Is the dorsal horn in the brain?
nerves. …the posterior gray column (dorsal horn) of the cord or ascend to nuclei in the lower part of the brain. Immediately lateral to the spinal ganglia the two roots unite into a common nerve trunk, which includes both sensory and motor fibres; the branches of this trunk distribute both…
What are the dorsal horns?
Medical Definition of dorsal horn : a longitudinal subdivision of gray matter in the dorsal part of each lateral half of the spinal cord that receives terminals from some afferent fibers of the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves.
Where are dorsal horn neurons?
In the spinal cord dorsal horn, peptidergic neurons largely terminate in lamina I and the outer/dorsal part of lamina II (I/IIo), while nonpeptidergic neurons terminate in the inner part of lamina II (IIi) (Braz, Nassar, Wood, & Basbaum, 2005).
Where is the dorsal and ventral horn?
the spinal cordThis section is from the thoracic region. This figure and the one below are oriented so that dorsal is at the top, and ventral is at the bottom. The dorsal horn is narrow and extends out to the edge of the spinal cord, while the ventral horn is rounded. There is also a lateral horn at this level of the spinal cord.
Where is dorsal horn of spinal cord?
The dorsal horn is found at all spinal cord levels and is comprised of sensory nuclei that receive and process incoming somatosensory information. From there, ascending projections emerge to transmit the sensory information to the midbrain and diencephalon.
What is the function of dorsal horn?
The dorsal horn functions as an intermediary processing center for this information, comprising a complex network of excitatory and inhibitory interneurons as well as projection neurons that transmit the processed somatosensory information from the spinal cord to the brain.
Where are horns located in the spinal cord quizlet?
Found in the T1-L2 parts of the spinal cord only. The lateral horns contain the cell bodies of autonomic motor neurons, which innervate cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands.
What is located in the horns of the spinal cord?
one of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord, the anterior horn contains cell bodies of alpha motor neurons, which innervate skeletal muscle to cause movement.
Is the dorsal horn afferent or efferent?
Keep in mind that the dorsal horns are the location of the cell bodies upon which the afferent nerves from the periphery synapse. Hence, the dorsal roots and rootlets contain afferent fibers carrying sensory information from the periphery to the CNS.
What is dorsal ventral horn?
In transverse sections, the gray matter is conventionally divided into dorsal (posterior) lateral and ventral (anterior) “horns.” The neurons of the dorsal horns receive sensory information that enters the spinal cord via the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves.
What does dorsal and ventral mean in anatomy?
Anterior or ventral - front (example, the kneecap is located on the anterior side of the leg). Posterior or dorsal - back (example, the shoulder blades are located on the posterior side of the body). Medial - toward the midline of the body (example, the middle toe is located at the medial side of the foot).
What is the ventral horn?
aka the anterior horn of the spinal cord. One of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord, the ventral horn contains cell bodies of alpha motor neurons, which innervate skeletal muscle to cause movement.
What does the dorsal horn connect to?
aka posterior horn; one of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord, the dorsal horn contains interneurons that make connections within the spinal cord as well as neurons that enter ascending sensory pathways. It contains the substantia gelatinosa.
What is the ventral horn?
The ventral horns contains the cell bodies of motor neurons that send axons via the ventral roots of the spinal nerves to terminate on striated muscles.
What are the dorsal columns?
AKA posterior columns, the dorsal columns refers to the posterior spinal cord, which contains ascending sensory pathways that carry information about tactile sensations and proprioception.
Is dorsal horn white matter?
' The dorsal horn is the part of the gray matter that receives sensory information entering the spinal cord via the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves.
What is the dorsal horn?
The dorsal horn of the spinal cord is one of the grey longitudinal columns found within the spinal cord. It primarily acts as the termination of primary afferent fibers via the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves.
How many layers are there in the dorsal horn?
The dorsal horn consists of six neuronal cell layers (laminae) which receive various sensory fibers
What is the shape of the spinal cord?
On transverse section of the spinal cord the spinal grey matter is described as being 'butterfly-shaped' or in an arrangement of the letter 'H'. The dorsal horns are bilateral structures which form the posterior projection of this shape. A thin fasciulus or tract (of Lissauer) separates the tip of the dorsal horn from the dorso-lateral surface of the spinal cord.
What is the dorsal horn?
The spinal cord dorsal horn contains the first relay for afferent inputs from the skin, muscles, and viscera of the body. The superficial dorsal horn contains at least some neurons that maintain the selectivity for modalities encoded by the primary afferent endings. These include a number of different modalities including innocuous warming, innocuous cooling, noxious mechanical, noxious thermal, noxious chemical, prurigenic (itch producing), metabolic (non-noxious signals from actively contracting muscles), and innocuous mechanical stimuli of various forms as well as other inputs from autonomic sensory neurons.
How are dorsal horn neurons modulated?
Dorsal horn neurons are modulated by inputs from higher brain centers. Inputs from other centers can greatly modify the amplitude of signals relayed from primary afferent neurons.
Why are neurons integrated into the dorsal horn?
In the majority of neurons in the dorsal horn, various combinations of these inputs are integrated to allow detection of features (such as edges, speed of movement, location on the skin, noxious hot objects, etc.). Such integration allows for useful motor outputs to be generated to compensate for the inputs received, e.g., moving a limb away from a hot object, scratching a biting insect, or wiping away an insect crawling on the skin.
Which nerves travel up the spinal cord and terminate directly in the hypothalamus?
In the spinohypothalamic tract, another ascending pain pathway, ipsilateral and contralateral fibers travel up the spinal cord and terminate directly in the hypothalamus. This pathway may explain pain-induced disturbances in temperature regulation, sleep, and other autonomic functions.
Which part of the brain is responsible for afferent inputs?
Many neurons in the dorsal horn also transmit selective afferent inputs, or integrated inputs to other regions of the central nervous system, including other parts of the spinal cord, the medulla, midbrain, and thalamus as well as the hypothalamus. Thus, the dorsal horn serves as the first integration and relay center for nociceptive as well as a variety of non-nociceptive inputs.
What is the dorsal horn?
The dorsal horn of the spinal cord is critical to processing distinct modalities of noxious and innocuous sensation, but little is known of the neuronal subtypes involved , hampering efforts to deduce principles governing somatic sensation. Here we used single-cell RNA sequencing to classify sensory neurons in the mouse dorsal horn.
Where is sensory information processed?
The incoming information from primary sensory neurons is processed in the dorsal spinal cord, involving microcircuits containing both excitatory and inhibitory neurons. These ultimately relay to projection neurons that transmit the information to several brain areas 9, 10, 11, 12.
What are the different types of neurons in the spinal cord?
a, Illustration of the analyzed spinal cord dorsal horn; cc, central canal; vh, ventral horn. Primary sensory neurons, C and Aδ peptidergic nociceptors, C non-peptidergic nociceptors, C and Aδ low threshold mechanoreceptors (C/Aδ LTMRs) and Aβ LTMRs input to different regions of the dorsal horn. The complexity of neuronal types in dorsal horn is schematically illustrated. Lines and numbers in the dorsal horn indicate Rexed laminae. b, Heat map displaying the single-cell expression profile of 1,545 dorsal horn spinal cord neurons organized into clusters defining neuronal types. Heat map is based on relative expression of each gene, dark green representing minimal and yellow maximal expression. c, Hierarchical clustering reveals the relationship between neuronal types. A greater distance indicates less similarity between neuron types and the reverse. d, t-SNE projection of all 1,545 dorsal horn neurons. e, Hierarchical representation of the different neuronal types, with emphasis on genes defining the splits between neuronal types. Red numbers at splits indicate the split number according to the biclustering shown in Supplementary Table 3.
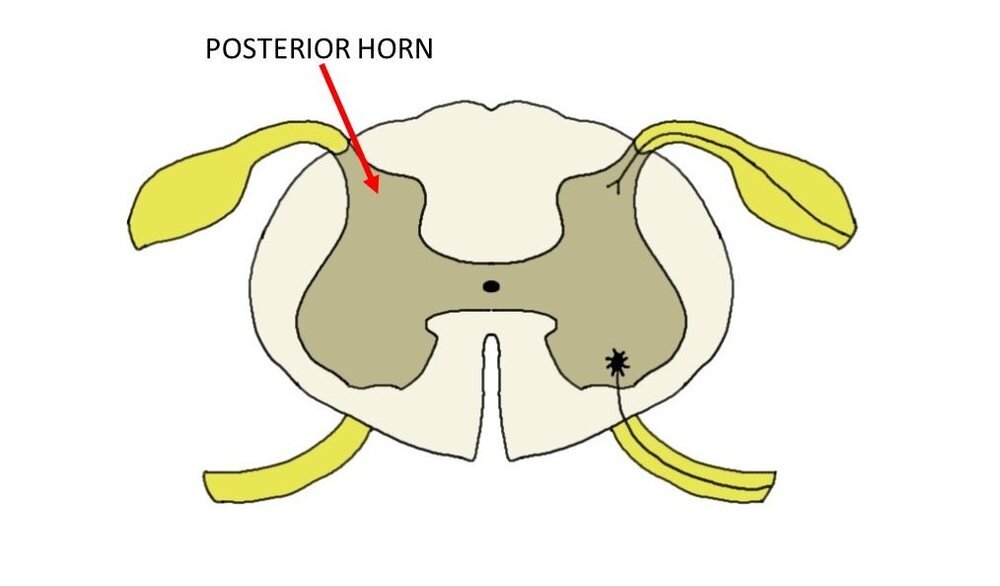
What is the posterior horn?
The posterior horn is the upper protrusion of grey matter, labeled with "2". The posterior grey column ( posterior cornu, dorsal horn, spinal dorsal horn, posterior horn, sensory horn) of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. It receives several types of sensory information from the body, including fine touch, ...
Where does the sensory system receive information?
It receives several types of sensory information from the body, including fine touch, proprioception, and vibration. This information is sent from receptors of the skin, bones, and joints through sensory neurons whose cell bodies lie in the dorsal root ganglion .
Where is the lamina V located?
Spinal lamina V, the neck of the posterior horn. Spinal lamina VI, the base of the posterior horn. The other four Rexed laminae are located in the other two grey columns in the spinal cord.
What is the posterior grey column?
The posterior grey column ( posterior cornu, dorsal horn, spinal dorsal horn, posterior horn, sensory horn) of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. It receives several types of sensory information from the body, including fine touch, proprioception, and vibration.
