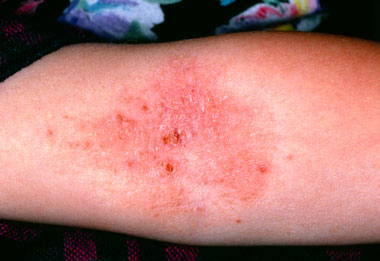
Complications
the h1n1 influenza a pandemic of 1918–1920 (colloquially, but likely inaccurately, known as the spanish flu) remains the deadliest pandemic of the modern age, with estimates of mortality ranging from 17 million to 100 million from an estimated 500 million infections globally (approximately a third of the global population at the time) over the …
Symptoms
While most people get over the common cold, the flu claims significantly more lives. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the flu is responsible for anywhere from 12,000 to 52,000 deaths annually in the United States. However, since not all cases of the flu are always reported, that number could be even higher.
Causes
The CDC estimates that an average of 36,000 people died of the flu each year over the past decade. The worst recent flu season was 2017-2018, when 61,000 people died from the flu.
Prevention
While there are no official figures documenting the exact number of deaths, it is estimated that between 20 million and 50 million people were killed as a result of the deadly virus. The flu was first seen in Europe, then the US and parts of Asia, before it rapidly spread throughout the entire world.
What is the worst flu ever?
How many Americans die from the flu each year?
How many people have died from the flu this year?
How many people died worldwide from influenza?

When and where does influenza most commonly occur?
In temperate climates, seasonal epidemics occur mainly during winter, while in tropical regions, influenza may occur throughout the year, causing outbreaks more irregularly. The time from infection to illness, known as the incubation period, is about 2 days, but ranges from one to four days.
Where might the flu virus spread most easily?
It mostly spreads through droplets in the air when people with flu cough, sneeze, or talk. It can spread from up to six feet away. Although it isn't as common, the flu can also spread from surfaces — for example, if you touch something the virus is on and then touch your nose, mouth, or eyes.
Where do people catch the flu?
Most experts think that flu viruses spread mainly by droplets made when people with flu cough, sneeze, or talk. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people who are nearby (usually within about 6 feet away) or possibly be inhaled into the lungs.
Can you get the flu from breathing air?
Key takeaways: The flu is mainly spread by breathing in air from infected people when they cough, sneeze, or talk. People can also get the flu by touching a surface that has the virus on it and then touching their eyes, nose, or mouth.
How do most people catch the flu?
The flu is caused by an influenza virus. Most people get the flu when they breathe in tiny airborne droplets from the coughs or sneezes of someone who has the flu. You can also catch the flu if you touch something with the virus on it, and then touch your mouth, nose, or eyes.
How long does a flu last?
The symptoms of flu usually develop within 1 to 3 days of becoming infected. Most people will feel better within a week. However, you may have a lingering cough and still feel very tired for a further couple of weeks.
When is flu most contagious?
“You can be contagious with the flu beginning about a day before you feel symptoms. You'll be most contagious with the flu for the first three or four days after you actually feel sick.
Why am I getting flu so often?
Chronic stress or sleep deprivation are factors that can often cause people to keep getting sick. Although simple lifestyle changes are sometimes enough to improve these issues, this is not always the case. Frequently getting sick can be disruptive as well as uncomfortable.
What is the flu?
What is Influenza (Flu)? Flu is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and sometimes the lungs. It can cause mild to severe illness, and at times can lead to death.
How do you get the flu?
Less often, a person might get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching their own mouth, nose or possibly their eyes.
How to prevent seasonal flu?
Preventing Seasonal Flu. The first and most important step in preventing flu is to get a flu vaccine each year. Flu vaccine has been shown to reduce flu related illnesses and the risk of serious flu complications that can result in hospitalization or even death.
How long does it take for the flu to start?
Onset of Symptoms. The time from when a person is exposed and infected with flu to when symptoms begin is about 2 days, but can range from about 1 to 4 days. Top of Page.
What are the complications of the flu?
Complications of flu can include bacterial pneumonia, ear infections, sinus infections and worsening of chronic medical conditions, such as congestive heart failure, asthma, or diabetes.
What does it mean when you have a fever?
fever* or feeling feverish/chills. cough. sore throat. runny or stuffy nose. muscle or body aches. headaches. fatigue (tiredness) some people may have vomiting and diarrhea, though this is more common in children than adults. *It’s important to note that not everyone with flu will have a fever.
What is the CDC's recommendation for preventing the spread of the flu?
CDC also recommends everyday preventive actions (like staying away from people who are sick, covering coughs and sneezes and frequent handwashing) to help slow the spread of germs that cause respiratory (nose, throat, and lungs ) illnesses, like flu.
How far away can you get the flu?
People with flu can spread it to others up to about 6 feet away . Most experts think that flu viruses spread mainly by droplets made when people with flu cough, sneeze or talk. These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people who are nearby or possibly be inhaled into the lungs. Less often, a person might get flu by touching a surface or object that has flu virus on it and then touching their own mouth, nose, or possibly their eyes.
How long does it take for a person to get the flu?
People with flu are most contagious in the first three to four days after their illness begins. Most healthy adults may be able to infect others beginning 1 day before symptoms develop and up to 5 to 7 days after becoming sick.
How long after a flu is it contagious?
People with flu are most contagious in the first 3-4 days after their illness begins.
Can you pass the flu to someone else?
That means that you may be able to pass on the flu to someone else before you know you are sick, as well as while you are sick. Some people can be infected with the flu virus but have no symptoms. During this time, those people may still spread the virus to others.
Can you infect people with the flu for a long time?
Some people, especially young children and people with weakened immune systems, might be able to infect others with flu viruses for an even longer time.
What are the complications of the flu?
Other possible serious complications triggered by flu can include inflammation of the heart (myocarditis), brain (encephalitis) or muscle (myositis, rhabdomyolysis) tissues, and multi-organ failure (for example, respirator y and kidney failure).
How long does it take to recover from the flu?
Most people who get flu will recover in a few days to less than two weeks, but some people will develop complications (such as pneumonia) as a result of flu, some of which can be life-threatening and result in death.
Can the flu cause death?
Influenza (flu) can cause mild to severe illness, and at times can lead to death . Flu is different from a cold. Flu usually comes on suddenly. People who have flu often feel some or all of these symptoms: some people may have vomiting and diarrhea, though this is more common in children than adults.
How many different subtypes of influenza are there?
Influenza A viruses are divided into subtypes based on two proteins on the surface of the virus: hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N). There are 18 different hemagglutinin subtypes and 11 different neuraminidase subtypes (H1 through H18 and N1 through N11, respectively).
What are the subtypes of influenza A?
Current subtypes of influenza A viruses that routinely circulate in people include: A (H1N1) and A (H3N2). Influenza A subtypes can be further broken down into different genetic “clades” and “sub-clades.”. See the “Influenza Viruses” graphic below for a visual depiction of these classifications. This graphic shows the two types ...
What type of virus is not known to cause illness?
Influenza type C infections generally cause mild illness and are not thought to cause human flu epidemics. Influenza D viruses primarily affect cattle and are not known to infect or cause illness in people. Influenza A viruses are divided into subtypes based on two proteins on the surface of the virus: hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N).
What are the two lines of influenza B?
Influenza B viruses are not divided into subtypes, but instead are further classified into two lineages: B/Yamagata and B/Victoria. Similar to influenza A viruses, influenza B viruses can then be further classified into specific clades and sub-clades. Influenza B viruses generally change more slowly in terms of their genetic and antigenic properties than influenza A viruses, especially influenza A (H3N2) viruses. Influenza surveillance data from recent years shows co-circulation of influenza B viruses from both lineages in the United States and around the world. However, the proportion of influenza B viruses from each lineage that circulate can vary by geographic location.
Which virus is more genetically and antigenically different from the other viruses?
Of all the influenza viruses that routinely circulate and cause illness in people, influenza A (H3N2) viruses tend to change more rapidly, both genetically and antigenically. Influenza A (H3N2) viruses have formed many separate, genetically different clades in recent years that continue to co-circulate.
Is there a co-circulation of influenza B?
Influenza surveillance data from recent years shows co-circulation of influenza B viruses from both lineages in the United States and around the world. However, the proportion of influenza B viruses from each lineage that circulate can vary by geographic location.
Who is more likely to get the flu?
Living or working conditions. People who live or work in facilities with many other residents, such as nursing homes or military barracks, are more likely to develop the flu. People who are staying in the hospital also are at higher risk.
What to do if you have the flu?
If you have flu symptoms and are at risk of complications, see your doctor right away. Taking antiviral drugs may reduce the length of your illness and help prevent more-serious problems. If you have emergency signs and symptoms of the flu, get medical care right away.
How long does it take for the flu to go away?
If you're young and healthy, the flu usually isn't serious. Although you may feel miserable while you have it, the flu usually goes away in a week or two with no lasting effects. But children and adults at high risk may develop complications that may include:
What is the name of the virus that attacks the respiratory system?
Influenza is a viral infection that attacks your respiratory system — your nose, throat and lungs. Influenza is commonly called the flu, but it's not the same as stomach "flu" viruses that cause diarrhea and vomiting.
How do viruses travel through the air?
Influenza viruses travel through the air in droplets when someone with the infection coughs, sneezes or talks. You can inhale the droplets directly, or you can pick up the germs from an object — such as a telephone or computer keyboard — and then transfer them to your eyes, nose or mouth.
What are the chronic illnesses?
People who have chronic illnesses, such as asthma, heart disease, kidney disease, liver disease and diabetes
How long is a person contagious after a virus?
People with the virus are likely contagious from about a day before symptoms appear until about five days after they start. Children and people with weakened immune systems may be contagious for a slightly longer time.
What is the peak month of flu activity?
The “peak month of flu activity” is the month with the highest percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza virus infection during that influenza season.
When do viruses circulate?
Do other respiratory viruses circulate during the flu season? While seasonal influenza (flu) viruses are detected year-round in the United States, flu viruses are most common during the fall and winter. The exact timing and duration of flu seasons can vary, but influenza activity often begins to increase in October.
What are the most common respiratory diseases in children?
These respiratory viruses include rhinovirus (one cause of the “common cold”) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), which is the most common cause of severe respiratory illness in young children as well as a leading cause of death from respiratory illness in those aged 65 years and older.
What is the most common cause of respiratory illness in young children?
These respiratory viruses include rhinovirus (one cause of the “common cold”) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), which is the most common cause of severe respiratory illness in young children as well as a leading cause of death from respiratory illness in those aged 65 years and older.
Is influenza reporting voluntary?
All influenza activity reporting by states, laboratories, and health care providers is voluntary. For more information about CDC’s influenza surveillance activities, see the Overview of Influenza Surveillance in the United States.
What Is the Flu?
Flu, or influenza, is a contagious respiratory in fection caused by a variety of flu viruses. Symptoms of flu involve muscle aches and soreness, headache, and fever.
What Are the Different Types of Flu?
There are three types of flu viruses: A, B , and C. Type A and B cause the annual influenza epidemics that have up to 20% of the population sniffling, aching, coughing, and running high fevers. Type C also causes flu; however, type C flu symptoms are much less severe.
What Is Type A Flu Virus?
Type A flu or influenza A viruses are capable of infecting animals, although it is more common for people to suffer the ailments associated with this type of flu. Wild birds commonly act as the hosts for this flu virus.
How Is Type C Flu Virus Different From the Others?
Influenza C viruses are also found in people. They are, however, milder than either type A or B. People generally do not become very ill from the influenza type C viruses. Type C flu viruses do not cause epidemics.
What Is the Bird Flu?
The avian influenza virus causes bird flu. Birds can be infected by influenza A viruses and all of its subtypes. Birds are not cap able of carrying either type B or C influenza viruses.
Should I Worry About Catching Bird Flu?
Also, people are not able to catch the bird flu virus by eating cooked chicken, turkey, or duck. High temperatures kill the virus.
Why is the avian flu so low?
The risk of avian flu is generally low in most people because the virus does not typically infect humans. Infections have occurred as a result of contact with infected birds. Spread of this infection from human to human has been reported to be extremely rare.