Where do you feel trigeminal nerve pain?
Trigeminal neuralgia usually affects one side of the face. In some cases it can affect both sides, although not usually at the same time. The pain can be in the teeth, lower jaw, upper jaw or cheek. Less commonly the pain can also be in the forehead or eye.
What can irritate the trigeminal nerve?
A variety of triggers may set off the pain of trigeminal neuralgia, including:Shaving.Touching your face.Eating.Drinking.Brushing your teeth.Talking.Putting on makeup.Breeze lightly blowing over your face.More items...•
What does trigeminal neuralgia pain feel like?
It doesn't usually run in families. Trigeminal neuralgia symptoms may include: Episodes of sharp, intense, stabbing pain in the cheek or jaw that may feel like an electric shock.
What causes inflammation of the trigeminal nerve?
This type of trigeminal neuralgia is known as primary trigeminal neuralgia. In most cases the pressure is caused by an artery or vein squashing (compressing) the trigeminal nerve. These are normal blood vessels that happen to come into contact with the nerve at a particularly sensitive point.
How do I calm my trigeminal nerve?
To treat trigeminal neuralgia, your doctor usually will prescribe medications to lessen or block the pain signals sent to your brain. Anticonvulsants. Doctors usually prescribe carbamazepine (Tegretol, Carbatrol, others) for trigeminal neuralgia, and it's been shown to be effective in treating the condition.
Does trigeminal neuralgia show on MRI?
Imaging tests such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan can be very helpful in diagnosing trigeminal neuralgia. An MRI can help your doctor see if there is pressure on the trigeminal nerve.
What is the best painkiller for neuralgia?
The anti-convulsant drug most commonly prescribed for trigeminal neuralgia is carbamazepine (Tegretol), which can provide at least partial pain relief for up to 80 to 90 percent of patients. Other anti-convulsants prescribed frequently for trigeminal neuralgia include: Phenytoin (Dilantin) Gabapentin (Neurontin)
How do you test for trigeminal neuralgia?
There's no specific test for trigeminal neuralgia, so a diagnosis is usually based on your symptoms and description of the pain. If you've experienced attacks of facial pain, the GP will ask you questions about your symptoms, such as: how often do the pain attacks happen.
Can trigeminal nerve pain go away?
Trigeminal neuralgia is usually a long-term condition, and the periods of remission often get shorter over time. However, most cases can be controlled to at least some degree with treatment.
Who is the best doctor for trigeminal neuralgia?
Mayo Clinic doctors trained in brain and nervous system conditions (neurologists), brain and nervous system surgery (neurosurgeons), and doctors trained in treating children who have brain and nervous system conditions (pediatric neurologists) diagnose and treat people who have trigeminal neuralgia.
What foods should you avoid if you have trigeminal neuralgia?
It's important to eat nourishing meals, so consider eating mushy foods or liquidising your meals if you're having difficulty chewing. Certain foods seem to trigger attacks in some people, so you may want to consider avoiding things such as caffeine, citrus fruits and bananas.
Can sinus affect trigeminal nerve?
Even mild sphenoid sinusitis can cause inflammation to spread to the maxillary nerve if no bony boundary exists between it and the sphenoid sinus. A coronal CT study is highly beneficial for clarifying the pathophysiological mechanism of trigeminal neuralgia limited to the maxillary nerve.
What foods should you avoid if you have trigeminal neuralgia?
It's important to eat nourishing meals, so consider eating mushy foods or liquidising your meals if you're having difficulty chewing. Certain foods seem to trigger attacks in some people, so you may want to consider avoiding things such as caffeine, citrus fruits and bananas.
Can stress cause trigeminal neuralgia to flare up?
While stress alone doesn't cause trigeminal neuralgia, stress can aggravate the condition. There isn't a lot of understanding about how or why, but one possibility is the relationship between stress and pain. Studies have shown that chronic pain can lead to stress-induced heightened pain sensitivity.
Can the trigeminal nerve be pinched?
Trigeminal neuralgia occurs when the trigeminal nerve is pinched or damaged. The trigeminal nerve connects many different parts of your face to your brain. It is made up of three branches. The upper branch links the brain to the scalp and forehead.
Can sinus infection affect trigeminal nerve?
Even mild sphenoid sinusitis can cause inflammation to spread to the maxillary nerve if no bony boundary exists between it and the sphenoid sinus. A coronal CT study is highly beneficial for clarifying the pathophysiological mechanism of trigeminal neuralgia limited to the maxillary nerve.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve is most commonly associated with trigeminal neuralgia, a condition characterized by severe facial pain. Since it is large and has several divisions, the trigeminal nerve or its branches can also be affected by a number of medical conditions including infections, trauma, and compression from tumors or blood vessels.
Where are the trigeminal nerve roots located?
Location. The trigeminal nerve roots and ganglion, like those of other cranial nerves, are located right outside the brainstem. The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that serves as the physical connection between the spinal cord and the cerebral cortex of the brain. All 12 cranial nerves (12 in each side) emerge from the brainstem.
What is the most common problem associated with the trigeminal nerve?
A condition called trigeminal neuralgia is the most common problem associated with the trigeminal nerve. There are also several other medical problems that can involve the trigeminal nerve or its branches.
What causes nerve pain in the trigeminal nerve?
It can occur without any specific cause, and sometimes it can be triggered by an injury or inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. This condition often causes pain that is severe in intensity. Medications used for pain management include antidepressants and anticonvulsants, both of which are frequently used for nerve pain.
What can be done to prevent permanent deficits of the trigeminal nerve?
Treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medication, if started in a timely manner, can prevent permanent deficits of the trigeminal nerve in the setting of infection.
Which nerve is smaller than the sensory nerve?
The motor nerve branch of the trigemin al nerve is smaller than the sensory branches ...
Which nerves are located in the head?
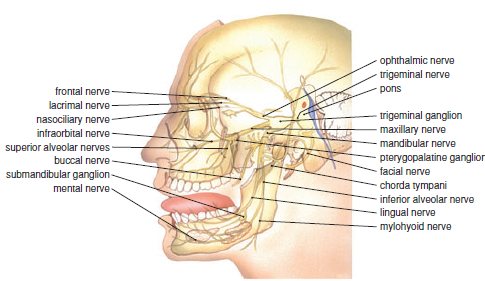
Ophthalmic. The frontal nerve, the lacrimal nerve, and the nasociliary nerves converge in the ophthalmic nerve. These nerves and their small branches are located in and around the eye, forehead, nose, and scalp. The ophthalmic nerve enters into the skull through a small opening called the superior orbital fissure before it converges in ...
How many nuclei are there in the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerves begin within four nuclei — or collections of nerve cell bodies — in your brain. Three of these nuclei control the functioning of your senses. The fourth controls motor function (or your movement).
Where is the trigeminal ganglion located?
(A ganglion is a collection of nerves outside the nervous system.) Each trigeminal ganglion is located near your temple at the side of your head, in front of your ear.
How many nerves does the trigeminal ganglion have?
The trigeminal ganglion splits into three trigeminal nerve branches. These branches travel along each side of your head to different parts of your face.
What nerves help with pain?
The trigeminal nerves play essential roles in helping your face feel pain, touch, warmth or cold. The mandibular branches of the trigeminal nerves help you bite, chew and swallow. In some cases, people develop numbness or other signs of trigeminal neuropathy from an accident, dental procedure or facial surgery. Trigeminal neuralgia can cause stabbing, shock-like facial pain or a constant burning sensation. Talk to your provider about finding relief from these trigeminal nerve conditions.
What is the name of the condition where an artery wraps around the trigeminal nerve and causes irritation?
Primary trigeminal neuralgia occurs when an artery or vein wraps around the trigeminal nerve and causes irritation.
What is the pain on one side of the face?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a type of trigeminal neuropathy brought on by nerve damage. The condition causes sudden, intense facial pain on one side of your face. The pain can feel like an electrical shock. Approximately 150,000 people develop trigeminal neuralgia every year. It's also called tic douloureux.
What is the fifth cranial nerve?
The trigeminal nerve, also called the cranial nerve V (that's the Roman numeral five), is the fifth of 12 cranial nerves.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
As the name suggests, the trigeminal nerve is a tripartite entity made up of distinct terminal divisions. Each component of the nerve is responsible for a specific region of the face, and transmits specific impulses. The three divisions of the trigeminal nerve are:
How many nuclei does the trigeminal nerve have?
Unlike the other cranial nerves, the trigeminal nerve is quite large. It has four nuclei that send fibers to form its tracts and is associated with three separate branches. Key facts about the trigeminal nerve (CN V) Type. Mixed (motor and sensory) Nuclei. Motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve.
How do axons form the mesencephalic tract?
As the myelinated axons leave the mesencephalic nucleus, they coalesce to form the mesencephalic tract. The individual axon s then split into central and peripheral branches. The central branches convey impulses from the neuromuscular spindles within the muscles of mastication, and from the bite force reflex arcs, to the motor neuron of the trigeminal nerve. Other central fibers also integrate with the reticular formation and the sensory trigeminal nerve. Others also gain access to the cerebellum by way of the superior cerebellar peduncle. This interplay between the proprioceptive and motor divisions of the trigeminal nerve helps to regulate the activity of the stretch muscles; and by extension, the process of mastication.
What nerve is CN V?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V): want to learn more about it?
Where does the ophthalmic nerve receive its meningeal tributary?
Once formed, the ophthalmic nerve also receives its meningeal tributary from the dura of the anterior cranial fossa. Key facts about the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V1) Branches. Nasociliary nerve.
Which nerve is responsible for the motor, sensory, and autonomous functions of the head and neck?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V) The principal regulator of the sensory modalities of the head is the trigeminal nerve. This is the fifth of twelve pairs of cranial nerves that are responsible for transmitting numerous motor, sensory, and autonomous stimuli to structures of the head and neck . While the trigeminal nerve (CN V) is largely a sensory nerve, ...
Where do the remaining sensory fibers travel?
The remaining sensory fibers will travel dorsomedially toward the main sensory nucleus, while the motor fibers will take a similar course to reach the motor nucleus. Skull exit locations of the trigeminal nerve branches are frequently tested on anatomy exam.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
e. The trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve, or simply CN V) is a nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name ("trigeminal" = tri-, or three, and - geminus, or twin: thrice-twinned) derives from the fact that each of the two nerves ...
Where does the trigeminal nerve originate?
The motor division of the trigeminal nerve derives from the basal plate of the embryonic pons, and the sensory division originates in the cranial neural crest. Sensory information from the face and body is processed by parallel pathways in the central nervous system .
What are the areas of cutaneous distribution of the trigeminal nerve?
The areas of cutaneous distribution (dermatomes) of the three sensory branches of the trigeminal nerve have sharp borders with relatively little overlap (unlike dermatomes in the rest of the body, which have considerable overlap). The injection of a local anesthetic, such as lidocaine, results in the complete loss of sensation from well-defined areas of the face and mouth. For example, teeth on one side of the jaw can be numbed by injecting the mandibular nerve. Occasionally, injury or disease processes may affect two (or all three) branches of the trigeminal nerve; in these cases, the involved branches may be termed:
What are the three branches of the trigeminal nerve?
The three major branches of the trigeminal nerve—the ophthalmic nerve (V 1 ), the maxillary nerve (V 2) and the mandibular nerve (V 3 ) —converge on the trigeminal ganglion (also called the semilunar ganglion or gasserian ganglion), located within Meckel's cave and containing the cell bodies of incoming sensory-nerve fibers.
What nerve is involved in numbed teeth?
For example, teeth on one side of the jaw can be numbed by injecting the mandibular nerve. Occasionally, injury or disease processes may affect two (or all three) branches of the trigeminal nerve; in these cases, the involved branches may be termed: V1/V2 distribution – Referring to the ophthalmic and maxillary branches.
Which ganglia contains sensory fibers?
The trigeminal ganglion is analogous to the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord, which contain the cell bodies of incoming sensory fibers from the rest of the body. From the trigeminal ganglion, a single, large sensory root (portio major) enters the brainstem at the level of the pons.
Where are motor fibers located in the pons?
Motor fibers pass through the trigeminal ganglion without synapsing on their way to peripheral muscles, but their cell bodies are located in the nucleus of the fifth nerve, deep within the pons.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
The Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) The trigeminal nerve, CN V, is the fifth paired cranial nerve. It is also the largest cranial nerve. In this article, we shall look at the anatomical course of the nerve, and the motor, sensory and parasympathetic functions of its terminal branches.
Where does the trigeminal nerve originate?
The trigeminal nerve originates from three sensory nuclei (mesencephalic, principal sensory, spinal nuclei of trigeminal nerve ) and one motor nucleus (motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve) extending from the midbrain to the medulla.
What are the 3 divisions of the trigeminal ganglion?
The peripheral aspect of the trigeminal ganglion gives rise to 3 divisions: ophthalmic (V1) , maxillary (V2) and mandibular (V3) . The motor root passes inferiorly to the sensory root, along the floor of the trigeminal cave. Its fibres are only distributed to the mandibular division.
How many terminal branches does the maxillary nerve have?
Maxillary nerve gives rise to 14 terminal branches, which innervate the skin, mucous membranes and sinuses of derivatives of the maxillary prominence of the 1st pharyngeal arch:
Which ganglion is associated with the lacrimal gland?
Lacrimal gland: Post ganglionic fibres from the pterygopalatine ganglion (derived from the facial nerve), travel with the zygomatic branch of V2 and then join the lacrimal branch of V1. The fibres supply parasympathetic innervation to the lacrimal gland.
Which nerve gives rise to 3 terminal branches?
Ophthalmic nerve gives rise to 3 terminal branches: frontal, lacrimal and nasociliary, which innervate the skin and mucous membrane of derivatives of the frontonasal prominence derivatives:
Where is the trigeminal ganglion located?
The trigeminal ganglion is located lateral to the cavernous sinus, in a depression of the temporal bone. This depression is known as the trigeminal cave. The peripheral aspect of the trigeminal ganglion gives rise to 3 divisions: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2) and mandibular (V3).
What causes trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia can also be caused by a tumor compressing the trigeminal nerve. Some people may experience trigeminal neuralgia due to a brain lesion or other abnormalities. In other cases, surgical injuries, stroke or facial trauma may be responsible for trigeminal neuralgia.
How does trigeminal neuralgia feel?
Trigeminal neuralgia symptoms may include one or more of these patterns: Episodes of severe, shooting or jabbing pain that may feel like an electric shock. Spontaneous attacks of pain or attacks triggered by things such as touching the face, chewing, speaking or brushing teeth. Bouts of pain lasting from a few seconds to several minutes.
What is the pain in the face called?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain. If you have trigeminal neuralgia , even mild stimulation of your face — such as from brushing your teeth or putting on makeup — may trigger a jolt of excruciating pain.
What nerve causes pain in the cheek and jaw?
Constant aching, burning feeling that may occur before it evolves into the spasm-like pain of trigeminal neuralgia. Pain in areas supplied by the trigeminal nerve, including the cheek, jaw, teeth, gums, lips, or less often the eye and forehead.
What is the name of the nerve that is disrupted by blood pressure?
In trigeminal neuralgia, also called tic douloureux, the trigeminal nerve's function is disrupted. Usually, the problem is contact between a normal blood vessel — in this case, an artery or a vein — and the trigeminal nerve at the base of your brain. This contact puts pressure on the nerve and causes it to malfunction.
Can trigeminal neuralgia cause pain?
You may initially experience short, mild attacks. But trigeminal neuralgia can progress and cause longer, more-frequent bouts of searing pain. Trigeminal neuralgia affects women more often than men, and it's more likely to occur in people who are older than 50.
Where is the pain of trigeminal neuralgia felt?
Depending on which branch and which part of the nerve is irritated, trigeminal neuralgia pain can be felt anywhere in the face. Most commonly, it is felt in the lower part of the face. The intensity of the pain is exceptional: Some people report it to be more severe than experiencing a heart attack, passing a kidney stone or even giving birth.
What causes trigeminal neuralgia?
The condition may be caused by a blood vessel pressing against the trigeminal nerve , also known as vascular compression.
What nerve is irritated in the face?
Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain. The trigeminal nerve splits off into three branches: ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular. Each branch provides sensation to different areas of the face. Depending on which branch and which part of the nerve is irritated, trigeminal neuralgia pain can be felt anywhere in the face.
How does a rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia work?
The surgeon inserts a long needle through the cheek on the affected side of the face and uses an electrical current (heat) or a chemical (glycerin or glycerol) to deaden the pain fibers of the trigeminal nerve. For those undergoing trigeminal neuralgia rhizotomy for the first time, the chemical approach is typically recommended. Those who have the procedure repeated often benefit from both the chemical and the heat treatment delivered in the same session.
How long does a trig neuralgia pain last?
The pain travels through the face in a matter of seconds, but as the condition progresses, the pain can last minutes and even longer. Trigeminal neuralgia is sometimes known as tic douloureux, ...
How many nerves are there on each side of the face?
We have two trigeminal nerves for each side of our face, but trigeminal neuralgia pain most commonly affects only one side. The pain of trigeminal neuralgia is unlike facial pain caused by other problems.
Is trigeminal neuralgia more common in older people?
Trigeminal neuralgia occurs more often in women than men, is more common in older people (usually 50 and older), and occurs more on the right than the left. It doesn’t usually run in families.