Where does the splenic artery arise from?
the celiac trunkThe splenic artery is the largest and most tortuous branch of the celiac trunk. After originating from the celiac trunk, the artery courses laterally, posterior to the stomach, and along the superior border of the pancreas.
What side is the splenic artery?
leftSplenic Artery Aneurysm. A splenic artery aneurysm is a bulging, weakened section of the artery that supplies blood to your spleen and parts of your pancreas and stomach. Many people have no symptoms, but a common symptom is pain in the upper left side of your belly.
What is the function of the splenic artery?
In human anatomy, the splenic artery or lienal artery is the blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the spleen. It branches from the celiac artery, and follows a course superior to the pancreas. It is known for its tortuous path to the spleen.
How common is a splenic artery aneurysm?
Splenic artery aneurysm is a rare condition with a prevalence of 1%. It accounts for about 60% of all splanchnic arterial aneurysms. It only follows aortic and iliac arteries aneurysms as the third most common intra-abdominal aneurysm.
What organ is supplied by splenic artery?
the spleenThe splenic artery, also known as the lienal artery, is an unpaired artery arising as the longest branch of the celiac trunk. This artery supplies the spleen, as well as large portions of the pancreas and stomach.
How often should a splenic artery aneurysm be checked?
If intervention is not planned, surveillance is recommended at 6 months after diagnosis and then annually.
Can you live without a spleen?
The spleen is a fist-sized organ in the upper left side of your abdomen, next to your stomach and behind your left ribs. It's an important part of your immune system, but you can survive without it. This is because the liver can take over many of the spleen's functions.
How big is the splenic artery?
The median internal diameter of the splenic artery was 5.35 mm (IQR: 4.67-6.18 mm) in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension and 4.60 mm (IQR: 4.32-5.32 mm) in healthy controls.
What is a splenic artery aneurysm?
Splenic artery aneurysm is defined as a condition where there is a focal dilation in the diameter of the splenic artery that is 50% greater than the normal vessel diameter. This is the most common visceral artery aneurysm reported making up about 60% to 70% of patients diagnosed with visceral artery aneurysms.
What doctor treats splenic artery aneurysm?
Aneurisms of the splenic artery are rare clinical findings. Surgeons and interventional radiologists should co‐operate in the management of this challenging disease; we describe here a surgical option. Question 1: What is your diagnosis when you look at the CT angiographic slice of the abdomen?
Can splenic artery aneurysm cause back pain?
Patients are often asymptomatic, and only 20% have symptoms such as vague left upper quadrant or epigastric discomfort or back pain, and most splenic artery aneurysms are detected incidentally during diagnostic imaging performed for other indications [6-8,10].
Is a splenic artery aneurysm an emergency?
Splenic artery aneurysm (SAA) is an uncommon, but potentially life-threatening, condition.
How do you know if you have a splenic artery?
The splenic artery is one of the terminal branches of the celiac trunk, passing left from the celiac axis across the left crus of diaphragm and left psoas muscle. It is a tortuous artery, running superior to the pancreas before turning forward into the splenorenal ligament to the hilum of the spleen.
What causes a splenic artery aneurysm to rupture?
The cause of splenic artery aneurysms may be from portal hypertension secondary to liver cirrhosis [2], atherosclerosis [3] and pregnancy [4]. It is not fully understood why pregnancy is a cause but it may be due to multiparity and associated hormonal effect and portal hypertension causing dilatation of the aneurysm.
What organ does the left gastric artery supply?
The splenic artery branches into the short gastric artery, left gastroepiploic artery, and posterior gastric artery, which supplies blood to the stomach, spleen, and pancreas.
Is splenic artery an end artery?
Arteries which do not anastomose with their neighbors are called end arteries. There is no collateral circulation present besides the end arteries. Examples of an end artery include the splenic artery that supplies the spleen and the renal artery that supplies the kidneys.
Which artery is the splenic artery?
The splenic artery is, along with the gastric and common hepatic arteries, one of the three main branches of the celiac artery.
What are the branches of the splenic artery?
The branches of the splenic artery are the short gastric, the left gastroepiploic, the posterior gastric, and the branches to the pancreas. The short gastric arteries consist of five to seven small branches that run along the greater curvature of the stomach.
Which artery runs through the stomach?
The left gastroepiploic artery is the largest branch of the splenic artery and runs toward the interior of the stomach through the greater omentum, a large membrane that hangs down from the stomach. The branches to the pancreas consist of numerous, small, blood vessels that run behind the upper border of the pancreas, supplying it with blood.
Where is the splenic artery?
The splenic artery is one of the terminal branches of the celiac trunk, passing left from the celiac axis across the left crus of diaphragm and left psoas muscle. It is a tortuous artery, running superior to the pancreas before turning forward into the splenorenal ligament to the hilum of the spleen.
How many segments does the splenic artery have?
Near the splenic hilum the splenic artery divides into superior and inferior terminal branches, with each terminal branch further dividing into four to six intrasplenic segmental branches.
Which branch of the celiac trunk supplies the stomach and pancreas?
Splenic artery. The splenic artery is one of the three branches of the celiac trunk, which supplies the spleen as well as large parts of the stomach and pancreas.
Which artery supplies the body and tail of the pancreas?
pancreatic branches including the dorsal pancreatic artery, trans verse pancreatic artery and greater pancreatic artery (arteria pancreatica magna) supply neck, body and tail of the pancreas. short gastric arteries. arising before the splenic artery enters the splenic hilum. run in the gastrosplenic ligament to supply the fundus and upper part ...
Which artery runs in the greater omentum along the greater curvature of the stomach to anas?
runs in the greater omentum along the greater curvature of the stomach to anastomose with the right gastroepiploic artery
Which artery supplies the cardia and fundal regions of the stomach?
supplies cardia and fundal regions of the stomach. left gastroepiploic artery. runs in the greater omentum along the greater curvature of the stomach to anastomose with the right gastroepiploic artery.
Which ligament runs in the stomach?
run in the gastrosplenic ligament to supply the fundus and upper part of greater curvature of the stomach, and anastomose with the left gastric artery over the fundus
Why does my spleen artery dilate?
Multiparity and pregnancy-associated hormonal effects as well as portal hypertension are believed to cause dilatation of the weak walls of the splenic artery. Other possible causes include congenital defects such as berry aneurysms ...
How long does it take to follow up a splenic artery aneurysm?
A follow-up period of one year is recommended, but it may be extended if other medical risks are present.
How to treat aneurysmal aneurysm?
Treatment consists of putting steel or platinum coils into the artery to block the aneurysmal portion.
Is splenic aneurysm more common in women?
Splenic artery aneurysm is more common among women, particularly in patients around 50 years old. Other factors that increase your risk of the disease include:
Are There Any Symptoms of Splenic Artery Aneurysm?
Initially, most patients do not experience any symptoms, and a splenic artery aneurysm may be diagnosed incidentally on imagin g. However, some patients experience nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. In some patients, serious life-threatening complications like rupture of the aneurysm can occur.
Where does the arterial supply of the spleen come from?
The arterial supply of the spleen comes from the tortuous splenic artery, which reaches the spleen as it travels through the splenorenal ligament. This artery emerges from the celiac trunk, which is a branch of the abdominal aorta .
Where is the spleen located?
More precisely, the spleen is located posterior to the stomach and anterior to the left hemidiaphragm at the level of ribs 9-10.
What is the microscopic anatomy of the spleen?
Understanding the microscopic anatomy of the spleen is important for understanding its function. Numerous septa called trabeculae extend from the dense irregular fibroelastic connective tissue of the capsule into the parenchyma of the spleen. Both the capsule and trabeculae contain myoepithelial cells which have the ability to contract. As the spleen stores a significant amount of blood, the contraction of myoepithelial cells pumps stored blood into the circulatory system when the body is in need; for example during intense physical activity or massive hemorrhage.
What is the medial surface of the spleen?
Medial surface of the spleen shows three areas of impression. The colic area is the impression of the left colic flexure, the gastric area is the impression of the stomach, and the renal area is the impression of the left kidney. The splenic hilum is found in the central part of this surface.
What is the parenchyma of the spleen?
The parenchyma of the spleen is called pulp. Based on the color of the pulp on fresh sections, white and red pulp can be distinguished. White pulp is the main lymphoid tissue of the spleen. It is the accumulation of lymphocytes around an arterial vessel. This aggregation of lymphocytes constitutes the lymphoid tissue known as periarterial lymphoidsheath ( PALS) and it is the first to react if microbes reach the spleen through the bloodstream. The central arterial vessels in PALS nodules are branches of the splenic artery. Red pulp consists of splenic venous sinuses and cords (of Billroth), linings of splenic macrophages around the sinuses. The central artery of PALS continues from the white pulp and enters the red pulp as a capillary. These capillaries empty into the splenic cords, where macrophages phagocyte old and damaged erythrocytes. From there, blood diffuses into the splenic sinuses, thus returning to the venous circulation.
How many borders does the spleen have?
The spleen has three borders (superior, inferior, and anterior) as well as two extremities (anterior and posterior). The superior border bounds the gastric area, the inferior border bounds the renal area and the anterior border bounds the colic area.
Which ligament connects the hilum of the spleen to the left kidney?
The splenorenal ligament connects the hilum of the spleen with the left kidney. It transmits the splenic artery and vein. Lastly, the spleen sits on the phrenicocolic ligament which originates from the colon and is also known as the sustentaculum lienis.
Where is the splenic flexure?
The splenic flexure is a part of your colon, or your large intestine, where it bends near your spleen, an organ that mainly filters your blood. It's also the place where many blood vessels come together. Your doctor might mention the involvement of your splenic flexure if you're experiencing a lot of pain in your upper left abdomen ...
What Affects the Blood Flow at Your Splenic Flexure?
Injuries to your colon. A serious injury near your splenic flexure could damage your colon and affect blood flow in the area.
Why Is the Splenic Flexure Important?
Many blood vessels come together at the splenic flexure, so the area is important for blood flow. Injuries to the colon near the splenic flexure can cause blood loss or low blood pressure.
How to treat splenic flexure syndrome?
Treatment. As mentioned, some doctors recommend eating fewer carbohydrates, sugar substitutes, and eating more fiber-rich foods. Because stress and mental health can also contribute to IBS and thus to splenic flexure syndrome, your doctor may recommend treatments targeting your mental health like psychotherapeutic drugs and therapy. Biofeedback therapy, a form of therapy where a therapist monitors your body functions as you try techniques to relax and reduce stress, may be effective as well.
What happens if you have a splenic flexure?
Since the splenic flexure is a bend in the colon, gas can build up in that area. If the gas build-up too much, you can get “splenic flexure syndrome”.
Why is it important to be careful when operating near the splenic flexure?
Surgeons have to be especially careful when operating near the splenic flexure for many reasons, but the most important one is that many blood vessels are found in the area. Vascular disease. Vascular disease affects the blood flow in your blood vessels. There are many types and causes of vascular disease.
Can irritable bowel syndrome cause splenic flexure?
People with irritable bowel syndrome, or IBS, are most likely to have splenic flexure syndrome, with some experts even considering it to be a type of IBS. Because stress can exacerbate IBS, it may also cause splenic flexure syndrome. Some doctors think that what you eat can cause splenic flexure syndrome.
How common is a splenic artery aneurysm?
Epidemiology. the true prevalence of splenic artery aneurysm is unknown. estimates vary widely from 0.2% to 10.4%, but generally it is the third most common site of intra-abdominal aneurysms after abdominal aorta and iliac arteries 1,6.
How big is a splenic aneurysm?
Size of splenic artery aneurysms can range from 2 to 9 cm, but usually it is smaller than 3 cm. Those may be single or multiple and are most commonly involving the distal portion of the artery. Peripheral calcification is common, and mural thrombus may be present 12 .
What is the most common type of aneurysm?
Splenic artery aneurysms are the most common visceral arterial aneurysm formation as well as the third most common abdominal aneurysm (after the aorta and iliac vessels ). Aneurysms are usually saccular in configuration and they can either be in the form of a true aneurysm (much more common) or as a pseudoaneurysm.
Is an aneurysm a saccular aneurysm?
Aneurysms are usually saccular in configuration and they can either be in the form of a true aneurysm (much more common) or as a pseudoaneurys m. This article focus on the true splenic artery aneurysm, please refer on splenic artery pseudoaneurysms for a specific discussion on this entity. On this page:
Where is the splenic artery located?
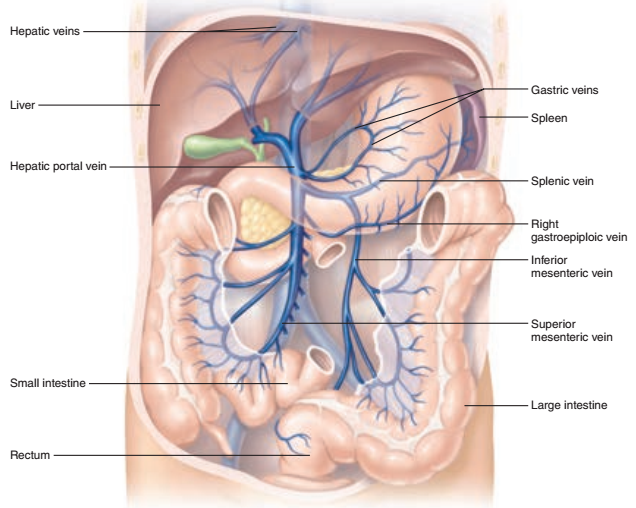
The splenic artery arises from the celiac trunk and passes to the left running along the upper border of the pancreas and often partially embedded in the upper pancreas (Figure 5). As it traverses along the upper border of the pancreas the splenic artery sends many branches into the body of the pancreas. (The splenic vein also has an intimate relationship to the pancreas.
Why is the parenchyma of the spleen difficult to suture?
The parenchyma of the spleen is difficult to suture because it is very friable. Furthermore, because the functions of the spleen including its hematopoietic functions are replicated in other organs, particularly, bone marrow, splenectomy is done in cases of splenic injury.
What is the history of a 58 year old woman with a pleural effusion?
A 58-year-old woman had a history of acute pancreatitis, chronic alcoholism and left pleural effusion in the last 12 months. Due to the abdominal pain, the patient underwent an abdominal ultrasound and CT scan. These scans revealed biliary lithiasis (gallstones) and the presence of three large cystic masses in her pancreas and spleen, as well as the pleural effusion (Figures 1-4). The patient declined surgical intervention at the time.
What is the fluid in the pleural cavity?
Presence of fluid in the pleural cavity. Depending on the type of fluid, it can be hydrothorax (serous fluid), hemothorax (blood), chylothorax (lymph) and pyothorax (pus). Cystic lesion that is lined with the fibrous tissue rather than epithelial or endothelial cells as it is in the true cyst.
What is the term for an organ that is on all surfaces surrounded by peritoneum?
Intraperitoneal organ. Organ that is on all surfaces surrounded by peritoneum. Splenectomy. Method of choice after injuries of the spleen. Suturing of the spleen is not recommended since the tssue is very friable, and the hematopietic functions of the spleen are replicated in the bone marrow.
Where does pancreatic fluid escape?
In pancreatitis, the pancreatic duct is often occluded and pancreatic fluid escapes into the mediastinum and through one of the hiatuses in the diaphragm (e.g., aortic; Figure 7) and then penetrates the pleura to enter the pleural cavity forming a pancreatic pleural effusion, which is likely the situation in this patient.
Can you differentiate splenic artery from vein?
Based solely on this single CT scan it would be impossible to differentiate splenic artery from vein, and incidentally, based on the cadaver image shown in Figure 1, the labeling in the CT would likely be reversed. But both of these vessels typically meander superior or slightly posterior to the pancreas, and one cannot generalize about the amount of undulation from one person to another).