What is located at the crista terminalis?
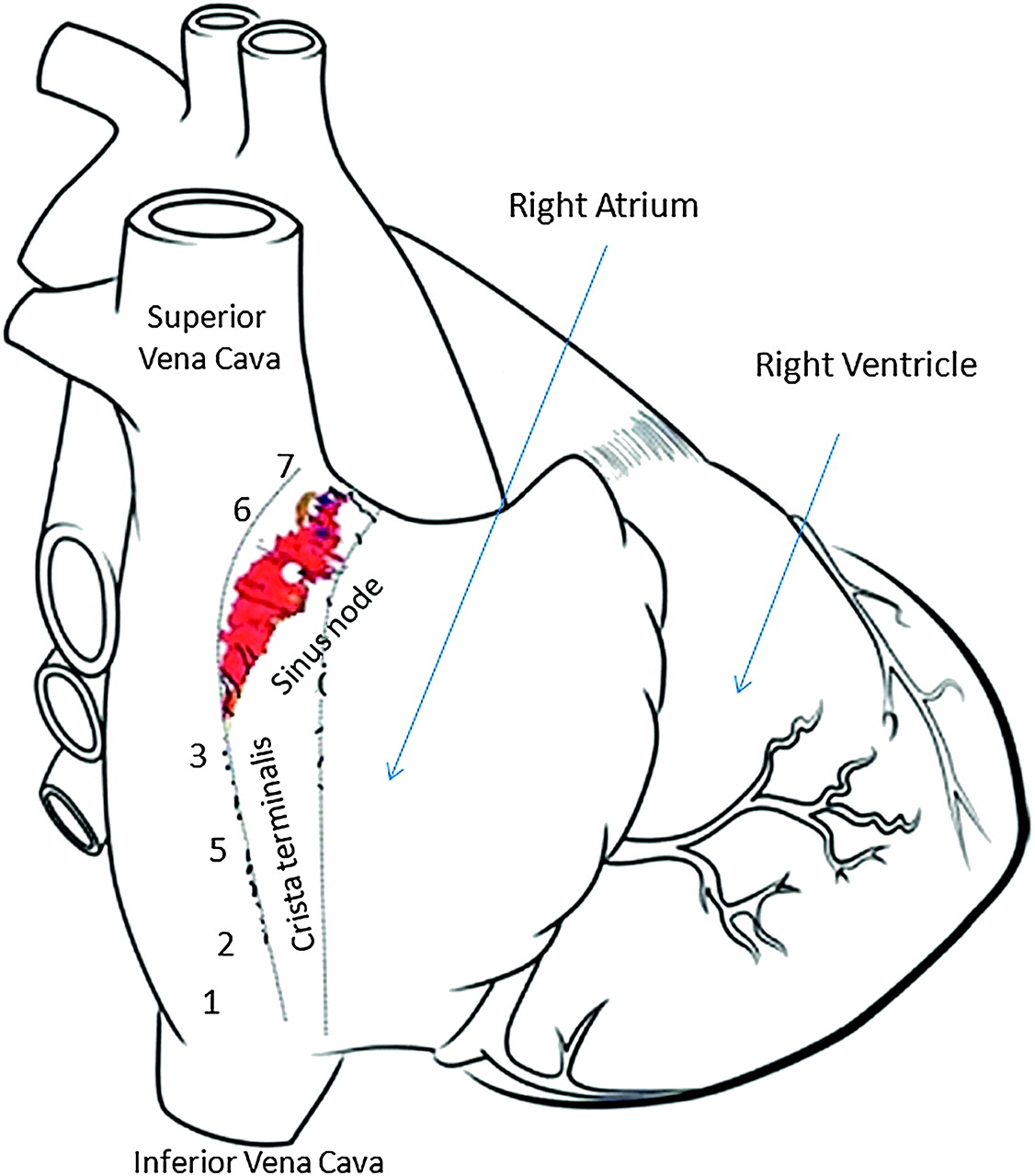
The crista terminalis (terminal crest) is a C-shaped ridge located in the endocardial aspect of the right atrium of the heart....Crista terminalis.TerminologyEnglish: Crista terminalis Latin: Crista terminalis Synonym: Terminal crestLocationPosterolateral endocardial wall of right atrium of heart1 more row
Is crista terminalis only in right atrium?
The crista terminalis is generally a smooth-surfaced, thick portion of heart muscle in a crescent shape at the opening into the right atrial appendage. On the external aspect of the right atrium, corresponding to the crista terminalis is a groove, the terminal sulcus....Crista terminalisFMA9236Anatomical terminology6 more rows
What is the significance of crista terminalis?
A prominent crista terminalis is a well-defined fibromuscular ridge formed by the junction of the sinus venosus and primitive right atrium (RA) extending along the posterolateral aspect of the right atrial wall, which is a normal anatomic variant and recognized by echocardiography occasionally [1, 2].
What does the crista terminalis separate?
The crista terminalis is found closely associated with the posterolateral right atrial wall. It divides the right atrium into smooth posteromedial and trabeculated anterolateral portions.
What is Koch's triangle?
Koch's triangle is an important area of human heart, which is located in the superficial paraseptal endocardium of the right atrium, used as an anatomical landmark to locate the atrioventricular (AV) node.
What is a Chiari network in right atrium?
The Chiari network, encountered infrequently in the right atrium, is a fenestrated, net-like embryonic remnants of valves of sinus venosus, lying closely in relation to the inferior vena cava and coronary sinus, sometimes connecting these with other right atrial structures [1].
Where is fossa ovalis located?
The fossa ovalis is a depressed structure, of varying shapes, located in the inferior aspect of the right interatrial septum.
Where is the crista terminalis located?
The crista terminalis is located at the junction of the trabeculated right atrial appendage and the smooth muscle of the right atrium.
What is the crista terminalis?
The crista terminalis represents the junction between the sinus venosus and the heart in the developing embryo.
What is the crista terminalis?
The crista terminalis, also referred to as the terminal crest, is a C-shaped muscular ridge on the lateral endocardial aspect of the RA (see Fig. 5.3 ). It separates the smooth venous component of the RA, formed by the sinus of vena cava (sinus venarum) posteriorly, from the rough pectinate musculature of the RAA anteriorly.
Why is the crista terminalis important?
The crista terminalis also has clinical relevance because atrial arrhythmias, which commonly originate from it, can be eliminated by ablation of that area. 5,6
Where does focal tachycardia occur?
Focal atrial tachycardias may also arise from the superior vena cava.2324 Atrial tachycardia arising from the area of the superior vena cava may conduct to the right atrium. There are also reports of fibrillatory conduction in the superior vena cava with exit block to the right atrium masquerading as a focal right atrial tachycardia. In one occurrence, use of a basket catheter demonstrated a conduction delay in the superior vena cava-right atrial junction, contributing to tachycardia initiation. 24
Where is the ectopy located in the crista terminalis?
For ectopy from the crista terminalis, we perform focal ablation of the earliest activation site of the ectopy until there is total elimination of the ectopy initiating AF or greater than 50% reduction in the initial electrogram amplitude of the ectopic focus.14 The crista terminalis ectopy is usually located around the transverse gap conduction region in the crista terminalis. For patients who have accompanying right atrial atypical flutter involving the transverse gap conduction region in the crista terminalis, we perform linear ablation around the gap to eliminate the ectopy and to block transverse conduction through this gap (see Fig. 16-3 ). 50 Intracardiac echocardiography is helpful to clarify the anatomic relation between the crista terminalis and the catheter position during ablation.
Which axis of the crista is oriented to facilitate preferential conduction?
Clinical Correlation. Myocytes are oriented along the long axis of the crista, thereby facilitating preferential conduction in the longitudinal direction. 14 However, the interlacing bundles of the crista terminalis trabeculations predispose to conduction delay and block transversely across the crista, which can set up the conditions for intraatrial reentry (focal atrial tachycardia). 15 It also serves as an anatomic barrier to conduction traversing across the lateral RA wall during most typical atrial flutters. 9
Where is the right ventricle located?
The right ventricle is located anterior and to the left of the ascending aorta. Note coronary arteries coursing within the coronary or atrioventricular grooves, which separate the atria from the ventricles.
Where is the Crista terminalis located?
The crista terminalis is a smooth muscular ridge in the superior aspect of the right atrium, formed following resorption of the right valve of the sinus venosus. It represents the junction between the sinus venarum, the "smooth" portion of the right atrium derived from the embryologic sinus venosus, and the heavily trabeculated right atrial appendage.
Which part of the right atrium divides into smooth posteromedial and trabeculated antero?
The crista terminalis is found closely associated with the posterolateral right atrial wall. It divides the right atrium into smooth posteromedial and trabeculated anterolateral portions.
Is the crista terminalis pathologic?
While its presence is of no pathologic significance, unusual prominence of the crista terminalis has been associated with:
Where is the crista terminalis?
The crista terminalis is a muscle ridge that extends from the right sides of the superior vena cava (SVC) and IVC and continues cephalad to the right atrial appendage.1
Where is the ectopy located in the crista terminalis?
For ectopy from the crista terminalis, we perform focal ablation of the earliest activation site of the ectopy until there is total elimination of the ectopy initiating AF or greater than 50% reduction in the initial electrogram amplitude of the ectopic focus.6 The crista terminalis ectopy is usually located around the transverse gap conduction region in the crista terminalis. For patients who have accompanying RA atypical flutter involving the transverse gap conduction region in the crista terminalis, we perform linear ablation around the gap to eliminate the ectopy and to block transverse conduction through this gap ( Fig. 16- 4 ). 62 Intracardiac echocardiography is helpful to clarify the anatomic relation between the crista terminalis and the catheter position during ablation.
What is the tip temperature of a multipolar catheter?
A standard ablation catheter with a 4- or 8-mm-tip or an irrigated-tip catheter is used for RF application. RF power is adjusted to achieve a tip temperature of 50° to 60°C or an impedance drop of 5 to 10 Ω, or both. RF lesions are applied as guided by the earliest atrial activation time, usually along superior regions of the crista terminalis using the guidance of the crista catheter. The local endocardial activation time recorded by the ablation catheter at successful sites typically precedes the onset of the surface P wave during the tachycardia by 25 to 45 milliseconds ( Fig. 16-5 ).
Why are ATs clustered in CT?
One physiological factor contributing to the clustering of ATs in this area is that the CT demonstrates marked anisotropy due to poor transverse cell-to-cell coupling, which could contribute to slow conduction and microreentry. Another contributory factor is that the CT contains clusters of cells with automaticity. The ECG characteristics of these tachycardias were described earlier and depend on site of origin from the CT (e.g., superior vs. inferior). Intracardiac echocardiography may be particularly useful to demonstrate the close anatomical proximity of the tachycardia focus to the crista during mapping. Ablation of tachycardias arising from the superior CT carries a small risk of damage to the phrenic nerve with diaphragmatic paralysis.
Which part of the crista should be targeted first?
The medial portion of the crista as it courses in front of the SVC is usually the site of earliest activation for the fastest sinus rates; this portion of the crista should be targeted by RF ablation first. Progressively inferior portions of the crista are then ablated until target heart rate reduction is achieved.
Can you see a crista terminalis on fluoroscopy?
The crista terminalis is not visible on fluoroscopy and has a varied course among patients. Therefore, some operators prefer using ICE to help identify the crista, position the tip of the ablation catheter with firm contact on the crista, and assess the RF lesion (see Fig. 11-23). 19,20