Where is the internal thoracic vein located?
In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein (previously known as the internal mammary vein) is a vessel that drains the chest wall and breasts. Bilaterally, the internal thoracic vein arises from the superior epigastric vein, and accompanies the internal thoracic artery along its course.
Which veins drain into the brachiocephalic veins?
The internal thoracic veins drain into the brachiocephalic veins .] Posterior surface of sternum and costal cartilages, showing Transversus thoracis. (Internal mammary vessels labeled at center top.) In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein (previously known as the internal mammary vein) is a vessel that drains the chest wall and breasts.
What vein drains the thoracic and abdominal wall?
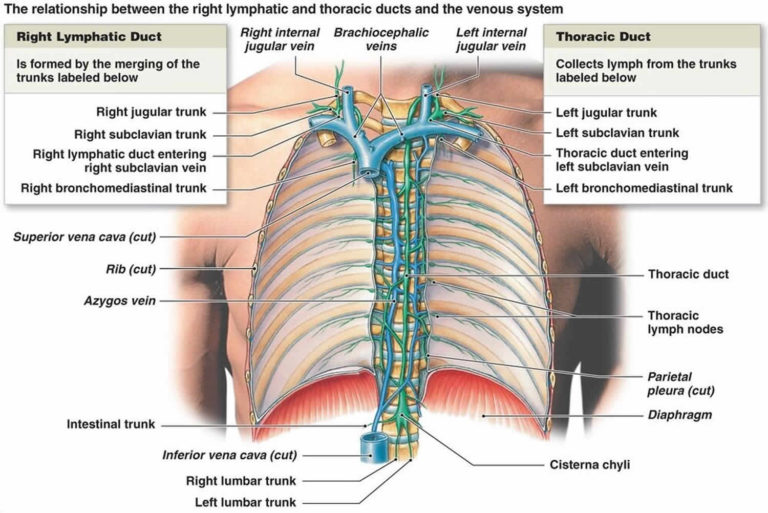
The azygos vein drains the posterior thoracic and abdominal wall, and is formed by the confluence of the ascending lumbar veins and the right subcostal vein at vertebral level T12. The azygos vein arches over the right main bronchus, in order to join the superior vena cava. The azygos vein also drains the pericardial veins,...
What does the right thoracic vein bifurcate?
The right internal thoracic vein may bifurcate between ribs 2-4 or remain as a single vein. The internal thoracic vein drains the chest wall and the breasts. The internal thoracic vein can act as a collateral circulation for blood from the inferior vena cava to the superior vena cava.

Does the internal thoracic vein drains into the subclavian vein?
Normally, the internal thoracic veins develop from the local venous plexus, and on the right side they drain into the right anterior cardinal vein proximal to the transverse anastomosis with the left anterior cardinal vein; on the left side they drain into the left anterior cardinal vein just distal to the junction of ...
What does the internal thoracic vein supply?
The internal thoracic artery runs under the fascia and deep to the intercostal muscles. In the proximal part, the internal thoracic artery also gives off other vessels which supply the breast, thymus, mediastinum, and sternum. At each intercostal rib, it gives off an anterior and posterior branch.
What veins form the internal thoracic vein?
The internal thoracic vein arises from the superior epigastric vein. It forms venae comitantes to the internal thoracic artery and accompanies it in its course, before uniting to form a single vein 1. After uniting, each internal thoracic vein drains into its respective brachiocephalic vein 2.
Are there two internal thoracic veins?
There is either one or two internal thoracic veins accompanying the corresponding artery (internal thoracic artery). If internal thoracic vein is single, it usually runs medial to the artery. If there are double thoracic veins, they run on either side of the internal thoracic artery.
What drains into the lateral thoracic vein?
The lateral thoracic vein drains blood from the anterior serratus and pectoral muscles.
Why is internal thoracic artery used for bypass?
The internal thoracic artery (ITA), namely, the left ITA (LITA), is arguably the most vital conduit for the conduct of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) due to its superior long-term patency and mortality benefit.
Where does the internal thoracic artery go?
0:443:45Internal thoracic Artery - Animated Anatomy - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipCourse the internal thoracic artery descends posterior to the medial end of the clavicle. And upperMoreCourse the internal thoracic artery descends posterior to the medial end of the clavicle. And upper 6 costal cartilages. Around one centimeter away from the layer margin of the sternum. It ends in the
What are the veins draining to the superior vena cava?
The superior vena cava derives from the proximal portion of the right anterior cardinal vein and the right common cardinal vein at a point that is caudal to the transverse anastomosis in the embryo.
What drains into superior vena cava?
The superior vena cava is formed by the left and right brachiocephalic veins, which receive blood from the upper limbs, head and neck, behind the lower border of the first right costal cartilage.
What vein does the brachiocephalic drain into?
superior vena cavaYour right and left brachiocephalic veins merge to form your superior vena cava. This large vein is located above your heart, and it extends downward to drain blood into your right atrium (top right heart chamber).
Is the internal thoracic artery an end artery?
In human anatomy, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), previously commonly known as the internal mammary artery (a name still common among surgeons), is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts....Internal thoracic arteryMeSHD008323TA98A12.2.08.029TA24576FMA39608 more rows
How many internal thoracic arteries are there?
There is one internal thoracic artery, previously called the internal mammary artery, originating from the first part of the subclavian artery, at the root of the neck on each side. It passes inferiorly, posterior to the respective brachiocephalic vein and medial to the scalenus anterior muscle.
Is the internal thoracic artery paired?
In human anatomy, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), previously known as the internal mammary artery (a name still common among surgeons), is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running on each side of the body.
Which arteries supply blood to the thoracic wall?
Anteriorly, the blood supply of the thoracic wall is predominantly from the internal mammary (thoracic) arteries, which travel deep to the costal cartilages from the subclavian artery.
Where does the inferior vena cava start and end?
The inferior vena cava begins as the left and right common iliac veins behind the abdomen unite, at about the level of L5. It passes through the thoracic diaphragm at the caval opening at the level of T8 - T9. It passes to the right of the descending aorta.
Where does the brachial vein drain blood from?
Brachial veinsSourceradial veins, ulnar veinsDrains toaxillary veinArterybrachial arteryIdentifiers7 more rows
What do the intercostal arteries supply?
The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the superior intercostal artery (upper two spaces) and the descending aorta (lower nine spaces). They supply the chest wall, parietal pleura, and, through their dorsal branches, the skin and muscles of the back and the spine and its contents.
What nerves supply the intercostal muscles?
The intercostal nerves are part of the somatic nervous system, aiding in the contraction of muscles and the return of sensory information from the skin and parietal pleura. The intercostal nerves arise from the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11 and are situated between adjacent ribs.
What does the thoracoepigastric vein do?
The thoracoepigastric vein provides a communication between the superficial epigastric vein and the lateral thoracic vein as it ascends superficially on the anterolateral chest and abdominal wall.
Where does the brachiocephalic vein drain blood into?
right atriumYour right and left brachiocephalic veins merge to form your superior vena cava. This large vein is located above your heart, and it extends downward to drain blood into your right atrium (top right heart chamber).
What is the internal thoracic vein?
In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein (previously known as the internal mammary vein) is a vessel that drains the chest wall and breasts.
What vein drains the intercostal veins?
Bilaterally, the internal thoracic vein arises from the superior epigastric vein, and accompanies the internal thoracic artery along its course. It drains the intercostal veins, although the posterior drainage is often handled by the azygous veins. It terminates in the brachiocephalic vein. It has a width of 2-3 mm.
What are the branches of the thoracic cage?
Tracheal branches. Terminal branches: Superior epigastric artery. Musculophrenic artery. Supply. Skin and muscles of the anterior aspect of the thoracic cage and superior aspect of the abdominal wall, typical ribs, breasts, parietal pleura, sternum, pericardium and thymus.
What are the three branches of the thoracic artery?
Additionally, the branches of the internal thoracic artery split into three separate categories; anterior, posterior and terminal branches.
What is the superior epigastric artery?
The superior epigastric artery is a distal continuation of the internal thoracic artery. It supplies the superior aspect of the rectus abdominis muscle. Upon appearing in the umbilical region, it anastomoses with the inferior epigastric artery.
What is the proximal segment of the artery?
Due to its anterior position within the thorax, the proximal segment of the artery (proximal to second or third costal cartilage) is separated from the parietal pleura by a strong layer of fascia and distally by the transversus thoracis muscle. The artery is accompanied, on its course, by the internal thoracic vein that lies medial to the artery.
How long is the reading time for the Arteria thoracica interna?
Last reviewed: May 31, 2021. Reading time: 7 minutes. Internal thoracic artery (Arteria thoracica interna) The internal thoracic artery (internal mammary artery) is a long, paired vessel that originates from the proximal part of the subclavian artery. It runs inferomedially and enters the thoracic cage deep to the clavicle and the first rib.
Where do the anterior intercostal branches diverge?
Anterior intercostal branches diverge laterally from the internal thoracic artery to run into the first six intercostal spaces. They supply the intercostal, pectoral muscles and the adjacent skin, anastomosing with their posterior counterparts near the posterior trunk. Perforating branches stem from the medial aspects of ...
Where does the artery end?
The artery ends at the level of the sixth rib or sixth intercostal space, by splitting into two terminal branches: superior epigastric artery and musculophrenic arteries.
Which veins run above the intercostal nerves?
The anterior intercostal veins follow the arteries. The intercostal veins run above the intercostal arteries, which run above the intercostal nerves. The posterior intercostal veins drain into the azygos vein (right side), and hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins (left side). The latter two veins ultimately drain into the azygos vein.
Where is the pleural drain needle inserted?
Pleural drain- For pleural drainage a needle is inserted just above the rib in order to avoid damage to the neurovascular bundle which runs at the lower border of the rib.
What is the azygos vein?
The azygos vein drains the posterior thoracic and abdominal wall, and is formed by the confluence of the ascending lumbar veins and the right subcostal vein at vertebral level T12. The azygos vein arches over the right main bronchus, in order to join the superior vena cava. The azygos vein also drains the pericardial veins, bronchial veins and vertebral venous plexuses.
How many intercostal veins are there in the arteries?
Each space contains one posterior and two anterior intercostal veins which runs with the arteries of the same name. The anterior intercostal veins follow the same course as the arteries, and drain into internal thoracic and musculophrenic veins.
What is the space between the ribs?
Intercostal veins. The intercostal space is the space between the ribs, and it is comprised of three muscular layers and a neurovascular bundle which runs between the intermediate and inner layers of these muscles. In this article we will discuss the gross and functional anatomy of the intercostal veins.
Which veins are located in the hemiazygos vein?
The accessory hemiazygos vein receives posterior intercostal veins from 4th to 8th space and left bronchial veins. The hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos vein drain into the azygos vein at the level of T7-8 that drains into the superior vena cava (at T5-T6).
What is the neurovascular bundle of the ribs?
The neurovascular bundle of each rib consists of the intercostal artery, vein and nerve. The neurovascular bundle runs directly under the lower border of each rib. The vein is the superior most of the three, with the artery below, and the nerve lowest.
Overview
Structure
Bilaterally, the internal thoracic vein arises from the superior epigastric vein, and accompanies the internal thoracic artery along its course. It drains the intercostal veins, although the posterior drainage is often handled by the azygous veins. It terminates in the brachiocephalic vein. It has a width of 2-3 mm.
There is either one or two internal thoracic veins accompanying the corresponding artery (interna…
Function
The internal thoracic vein drains the chest wall and the breasts.
Clinical significance
Knowledge on the course of internal thoracic vein and artery is important during interventional procedures through the anterior chest wall such as biopsy and empyema drainage. This is to avoid puncturing the vessels and cause massive bleeding.
Accidental placement of central venous catheter in the internal thoracic vein can cause pleural effusions, chest wall abscess, pulmonary edema, shortness of breath and chest pain.
Other animals
Internal thoracic vein runs just lateral to the sternum.
The internal thoracic vein can act as a collateral circulation for blood from the inferior vena cava to the superior vena cava. This can work in either direction. It may partially compensate for disturbances to blood flow.
Additional images
• Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery.
External links
• Internal thoracic vein - thefreedictionary.com