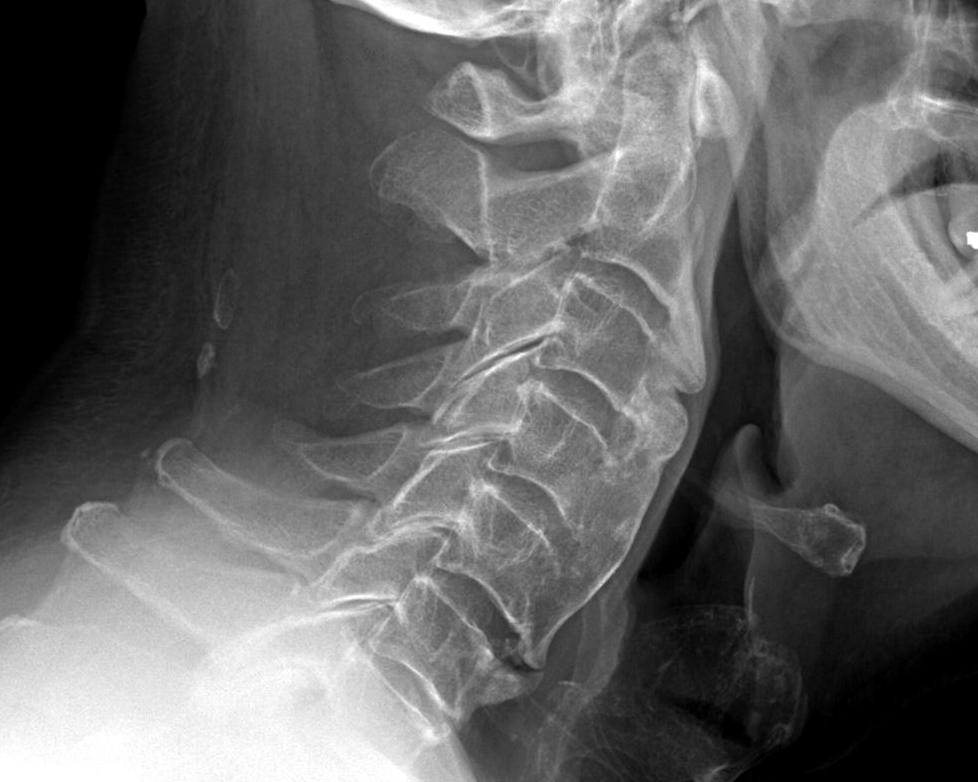
Where is the cervical and thoracic vertebrae?
The thoracic spine is the longest region of the spine, and by some measures it is also the most complex. Connecting with the cervical spine above and the lumbar spine below, the thoracic spine runs from the base of the neck down to the abdomen. It is the only spinal region attached to the rib cage.
Where does cervical spine end and thoracic begin?
The cervical spine is made up of the first seven vertebrae in the spine. It starts just below the skull and ends just above the thoracic spine. The cervical spine has a lordotic curve (a backward C-shape) - just like the lumbar spine.
Is thoracic spine the same as cervical spine?
The Anatomy of Your Spine This is how the regions of your spine are defined: Cervical spine: Beginning at your skull, the cervical vertebrae are the first seven. They are the smaller, lighter vertebrae of your neck. Thoracic spine: The next 12 vertebrae run from your neck down your mid-back.
Where do you feel thoracic spine pain?
Thoracic back pain is described as pain and discomfort felt in the middle and upper back areas. The thoracic region of the spine begins at the base of the neck and ends at the area just below the chest area.
What are the symptoms of thoracic spine nerve damage?
What Are the Symptoms of Thoracic Spine Nerve Damage?Significant leg weakness or loss of sensation.Loss of feeling in genitals or rectal region.No control of urine or stool.Fever and lower back pain.A fall or injury that caused the pain.
What does thoracic pain feel like?
Thoracic back pain can feel like: Sharp pain localised to one spot either on the spine or to one side. General ache or throbbing pain affecting a wider area. A stiffness causing a loss of normal movement.
What organs are affected by thoracic spine?
The nerves that branch off from your spinal cord in your thoracic spine transmit signals between your brain and major organs, including your:Lungs.Heart.Liver.Small intestine.
What does an MRI of thoracic spine show?
A thoracic spine MRI provides detailed images of the vertebrae, soft tissues, and surrounding organs to help detect a variety of conditions including fractures, improper spine curvature, inflammation, infection, herniated discs, tumors, and spinal cord damage.
Why is thoracic back pain a red flag?
Red flags However, many patients with thoracic back pain have a benign, mechanical cause. Red flags for possible serious spinal pathology include: Recent violent trauma (such as a vehicle accident or fall from a height). Minor trauma, or even just strenuous lifting, in people with osteoporosis.
Can neck problems cause thoracic pain?
Following injection studies on the cervical discs and more recent studies using discography, cervical disc injuries can render the cervical spine rather symptom-free, but produce high levels of “thoracic” pain (Fig. 3).
Can thoracic spine cause neck pain?
Neck pain is a common condition with several proposed biomechanical contributing factors. Thoracic spine dysfunction is hypothesized as one of the predisposing factors, which necessitates the need to explore the contribution of thoracic posture and mobility toward neck pain.
Can you have a pinched nerve in your thoracic spine?
A thoracic pinched nerve refers to a nerve under pressure. It is often the result of a degenerative condition in the thoracic spine (middle of the back) that causes a disc or bony spur to encroach on or compress a nerve, resulting in pain and other symptoms.
Where are cervical vertebrae located?
Cervical Vertebrae: Cervical vertebrae is found in the neck, immediately below the skull. Thoracic Vertebrae: Thoracic vertebrae is found in the middle segment of the vertebral column between the cervical and lumber vertebrae.
What is the shape of the thoracic vertebrae?
The vertebral body of the thoracic vertebrae is heart-shaped. It is broad in both antero-posterior and the transverse directions. The anatomy of the human thoracic vertebrae is shown in figure 5.
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
Cervical Vertebrae: There are seven cervical vertebrae (C1-C7) in the vertebral column.
What are the main structural components of vertebrae?
Spinous process, laminae, facets, transverse process, foramina, and the vertical body are the main structural components of typical vertebrae. Based on the region, these vertebrae can be categorized as cervical (C1-C7), thoracic (T1-T12), lumber (L1-L5), sacrum (S1-S5), and coccyx (fused) vertebrae. The main difference between cervical and thoracic ...
How many bones are in the thoracic vertebrae?
The thoracic vertebrae refer to the twelve bones to which the ribs are attached. The first thoracic vertebra occurs just below the last cervical vertebra. The twelve thoracic vertebrae occur in the thoracic region of the body. They are abbreviated from T1 to T12 from top to bottom. In addition to protecting the spinal cord and support, the thoracic vertebrae provide attachment sites for the ribs. Therefore, the thoracic vertebrae are more stable than the cervical and lumber vertebrae. The position of the thoracic vertebrae is shown in figure 4.
What is the function of the cervical vertebrae?
The main function of the cervical vertebrae is to protect the brain stem as well as the spinal cord. They also support the skull and allow a wide range of head movement. The position of the cervical vertebrae is shown in figure 1.
Which type of cartilaginous joint is associated with the protection of the spinal cord?
The intervertebral disks joint the adjacent vertebral bodies. This type of cartilaginous joints is known as symphysis. The vertebral arches join each other through the superior and inferior articular processes in a synovial type joint.
What are the parts of the cervical spine?
Cervical spine: diaphragm (breathing), shoulders, parts of the arms, esophagus, part of the chest. Thoracic spine: parts of the arm and esophagus, trachea, heart, lungs, liver, gallbladder, small intestine. Lumbar spine: legs and feet. Sacrum: bowel, bladder, sexual function. Detailed illustration of the human nervous system.
What are the parts of the spinal column?
Listed below are parts of the body associated with regions of the spinal column: 1 Cervical spine: diaphragm (breathing), shoulders, parts of the arms, esophagus, part of the chest 2 Thoracic spine: parts of the arm and esophagus, trachea, heart, lungs, liver, gallbladder, small intestine 3 Lumbar spine: legs and feet 4 Sacrum: bowel, bladder, sexual function
What are the structures that are anchored in place by vertebral endplates?
First among these structures are the spinal discs, called intervertebral discs. Each disc is similar to a fibrous pad of tissue (called fibrocartilage) and anchored in place by vertebral endplates (called cartilaginous endplates) starting at C3 through L5-sacrum. These discs act as interbody spacers and shock absorbers.
How many bones are in the spinal column?
The entire spinal column consists of 24 individual bones called vertebrae (singular vertebra ), plus 2 sections of naturally fused vertebrae—the sacrum and the coccyx—located at the very bottom of the spine. When most people talk about the spinal column, they’re actually referring to the vertebral column: the 24 circular vertebrae ...
What is the coccyx?
Sometimes the coccyx is termed the coccygeal vertebrae. Although the tailbone is very small and may seem insignificant, it plays an important role in supporting your weight when you sit. The lower lumbar spine (orange) connects to the sacrum (red); the coccyx, or tailbone is below the sacral spine.
How do spinal nerves exit the spinal canal?
Each set of spinal nerves exit the spinal canal through the foramina associated with a particular part of the body that nerve system supports—nerves enable the function (motor) and feeling (sensation). For example, the nerves that provide sensation to the fingers exit the spinal canal via foramina in the cervical spine—because that segment is located nearest the hands.
What bones are below the sacrum?
Immediately below the sacrum are 3 to 5 small bones that naturally fuse together at adulthood forming the coccyx or tailbone. Sometimes the coccyx is termed the coccygeal vertebrae.
Where is the thoracic spine located?
Connecting with the cervical spine above and the lumbar spine below, the thoracic spine runs from the base of the neck down to the abdomen. It is the only spinal region attached to the rib cage. The thoracic spine is one of the four major regions of the spine. Watch: Spine Anatomy Overview Video.
What is the thoracic spine?
The thoracic spine is one of the four major regions of the spine. Watch: Spine Anatomy Overview Video. This article discusses how the thoracic spine functions and how spinal anatomy can factor into thoracic spine pain, stiffness, and some types of chest, arm, and/or abdominal pain. See All About Upper Back Pain.
How many vertebrae are in the thoracic spine?
The thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae stacked on top of each other, labeled from T1 down to T12. These vertebrae form the foundation of the thoracic region’s sturdy spinal column that supports the neck above, the rib cage, soft tissues, flexible joints, blood vessels, and nerves.
What causes upper back pain?
Upper back pain is typically due to one of the following: 1 Muscular problems. Upper back pain is most commonly caused by muscle irritation or tension, also called myofascial pain. The cause may be poor posture (such as forward head posture) or any type of irritation of the large back and shoulder muscles, including muscle strain or spasms. 2 Joint dysfunction. Thoracic spinal joints can become painful in various ways. For example, cartilage tears and degeneration can develop in the facet joints where adjacent thoracic vertebrae articulate with each other. It is also possible for a rib to become misaligned or displaced from the vertebrae. In many cases, facet joint degeneration (osteoarthritis) and degenerative disc disease can happen at the same time.
What is the spinal cord?
Protect the spinal cord. The spinal cord is a critical bundle of nerves that sends electrical signals throughout the body. It runs from the base of the brain down through the bony vertebral canal of the cervical spine and thoracic spine before branching into smaller nerve bundles in the lumbar spine. See Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots.
Which spine supports the heart and lungs?
See Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve Roots. Anchor the rib cage. The rib cage, supported by the thoracic spine in the back, forms a bony structure to surround and protect vital organs, such as the heart and lungs. While the cervical spine and lumbar spine are built more for mobility, the thoracic spine is built more for stability.
Which spine is more stable?
While the cervical spine and lumbar spine are built more for mobility, the thoracic spine is built more for stability.
What is the cervical spine?
Cervical Spine Anatomy. The neck, also called the cervical spine, is a well-engineered structure of bones, nerves, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The cervical spine is delicate—housing the spinal cord that sends messages from the brain to control all aspects of the body—while also remarkably strong and flexible, ...
Which part of the spine is connected to the skull?
The top of the cervical spin e connects to the skull, and the bottom connects to the upper back at about shoulder level. As viewed from the side, the cervical spine forms a lordotic curve by gently curving toward the front of the body and then back.
What is the role of the cervical spine in the circulation of blood?
Facilitating flow of blood to the brain. Small holes (foramina in the transverse processes) in the cervical spine provide a passageway for vertebral arteries to carry blood to the brain. These openings for the blood vessels are present only in the vertebrae of the cervical spine from C1 down to C6 (not in C7 or lower).
What is the movement of the neck and head?
Head and neck motions typically involve one or more of the following movements of the cervical spine: Flexion. The cervical spine bends directly forward with the chin tilting down. Neck flexion typically occurs when looking downward or while in forward head posture, such as when sitting with poor posture at a computer. Extension.
How much does the cervical spine weigh?
The cervical spine handles a heavy load, as the head weighs on average between 10 and 13 pounds. In addition to supporting the head, the cervical spine allows for the neck’s flexibility and head’s range of motion. Facilitating flow of blood to the brain. Small holes (foramina in the transverse processes) in the cervical spine provide ...
How many vertebrae are there in the neck?
The neck is connected to the upper back through a series of seven vertebral segments. The cervical spine has 7 stacked bones called vertebrae, labeled C1 through C7. The top of the cervical spine connects to the skull, and the bottom connects to the upper back at about shoulder level. As viewed from the side, the cervical spine forms ...
What is the hole in the spinal cord called?
Each vertebra has a large hole (vertebral foramen) for the spinal cord to pass through. Together, these vertebrae keep the spinal cord shielded inside a bony tunnel called the spinal canal. Watch Cervical Spinal Cord Anatomy Animation. Supporting the head and its movement. The cervical spine handles a heavy load, ...
What is the last bone in the thoracic spine?
The lowest or last ribs connect to T12, which is also the last bone in the thoracic spine. The bone below T12 is L1, or your first lumbar (low back) vertebra. Because the thoracic region is large, it is often divided into upper and lower areas for diagnosis and communication purposes. 4 .
Why does my thoracic spine hurt?
There are a number of possible causes of thoracic spine pain. Mechanically, it can arise when something is going on in your thoracic spine or your cervical spine (neck). But it may also be due to issues in other areas of the body. For example, problems in your gastrointestinal tract, organs, cardiopulmonary system (heart and lungs), ...
Why are there fewer treatments for neck and lower back pain?
Because the amount of neck and low back pain in the general population far exceeds the amount of thoracic spine pain, fewer treatments are available for this area. 7
What causes thoracic pain?
For example, problems in your gastrointestinal tract, organs, cardiopulmonary system (heart and lungs), and/or your kidneys may refer pain to the thoracic region. Low bone density and myelopathy (symptoms that occur when your spinal cord is irritated) may also cause thoracic spine pain.
Where is the pain in the back located?
Thoracic spine pain is defined as pain in the back that is located between your first thoracic vertebra and your 12th thoracic vertebra.
How many ribs are there in the back?
There are 12 rib pairs in all, and in back, each attaches to one spinal bone. So T1, which is your first thoracic vertebra, provides a place of articulation for the first ribs; T2 provides a place of articulation for the second ribs, and so on down the line.
Can backpacking cause spine pain?
The 2009 review also found that teens may be prone to thoracic spine pain due to backpack use. 2 Textbooks and other things that go into a student's backpack can get pretty heavy, so watching for this risk factor in your child may be a good idea.