
What is the cubital fossa in the arm?
The cubital fossa is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm. It is located in a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint. It is also called the antecubital fossa because it lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin cubitus) when in standard anatomical position.
Why is it called the antecubital fossa?
It is also called the antecubital fossa because it lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin cubitus) when in standard anatomical position. The cubital fossa is triangular, and thus has three borders along with an apex which is directed inferiorly.
What innervates the lateral border of the cubital fossa?
The lateral border of the cubital fossa is formed by the brachioradialis which originates from the lateral supra-epicondylar ridge of the humerus. This muscle is innervated by the radial nerve, as it is located in the posterior compartment of the forearm.
What are the superficial veins of the cubital fossa?
The superficial veins of the cubital fossa include the basilic vein located medially, the cephalic vein located laterally and the median cubital vein which connects these two veins together. 4 Figure 3. Superficial veins of the cubital fossa. 2

What is the cubital fossa?
Introduction. The cubital fossa is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm. It is located in a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint. It is also called the antecubital fossa because it lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin cubitus) when in standard anatomical position.
What goes through the cubital fossa?
The tendon of Biceps Brachii- It is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the arm. The biceps tendon runs through the cubital fossa, attaching to the radial tuberosity, just distal to the neck of the radius.
How do you palpate cubital fossa?
1:132:46Elbow palpation lateral Collateral, triceps, biceps, cubital fossaYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow if we come just medial to that biceps tendon and we should palpate gently. What we can feel forMoreNow if we come just medial to that biceps tendon and we should palpate gently. What we can feel for is a pulsating structure and that's where our brachial artery would be right.
What structures lie in the cubital fossa?
The contents of the cubital fossa include the median nerve, radial nerve, brachial artery and biceps tendon.
What is the elbow armpit called?
The cubital fossa, chelidon, or elbow pit, is the triangular area on the anterior side of the upper limb between the arm and forearm of a human or other hominid animals. It lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin cubitus) when in standard anatomical position. Cubital fossa.
What causes pain in the cubital fossa?
What causes cubital tunnel syndrome? Cubital tunnel syndrome may happen when a person bends the elbows often (when pulling, reaching, or lifting), leans on their elbow a lot, or has an injury to the area. Arthritis, bone spurs, and previous fractures or dislocations of the elbow can also cause cubital tunnel syndrome.
Which nerve runs in cubital fossa?
Median nerveMedian nerve - originating from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, with contributions from C6-T1 roots. It can be found most medially within the cubital fossa, running between the two heads of pronator teres in the majority of the population.
What are the 3 main veins in the antecubital fossa?
The most site for venipuncture is the antecubital fossa located in the anterior elbow at the fold. This area houses three veins: the cephalic, median cubital, and basilic veins (Figure 1).
What nerves pass through the cubital fossa?
As mentioned above, two of the primary nerves of the arm run through the cubital fossa - the median and radial nerves.
What anatomical structures must be avoided when taking blood at the antecubital fossa?
When puncturing the cephalic vein is difficult because it is not visible, the median cubital vein at the cubital fossa is selected for venipuncture because of its cross-sectional area and visibility; however, care is needed to avoid penetrating the vein because the median nerve and brachial artery are present ...
Where is the cubital fossa located?
The Cubital Fossa is a triangular-shaped depression, located between the forearm and the arm on the anterior surface of the elbow, with the apex of the triangle pointing distally. It is also known as the “antecubital” because it lies anteriorly to the elbow. It is a space filled with different structures that makes up its content. It has three boundaries/borders, and it also has a floor and a roof .
What is the area of the cubital fossa used for?
Venipuncture – The area superficial to the cubital fossa is a common site used for the collection of venous blood specimens and blood transfusion. The basilic vein, median cubital vein, and cephalic vein are superficial veins that are frequently selected for venipuncture at the cubital fossa.
What is the median cubital vein?
Superficially, in the subcutaneous tissue overlying the cubital fossa are the median cubital vein, lying anterior to the brachial artery, the medial and lateral cutaneous nerves of the forearm, related to the basilic and cephalic veins.
What is bicipital aponeurosis?
The bicipital aponeurosis forms a partial protective covering to the median nerve, brachial artery, ulnar artery, and radial artery >. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations.
What is a supracondylar fracture?
Supracondylar humeral fracture - Supracondylar fractures are the most common type of upper arm injury in children. It is an injury to the humerus, or upper arm bone, at its narrowest point, just above the elbow. They are frequently caused by a fall on an outstretched elbow or a direct blow to the elbow such as the median and the radial nerve. The displaced fracture fragments may impinge and damage the contents of the cubital fossa such as the median and radial nerve. Direct damage or post-fracture swelling can cause interference to the blood supply of the forearm from the brachial artery. The resulting ischemia can cause Volkmann’s ischaemic contracture .
What causes a fracture in the cubital fossa?
The displaced fracture fragments may impinge and damage the contents of the cubital fossa such as the median and radial nerve.
How many structures are in the cubital fossa?
The cubital fossa contains four structures which from medial to lateral are :
Where is the cubital fossa located?
The lateral border of the cubital fossa is formed by the brachioradialis which originates from the lateral supra-epicondylar ridge of the humerus. This muscle is innervated by the radial nerve, as it is located in the posterior compartment of the forearm.
What are the boundaries of the cubital fossa?
Boundaries of the cubital fossa. The cubital fossa is a three-dimensional space which has a superior, lateral and medial border, as well as a roof and floor. It is bordered by two forearm muscles – brachioradialis laterally and pronator teres medially. 1.
What are the superficial veins of the cubital fossa?
Superficial veins of the cubital fossa. The superficial veins of the cubital fossa lie superior to the roof of the fossa and are separated from the brachial artery and median nerve by the bicipital aponeurosis. The superficial veins of the cubital fossa include the basilic vein located medially, the cephalic vein located laterally and ...
Where is the medial border of the cubital fossa located?
Medial border. The medial border of the cubital fossa is formed by the pronator teres muscle which origina tes from the medial epicondyle. This muscle is innervated by the median nerve and is located in the anterior compartment of the forearm.
Which veins connect the cubital fossa?
The superficial veins of the cubital fossa include the basilic vein located medially, the cephalic vein located laterally and the median cubital vein which connects these two veins together. 4
Which muscle is responsible for the cubital fossa?
The floor of the cubital fossa is formed mainly by the brachialis muscle proximally and the supinator muscle distally.
What is the area of transition between the anatomical arm and forearm?
It is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and forearm which several important structures traverse through. 1 Appreciation of its anatomy is essential to enable appropriate assessment of a patient sustaining trauma to this region and for performing procedures such as intravenous cannulation or venepuncture.
Where is the cubital fossa located?
Cubital Fossa Overview. The cubital fossa (Latin for “elbow”) is a triangular hollow on the front of the elbow. (It is similar to the lower limb’s popliteal fossa, which is located on the back of the knee.)
Where is the roof of a shallow cubital fossa?
Identify the structures that can be found in the roof of a shallow cubital fossa on the front of the elbow. Separate the lateral and medial boundaries created by the brachioradialis and pronator teres muscles, respectively.
Why is the cubital region important?
The cubital region is important for many reasons, some these are; The median cubital vein is used mostly for intravenous injections. The brachial artery in front of the elbow is universally used to measure blood pressure.
Which nerve passes between the two heads of pronator teres and gives branches to flexor carp?
The contents are as follows, from medial to lateral. The Median Nerve: It passes between the two heads of pronator teres and gives branches to flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor digitorum superficialis, and leaves the fossa.
Which muscles form the floor of the cubital fossa?
Recognize the brachialis and supinator muscles, which form the floor of the cubital fossa.
Where do interosseous branches arise?
The anterior ulnar recurrent, posterior ulnar recurrent, and common interosseous branches arise from the ulnar artery.
Is cubital tunnel syndrome a male or female condition?
Cubital tunnel syndrome’s precise pathophysiology is unclear. There have been some connection with smoking. Males are more likely to be affected than females, and the left side is more often affected.
Which boundary is formed by medial border of brachioradialis?
Lateral boundary is formed by medial border of brachioradialis.
Does the cubital fossa slip?
it is connected to deep vein by perforator vein, therefore it does not slip. bicipital aponeurosis in the roof of cubital fossa is deep to median cubital vein and during venipuncture protects the underlying brachial artery and median nerve.
Where is the cubital fossa located?
The cubital fossa is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm. It is located in a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint. It is also called the antecubital fossa because it lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin cubitus) when in standard anatomical position. The cubital fossa is triangular, and thus has three borders along with an apex which is directed inferiorly. It also has a floor and roof, and it is traversed by structures which make up its contents.[1][2][3][4]
What muscle is the cubital fossa?
The floor of the cubital fossa is formed proximally by the brachialis and distally by the supinator muscle. The roof consists of skin and fascia and is reinforced by the bicipital aponeurosis which is a sheet of tendon-like material that arises from the tendon of the biceps brachii. The bicipital aponeurosis forms a partial protective covering to the medial nerve, brachial artery and ulnar artery. Within the roof runs the median cubital vein, which can be accessed for venipuncture (see clinical significance below).
Where is the superficial vein in the cubital fossa?
One of the most common sites for venipuncture is the superficial veins in the cubital fossa of upper limbs which include the cephalic, basilic, median cubital, and antebrachial veins and their tributaries. Many superficial veins can cross this region. Median cubital vein connects the basilic and cephalic veins and can be accessed easily. This makes it a common site for venipuncture. It may also be used for the insertion of a peripherally inserted central catheter.
What is the medial border of the brachioradialis muscle?
Lateral border is the medial border of the brachioradialis muscle.
Is the radial nerve a cubital fossa?
Theradial nerve is not always strictly considered part of the cubital fossa, but is in the vicinity, passing underneath the brachioradialis muscle. As is does so, the radial nerve divides into its deep and superficial branches.
Where Is the Antecubital Fossa?
The antecubital fossa is the shallow depression located before or, in other words, in front of, the median cubital vein of your arm.
Where is the median cubital vein?
Now you may be saying to yourself, Okay, so then where is the median cubital vein? Well, it's the vein that pops out of the inside of your elbow when you make a fist.
Where is the basilic vein located?
These two veins are actually located in opposition to one another, meaning that, while the basilic vein runs up the underside of your forearm and along the underside of your arm, the cephalic vein runs up the top of your forearm and the outer side of your arm.
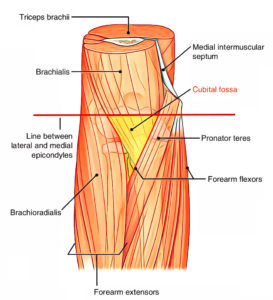
Cubital Fossa Overview
- The Cubital Fossa is a triangular-shaped depression, located between the forearm and the arm on the anterior surface of the elbow, with the apex of the triangle pointing distally. It is also known as the “antecubital” because it lies anteriorly to the elbow. It is a space filled with different structures that makes up its content. It has three boun...
Dissection
Boundaries
Contents
Clinical Anatomy
Few Last Words About Cubital Fossa
- Identify the structures that can be found in the roof of a shallow cubital fossa on the front of the elbow. Separate the lateral and medial boundaries created by the brachioradialis and pronator teresmuscles, respectively. Organize the contents: 1. The median nerve on the medial side of the brachial artery. 2. The terminal part of the brachial artery bifurcating into radial and ulnar arteries…