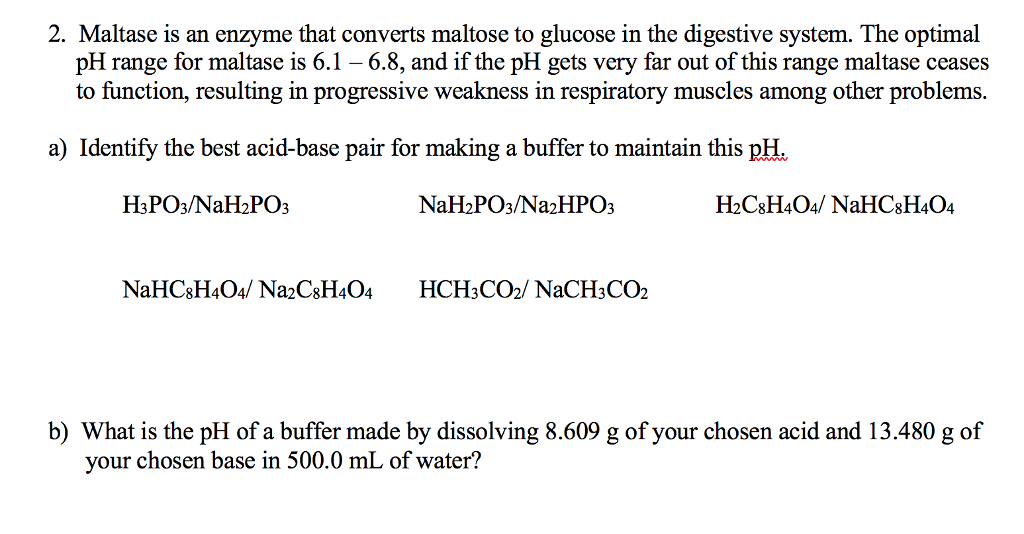
- AskingLot
- Where is maltase produced? ...
- Maltase is an enzyme produced by the cells lining the small intestine. ...
- During digestion, starch is partially transformed into maltose by the pancreatic or salivary enzymes called amylases; maltase secreted by the intestine then converts maltose into glucose. ...
Where is maltase found in the human body?
There are many moving parts that go into the proper digestion of food in our bodies and maltase enzymes are just as crucial as any of the other enzymes needed for proper digestion. Naturally, maltase is found in people’s saliva or mouths and it mainly aids the digestion within the small intestine and pancreas.
Where is maltase found in the body?
What are the 4 main digestive enzymes?
- Amylase.
- Maltase.
- Lactase.
- Lipase.
- Proteases.
- Sucrase.
Which element is present in maltase but not maltose?
Which element is present in maltase, but not in maltose? 1. carbon 2. hydrogen 3. oxygen 4. nitrogen Salivary amylase is an enzyme in humans that breaks down starch. The optimum pH for this reaction is 6.7.
Which enzyme breaks down maltose?
Salivary Amylase and Other Enzymes in Saliva
- Salivary Amylase. Salivary amylase is the primary enzyme in saliva. ...
- Salivary Kallikrein. As a group, kallikreins are enzymes that take high molecular weight (HMW) compounds, like kininogen, and cleave them to smaller units.
- Lingual Lipase. ...
- Other Minor Salivary Enzymes. ...
- Sources. ...
Is maltase produced in the pancreas?
During digestion, starch is partially transformed into maltose by the pancreatic or salivary enzymes called amylases; maltase secreted by the intestine then converts maltose into glucose.
Which intestine produces maltase?
small intestineEnzymes secreted in the small intestine specific to carbohydrate hydrolysis include α-amylase, α-glucosidases (sucrase, glucoamylase, maltase), and β-galactosidase (lactase).
Is maltase produced in the ileum?
So the second stage in the digestion of starch involves a second enzyme, maltase that is found embedded into the epithelial lining of the ileum. Maltase catalyses the breakdown of a molecule of maltose into two molecules of glucose which can be absorbed into the blood.
Where is maltase in the body?
Maltase is a type of alpha-glucosidase enzyme found in the small intestine's brush border. The hydrolysis of the disaccharide maltose into two simple sugars of glucose is catalysed by this enzyme.
What produces maltose during digestion?
Maltose is produced by the enzymatic hydrolysis of starch (a homopolysaccharide) catalyzed by the enzyme amylase. Maltose is further hydrolyzed by the enzyme maltase to produce two molecules of d-glucose.
What enzyme is produced in the small intestine?
Lipase. Lipase is produced in the pancreas and small intestine. A type of lipase is also found in breast milk to help a baby more easily digest fat molecules when nursing.
Is maltase in the small intestine?
The nutritional/clinical importance of small intestinal maltase and isomaltase activities are due to their crucial role in the digestion of food starches to absorbable free glucose.
Is maltase found in the stomach?
Which of the following statements about digestive processes is true? Amylase, maltase, and lactase in the mouth digest carbohydrates. Trypsin and lipase in the stomach digest protein. Bile emulsifies lipids in the small intestine.
What enzymes are produced in the stomach?
Pepsin is the main gastric enzyme. It is produced by the stomach cells called "chief cells" in its inactive form pepsinogen, which is a zymogen. Pepsinogen is then activated by the stomach acid into its active form, pepsin.
Which enzyme is maltase?
Maltase is part of a group of intestinal enzymes called FamilyGH13 (Glycoside hydrolase family 13) that are responsible for breaking apart the α-glucosidase linkages of complex carbohydrates into simple to use glucose molecules.
Is maltase found in intestinal juice?
Four enzymes present in the intestinal juice are maltase speeds up breakdown maltose to glucose, sucrase speeds up the breakdown of sucrose to glucose and fructose, lactase breaks down lactose to glucose and galactose and peptidase breaks down peptides into amino acids.
Is maltase present in pancreatic juice?
(a)Trypsin, lipase and maltase.
What is the duodenum?
(DOO-ah-DEE-num) The first part of the small intestine. It connects to the stomach. The duodenum helps to further digest food coming from the stomach. It absorbs nutrients (vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, proteins) and water from food so they can be used by the body.
Which enzyme is maltase?
Maltase is part of a group of intestinal enzymes called FamilyGH13 (Glycoside hydrolase family 13) that are responsible for breaking apart the α-glucosidase linkages of complex carbohydrates into simple to use glucose molecules.
What organ produces amylase?
In the human body, amylase is predominantly produced by the salivary glands and the pancreas.
1. Explain the Role of Maltase?
The most important role of maltase as an enzyme in the human digestive system (also called maltase digestive enzyme) can be found when the starch i...
2. Explain which enzyme falls under which type of biomolecule?
Usually, enzymes are said to be proteins. However, RNA can form different tertiary confirmations, some of which contain catalytic activities, calle...
3. Explain About Endonuclease Enzymes?
Restriction enzyme, which is аlѕо known as rеѕtrісtіоn endonuclease - a рrоtеіn produced by the bасtеrіа, that сlеаvеѕ DNA at specific ѕіtеѕ аlоng...
4. What are LDH Enzymes?
Typically, LDH means Lactate Dehydrogenase. It is defined as a tetramer having four subunits. Maybe, the subunits either H or M polypeptide chains....
5. How was maltase discovered in which year was it discovered and by whom?
The discovery of maltase was done back in the year 1806 when Napoleon Bonaparte issued his "Berlin decree," which proclaimed a continental blockade...
What is maltase enzyme?
Maltase is a member of the GH13 (Glycoside hydrolase family 13) of intestinal enzymes that are responsible for transforming complex carbohydrates' - glucosidase linkages into simple glucose molecules for usage. Then, these glucose molecules would be used as a sort of "food" for cells to produce the energy (it means, Adenosine triphosphate) during Cellular respiration. The genes that can code for maltase are given below:
What is the role of maltase in the digestive system?
Answer: The most important role of maltase as an enzyme in the human digestive system (also called maltase digestive enzyme) can be found when the starch is being assimilated into the maltose using pancreatic or salivary enzymes like amylase (amylase maltase).
What is the mechanism of all GH13 enzymes?
The hydrolysis of alpha-glucosidase linkage is the mechanism of all Family GH13 enzymes. Maltase focuses on dissolving maltose, which is a disaccharide with a - (1->4) bond connecting two units of glucose. The substrate size determines the rate of hydrolysis (or the carbohydrate size).
What enzymes are needed for starch digestion?
Six intestinal enzymes are needed for starch digestion, two of which are luminal endo-glucosidases, also known as alpha-amylases. The remaining four enzymes have been identified as various maltases, exo-glucosidases bound to the enterocytes' luminal surface. The sucrase-isomaltase system was linked to two of these maltase activities (maltase Ib, maltase Ia). The rest of the two maltases with no distinguishing characteristics were named maltase-glucoamylase (also called maltases II and III). Since they all digest linear starch oligosaccharides to glucose, these four maltases are also known as alpha-glucosidase.
What is the function of alpha-amylase?
Alpha-amylase contains an essential function in the degradation of starches, so it is extremely and commonly used in the industry of baking. Also, it is mostly used as a means of flavour, enhancing it to improve bread quality. With no alpha-amylase, the yeast would not be possible to ferment.
Is RNA a protein or a deoxyzyme?
However, RNA can form different tertiary confirmations, some of which contain catalytic activities, called Ribozymes. They contain deoxyzymes rarely, which are rare, and their ability to form different tertiary structures is limited by their double helix type of structure.
What enzyme is used to make maltose into glucose?
This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of disaccharide maltose into two simple sugars of glucose. Maltase is found in plants, bacteria, yeast, humans, and other vertebrates. It is thought to be synthesized by cells of the mucous membrane lining the intestinal wall. Digestion of starch requires six intestinal enzymes.
What is maltose glucoamylase used for?
Maltose-glucoamylase is commonly used as a fermentation source as it is able to cut starch into maltose, which is then used for brewing beers and sake. Other than brewing, maltose glucoamylase has been studied by introducing specific inhibitors to stop the hydrolysis of the α-glucosidase linkages.
What is AMD in biology?
AMD is a non sex linked autosomal recessive condition in which excessive accumulation of glycogen build up within lysosome vacuoles in nearly all types of cells all over the body.
What enzyme breaks apart complex carbohydrates?
Structure. Maltase is part of a group of intestinal enzymes called FamilyGH13 ( Glycoside hydrolase family 13) that are responsible for breaking apart the α-glucosidase linkages of complex carbohydrates into simple to use glucose molecules.
What are the two enzymes that are associated with sucrase-isomaltase?
Two of these enzymes are luminal endo-glucosidases named alpha-amylases. The other four enzymes have been identified as different maltases, exo-glucosidas es bound to the luminal surface of enterocytes. Two of these maltase activities were associated with sucrase-isomaltase (maltase Ib, maltase Ia).
When was maltase discovered?
The history of maltase discovery began when Napoleon Bonaparte declared a continental blockade in his “Berlin decree” in 1806. This initiated the search for alternative sources of sugar. In 1833 French chemists Anselm Payen and Jean-Francois Persoz discovered a malt extract that converted starch into glucose which they called diastase at the time. In 1880, H.T. Brown discovered mucosal maltase activity and differentiated it from diastase, now called amylase. In the 1960s advances in protein chemistry allowed Arne Dahlqvist and Giorgio Semenza to fractionate and characterize small intestinal maltase activities. Both groups showed there were four major fractions of maltase activity that were intrinsic to two different peptide structures, sucrase-isomaltase and maltase-glucoamylase. Fifty years later entering the genomic age, cloning and sequencing of the mucosal starch hydrolase confirmed Dahlqvist and Semenza’s findings.
Why is alpha amylase important?
Alpha-amylase has an important function in degradation of starches, so it extremely common used in the baking industry. It is mostly used a means of flavor enhancing to improve bread quality. Without alpha-amylase, yeast would not be able to ferment.
What happens to lactase in the colon?
(2) In lactase deficiency, this cleavage cannot take place leaving lactose intact until it reaches the colon where fermentation by intestinal microflora occurs resulting in gas formation.
What is the final step of carbohydrate digestion?
The final step of carbohydrate digestion, the conversion of oligosaccharides to monosaccharides, is performed by the disaccharidases of the small intestinal enterocytes. The main disaccharidases are maltase, sucrase-isomaltase and lactase (see Fig. 12.1). These enzymes are synthesized on the endoplasmic reticulum, transported to the Golgi apparatus and then to the brush border. They are distributed throughout the length of the small intestine, but sucrase and lactase are in highest concentrations in the jejunum. They are normally present in considerable excess, so that some reduction in activity does not normally result in symptoms.
What is the source of maltose?
The principal source of maltose and cellobiose is the enzymic degradation of starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Maltase (α-d -glucoside glucohydrolase) has been reported in several species of bacteria, and some studies have been done with the enzyme from Clostridium acetobutylicum ( French and Knapp, 1950 ).
What is alveolar hypoventilation?
Alveolar hypoventilation has been described in several cases of mild to moderate myopathy associated with adult-onset acid maltase deficiency, a variant of glycogen storage disease.187,19 7,218-220 In this condition, correct diagnosis can be established by performing respiratory function testing, EMG, and biochemical, histochemical, or morphologic examination of muscle biopsy samples. Hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and impaired hypercapnic ventilatory response may be seen in these patients. Diphragmatic dysfunction may account for the alveolar hypoventilation. Rose-now and Engel 218 suggested that the hypoxemia in their patients was secondary to a combination of hypoventilation due to muscle weakness and an impairment of ventilation-perfusion ratio resulting from compression atelectasis due to elevated diaphragm. The patient of Martin's group 220 on polygraphic study showed prolonged periods of hypopnea accompanied by oxygen desaturation. The patient improved considerably following inspiratory muscle training.
Where is lactase located?
Lactase is a disaccharidase located on the surface of intestinal microvilli, which cleaves lactose to glucose and galactose.
What is starch degraded to?
Starch is degraded first to dextrins and then to a mixture of glucose, maltose, and iso maltose (containing the α-1,6 linkages that are not digested by amylase). The major disaccharidases, located in the brush border of the intestinal lumen, are. •. Maltase —hydrolyzes maltose.
How is glucose transported?
Glucose and galactose are transported by an Na+ /K +-adenosine triphosphatase from the lumen into epithelial cells. As the concentration of glucose builds up in the epithelial cell, it moves downhill into blood by passive, facilitated transport.
Why do autistic kids have lower maltase levels?
Mainly because autistic kids have lower amounts of maltase, research studies are now considering providing maltase enzymes to ease their symptoms. Another study showcased that 18 of 36 autistic kids had gastrointestinal disorders because of the lack of digestive enzymes within the gut. Also, biopsies have shown that the same kids were suffering ...
How is starch converted into glucose?
Throughout digestion, starch is being converted in maltose by salivary or pancreatic enzymes also known as amylases. Afterwards, the maltase that is secreted will be transformed into glucose. Upon production, the glucose can be either used by the human body or stored within the liver as animal starch or glycogen.
What is maltase enzyme?
Maltase. Tweet. What is maltase? Found in people, yeasts, bacteria and plants, maltase is an enzyme that can break down disaccharide maltose. It can digest disaccharides into malt sugars also known as monosaccharides. Throughout digestion, starch is being converted in maltose by salivary or pancreatic enzymes also known as amylases.
Why is maltase important?
Simply put, maltase is really important when it comes to the overall enzymatic process because it is used efficiently by the body to digest sugars and starch found under the shape of grains and other foods based on grains that we consume daily. Health benefits. Maltase is known as an essential digestive enzyme found in people’s mouths and saliva.
Where is maltase secreted?
The process is halted and temporary reduced throughout more acidic digestion phases within the stomach; however, it is also resumed within the neutral pH of small intestines where maltase will be again secreted. The enzyme’s vegetarian form is created through a natural process of fermentation known as Aspergillis oryzae.
Where is maltese produced?
Even though the enzyme can be easily included in people’s diets, it is also believed to be produced in the human body by a mucus casing within the intestinal wall. When starch is ingested, the enzyme is digested only partially and converted in maltose by the pancreatic enzymes and the saliva enzymes. Maltese is also a carbohydrate-digesting enzyme ...
Does maltase help with autism?
Maltase can work as a support and preventive mechanism for various digestive complaints in kids who suffer from autism. Advanced technology has managed to develop tremendously and thus, the use of enzymes like maltase could have beneficial effects.
Overview
Maltase (EC 3.2.1.20, alpha-glucosidase, glucoinvertase, glucosidosucrase, maltase-glucoamylase, alpha-glucopyranosidase, glucosidoinvertase, alpha-D-glucosidase, alpha-glucoside hydrolase, alpha-1,4-glucosidase, alpha-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is one type of alpha-glucosidase enzymes located in the brush border of the small intestine. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis o…
Structure
Maltase is part of a group of intestinal enzymes called FamilyGH13 (Glycoside hydrolase family 13) that are responsible for breaking apart the α-glucosidase linkages of complex carbohydrates into simple to use glucose molecules. The glucose molecules would then be used as a sort of "food" for cells to produce energy (Adenosine triphosphate) during Cellular respiration. The following are genes that can code for maltase:
Mechanism
The mechanism of all FamilyGH13 enzymes is to break a α-glucosidase linkage by hydrolyzing it. Maltase focuses on breaking apart maltose, a disaccharide that is a link between 2 units of glucose, at the α-(1->4) bond. The rate of hydrolysis is controlled by the size of the substrate (carbohydrate size).
Industrial applications
Alpha-amylase has an important function in degradation of starches, so it extremely common used in the baking industry. It is mostly used a means of flavor enhancing to improve bread quality. Without alpha-amylase, yeast would not be able to ferment.
Maltose-glucoamylase is commonly used as a fermentation source as it is able to cut starch into maltose, which is then used for brewing beers and sake.
History
The history of maltase discovery began when Napoleon Bonaparte declared a continental blockade in his “Berlin decree” in 1806. This initiated the search for alternative sources of sugar. In 1833 French chemists Anselm Payen and Jean-Francois Persoz discovered a malt extract that converted starch into glucose which they called diastase at the time. In 1880, H.T. Brown discovered mucosal maltase activity and differentiated it from diastase, now called amylase. In t…
Maltase deficiency
Acid maltase deficiency (AMD) also known as Pompe disease was first described by Dutch pathologist JC Pompe in 1932. AMD is a non sex linked autosomal recessive condition in which excessive accumulation of glycogen build up within lysosome vacuoles in nearly all types of cells all over the body. It is one of the more serious glycogen storage diseases affecting muscle tissue.
AMD is categorized into three separate types based on the age of onset of symptoms in the affe…
See also
• Maltase-glucoamylase
• Sucrase-isomaltase
External links
• Maltases at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
• Structure and evolution of the mammalian maltase-glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase