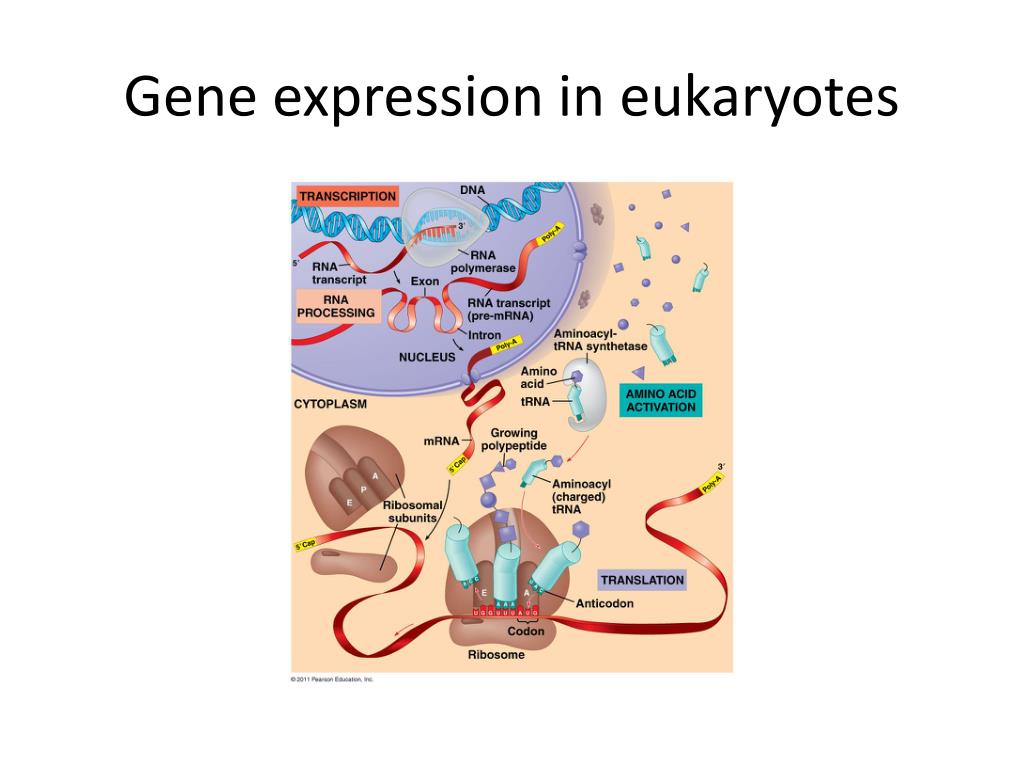
How are pre-mRNAs modified?
Eukaryotic pre-mRNAs are modified with a 5′ methylguanosine cap and a poly-A tail. These structures protect the mature mRNA from degradation and help export it from the nucleus. Pre-mRNAs also undergo splicing, in which introns are removed and exons are reconnected with single-nucleotide accuracy. Only finished mRNAs that have undergone 5′ capping, 3′ polyadenylation, and intron splicing are exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Pre-rRNAs and pre-tRNAs may be processed by intramolecular cleavage, splicing, methylation, and chemical conversion of nucleotides. Rarely, RNA editing is also performed to insert missing bases after an mRNA has been synthesized.
How much of a ribosome is RNA?
Mature rRNAs make up approximately 50 percent of each ribosome. Some of a ribosome’s RNA molecules are purely structural, whereas others have catalytic or binding activities. Mature tRNAs take on a three-dimensional structure through intramolecular hydrogen bonding to position the amino acid binding site at one end and the anticodon at the other end ( [link] ). The anticodon is a three-nucleotide sequence in a tRNA that interacts with an mRNA codon through complementary base pairing.
What are the exons of eukaryotic genes?
Eukaryotic genes are composed of exons, which correspond to protein-coding sequences ( ex- on signifies that they are ex pressed), and int ervening sequences called introns ( int- ron denotes their int ervening role), which may be involved in gene regulation but are removed from the pre-mRNA during processing. Intron sequences in mRNA do not encode functional proteins.
How many introns are present in mRNA?
Note that more than 70 individual introns can be present, and each has to undergo the process of splicing—in addition to 5′ capping and the addition of a poly-A tail—just to generate a single, translatable mRNA molecule.
How long does eukaryotic mRNA last?
Eukaryotic mRNAs last for several hours, whereas the typical E. coli mRNA lasts no more than five seconds.
Where is RNA synthesized in prokaryotes?
These include ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which forms part of the ribosomes and is exported to the cytoplasm to help translate the information in mRNA into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is synthesized in a specialized region of the nucleus called the nucleolus, which appears as a dense area within ...
What is rRNA in biology?
Alternative Titles: rRNA, ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), molecule in cells that forms part of the protein -synthesizing organelle known as a ribosome and that is exported to the cytoplasm to help translate the information in messenger RNA (mRNA) into protein. The three major types of RNA that occur in cells are rRNA, mRNA, ...
How many rRNAs are in a ribosome?
The encoded rRNAs differ in size, being distinguished as either large or small. Each ribosome contains at least one large rRNA and at least one small rRNA. In the nucleolus, the large and small rRNAs combine with ribosomal proteins to form the large and small subunits of the ribosome (e.g., 50S and 30S, respectively, in bacteria).
What is rRNA in encyclopaedia?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree.... See Article History. Alternative Titles: rRNA, ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), molecule in cells that forms part ...
What is ribosomal RNA?
Learn More in these related Britannica articles: nucleic acid: Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules are the structural components of the ribosome. The rRNAs form extensive secondary structures and play an active role in recognizing conserved portions of mRNAs and tRNAs.
Where are ribosomes synthesized?
Each ribosome contains at least one large rRNA and at least one small rRNA. In the nucleolus, the large and small rRNAs combine with ribosomal proteins to form the large and small subunits of the ribosome (e.g., 50S and 30S, respectively, in bacteria). (These subunits generally are named according to their rate of sedimentation, measured in Svedberg units [S], in a centrifugal field.) Ribosomal proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasm and transported to the nucleus for subassembly in the nucleolus. The subunits are then returned to the cytoplasm for final assembly.
Where are the subunits of RNA transcribed?
The subunits are then returned to the cytoplasm for final assembly. Scientific model of transcription and translation in a eukaryotic cell. Molecules of messenger RNA are transcribed in the nucleus and then transported to the cytoplasm for translation into proteins by ribosomal RNA.
Is rRNA processing important in eukaryotic cells?
In summary, it can be argued that the understanding of eukaryotic rRNA processing is no less important than the understanding of mRNA maturation, since the capacity of a cell to carry out protein synthesis is controlled, in part, by the abundance of ribosomes. Processing of pre-rRNA is highly regula …
Is rRNA processing regulated?
Processing of pre-rRNA is highly regulated, in volving many cellular components acting either alone or as part of a complex. Some of these components are directly involved in the modification and cleavage of the precursor rRNA, while others direct the packaging of the rRNA into ribosome subunits. As is the case for pre-mRNA processing, snoRNPs are clearly involved in eukaryotic rRNA processing, and have been proposed to assemble with other proteins into at least one complex called a "processosome" (17), which carries out the ordered processing of the pre-rRNA and its assembly into ribosomes. The formation of a processing complex clearly makes possible the regulation required to coordinate the abundance of ribosomes with the physiological and developmental changes of a cell. It may be that eukaryotic rRNA processing is even more complex than pre-mRNA maturation, since pre-rRNA undergoes extensive nucleotide modification and is assembled into a complex structure called the ribosome. Undoubtedly, features of the eukaryotic rRNA-processing pathway have been conserved evolutionarily, and the genetic approach available in yeast research (6) should provide considerable knowledge that will be useful for other investigators working with higher eukaryotic systems. Interestingly, it was originally hoped that the extensive work and understanding of bacterial ribosome formation would provide a useful paradigm for the process in eukaryotes. However, although general features of ribosome structure and function are highly conserved between bacterial and eukaryotic systems, the basic strategy in ribosome biogenesis seems to be, for the most part, distinctly different. Thus, the detailed molecular mechanisms for rRNA processing in each kingdom will have to be independently deciphered in order to elucidate the features and regulation of this important process for cell survival.
Which organelle is responsible for the packaging and secretion of molecules?
Endoplasmic reticulum. an organelle of eucaryotes that participates in packaging and secretion of molecules. golgi apparatus. a double-membrane organelle of eukaryotes that is the main site for aerobic respiration. mitochondria. An organelle containing chlorophyll that is found in photosynthetic eukaryotes. chloroplasts.
What is the cytoskeleton?
cytoskeleton. cellular cytoskeletal element formed by thin protein strands that attatch to cell membrane and form a network through the cytoplasm. responsible for movement of cytoplasm. microfilaments. long tubular structures made of protein that function in the structure, shape,, and movement of eukaryotic cells.
Where are tRNAs and rRNAs transcribed?
The tRNAs and rRNAs are structural molecules that have roles in protein synthesis; however, these RNAs are not themselves translated. Pre-rRNAs are transcribed, processed, and assembled into ribosomes in the nucleolus. Pre-tRNAs are transcribed and processed in the nucleus and then released into the cytoplasm where they are linked to free amino acids for protein synthesis.
How do guide RNAs interact with pre-mRNA?
One or more of these molecules interacts by complementary base pairing with some of the nucleotides in the pre-mRNA transcript. However, the guide RNA has more A nucleotides than the pre-mRNA has U nucleotides to bind with. In these regions, the guide RNA loops out. The 3′ ends of guide RNAs have a long poly-U tail, and these U bases are inserted in regions of the pre-mRNA transcript at which the guide RNAs are looped. This process is entirely mediated by RNA molecules. That is, guide RNAs—rather than proteins—serve as the catalysts in RNA editing.
How are pre-mRNAs modified?
Eukaryotic pre-mRNAs are modified with a 5′ methylguanosine cap and a poly-A tail. These structures protect the mature mRNA from degradation and help export it from the nucleus. Pre-mRNAs also undergo splicing, in which introns are removed and exons are reconnected with single-nucleotide accuracy. Only finished mRNAs that have undergone 5′ capping, 3′ polyadenylation, and intron splicing are exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Pre-rRNAs and pre-tRNAs may be processed by intramolecular cleavage, splicing, methylation, and chemical conversion of nucleotides. Rarely, RNA editing is also performed to insert missing bases after an mRNA has been synthesized.
How much of a ribosome is RNA?
Mature rRNAs make up approximately 50 percent of each ribosome. Some of a ribosome’s RNA molecules are purely structural, whereas others have catalytic or binding activities. Mature tRNAs take on a three-dimensional structure through intramolecular hydrogen bonding to position the amino acid binding site at one end and the anticodon at the other end ( [link] ). The anticodon is a three-nucleotide sequence in a tRNA that interacts with an mRNA codon through complementary base pairing.
What are the exons of eukaryotic genes?
Eukaryotic genes are composed of exons, which correspond to protein-coding sequences ( ex- on signifies that they are ex pressed), and int ervening sequences called introns ( int- ron denotes their int ervening role), which may be involved in gene regulation but are removed from the pre-mRNA during processing. Intron sequences in mRNA do not encode functional proteins.
How many introns are present in mRNA?
Note that more than 70 individual introns can be present, and each has to undergo the process of splicing—in addition to 5′ capping and the addition of a poly-A tail—just to generate a single, translatable mRNA molecule.
How long does eukaryotic mRNA last?
Eukaryotic mRNAs last for several hours, whereas the typical E. coli mRNA lasts no more than five seconds.