Where do you feel ureter pain?
If a kidney stone becomes lodged in the ureters, it may block the flow of urine and cause the kidney to swell and the ureter to spasm, which can be very painful. At that point, you may experience these symptoms: Severe, sharp pain in the side and back, below the ribs. Pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin.
How do I know if I have a blockage in my ureter?
Symptoms of a blocked ureter or urinary tract obstruction include: Pain in your abdomen, lower back or sides below your ribs (flank pain). Fever, nausea or vomiting. Difficulty urinating or emptying your bladder.
Are ureters in front or back?
The ureters leave the kidneys posterior to the renal vessels. Both ureters pass inferiorly over the abdominal surface of the psoas major, with the genitofemoral nerve behind it and the vessels of the gonads in front.
What are the symptoms of ureter problems?
SymptomsPain.Changes in how much urine you produce (urine output)Difficulty urinating.Blood in the urine.Urinary tract infections.High blood pressure (hypertension)
How do you unblock your ureter?
Drainage procedures. A ureteral obstruction that causes severe pain might require an immediate procedure to remove urine from your body and temporarily relieve the problems caused by a blockage. Your doctor (urologist) may recommend: A ureteral stent, which is a hollow tube inserted inside the ureter to keep it open.
Can a ureter heal on its own?
Occasionally, diversion of the urine stream with a nephrostomy or stent is the only intervention needed. Ureters without strictures heal in most patients. However, if a stricture does develop, it can be managed endoscopically with balloon dilation or endoureterotomy.
Can a stone get stuck in the ureter?
Some stones, especially wider ones, do get stuck in the ureter because it's the narrowest point in your urinary tract. This can cause severe pain and raise your risk of developing an infection.
Where is the ureter located in a female?
Urine exits the kidney through a long narrow tube called the ureter. The ureter exits into the bladder. It is in this ureter where kidney stones can get stuck.
What are the 3 functions of the ureters?
The ureters work constantly, emptying urine into the bladder about every 10 to 15 seconds. In addition to their role in eliminating waste from the body, the kidneys also balance fluids in the body, release hormones to regulate blood pressure, and control the production of red blood cells.
What does a swollen ureter mean?
Kidney swelling happens when urine can't drain from a kidney and builds up in the kidney as a result. This can occur from a blockage in the tubes that drain urine from the kidneys (ureters) or from an anatomical defect that doesn't allow urine to drain properly.
What is inflammation of the ureter?
Ureteritis refers to inflammation of the ureter, it is rare and is often associated with cystitis or pyelonephritis 1.
What causes ureter pain?
If a ureteral stone is large enough, it can block the flow of pee from your kidneys to your bladder. This blockage can cause severe pain. Ureteral stones form when minerals and salts build up in your pee. The minerals form crystals that grow into stones.
What happens when one ureter is blocked?
A ureteral obstruction is a blockage in one or both of the tubes (ureters) that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Ureteral obstruction can be cured. However, if it's not treated, symptoms can quickly move from mild — pain, fever and infection — to severe — loss of kidney function, sepsis and death.
What causes narrowing of the ureter?
A ureteral stricture frequently results from a buildup of scar tissue or inflammation around the ureter, often due to an external traumatic injury or as a complication of a previous surgery, such as a procedure to manage kidney stones or surgeries that affect the area surrounding the ureters, including gynecologic or ...
What is the home remedy for urine blockage?
Drinking unsweetened cranberry juice is one of the most well-known natural remedies for UTIs. If drinking unsweetened cranberry juice isn't your thing, you can also take it in capsule form. Cranberries work by helping to prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract.
Why does it feel like something is blocking my pee?
Infections and swelling In men, an infection of the prostate can cause it to swell. This causes it to press on the urethra to block the flow of urine. A urinary tract infection (UTI) can cause swelling of the urethra or weakness of the bladder, both of which can cause urinary retention.
Where is ureter located?
Ureter is located in the abdominopelvic visceral area, sharing place with the pancreas, the liver and the spine. This tube has very interesting characteristics, because it has the capacity to control the urinary flow, namely sphincter.
What is the purpose of ureter?
Clinical significance. Ureter is the canal through which urine is transported from the kidney to the bladder. The ureters are two deep tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder back. Each one has a length of 30 centimeters (approximate), which advance from the bottom of each kidney, following through the lower abdomen and the pelvis first area.
What is the anatomy of the urinary system?
The Anatomy of the Urinary System consist of: Kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Urine is created in the renal tubules, and it is stored in the kidney’s renal pelvis. Urine flows from the kidneys, passing through the ureters to the bladder. Urine builds up in the bladder until it is ejected from the body through the urethra.
What is ureter reimplantation?
Ureterovesical reimplantation is a surgical intervention that aims to reconnect the higher, healthy section of the ureter (to the bladder), when there is an obstruction to the proper passage of urine in the lower ureter (due to fibrosis, tumor, lithiasis, fistula, etc.), and to prevent the progressive kidney function loss.
What is the ureteral orifice?
Through a sequences of ureters walls contractions and relaxations, the tubular structure advances. Unified with the urinary bladder (the next section of the urinary tract) are located the ureteral orifices, which allow the urine pass through. The ureters regulate the course of the urine, in a single direction. However, they do not work like other body sphincters, preventing reflux. Thus, if there is any abnormality in ureter tubes (and orifices), it is probable the urine return to the kidneys, leading to physiologic complications.
How does the ureter work?
The kidneys produce urine by filtering excess water from our blood. The blood transports the debris to the kidneys. From there, the urine passes through two tiny tubes, ureters, into the bladder. The ureters measure between 20 and 26 cm. The muscles in the ureters walls contract and relax , in order to force the urine to go away from the kidneys. Small quantities of urine flow from the ureters to the bladder every single 10-15 seconds.
Why is the inner frame of the urine mucous?
The Ureter inner frame is mucous, in order to guarantee an operative transportation of the urine and those mixtures that shape in the kidneys.
How long is the ureter?
In a human adult, the ureters are usually 20–30 cm (8–12 in) long and around 3–4 mm (0.12–0.16 in) in diameter. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer in third closest to the bladder that assists with peristalsis .
What is the ureter lined with?
The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer in third closest to the bladder that assists with peristalsis . The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone.
How does a kidney stone get stuck in the ureter?
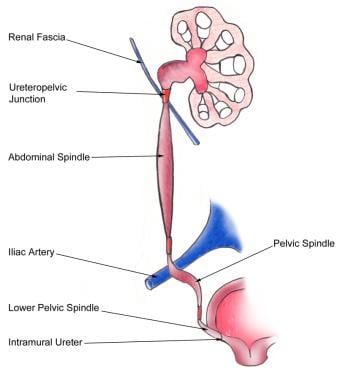
A kidney stone can move from the kidney and become lodged inside the ureter, which can block the flow of urine, as well as cause a sharp cramp in the back, side, or lower abdomen. Pain often comes in waves lasting up to two hours, then subsides, called renal colic. The affected kidney could then develop hydronephrosis, should a part of the kidney become swollen due to blocked flow of urine. It is classically described that there are three sites in the ureter where a kidney stone will commonly become stuck: where the ureter meets the renal pelvis; where the iliac blood vessels cross the ureters; and where the ureters enter the urinary bladder, however a retrospective case study, which is a primary source, of where stones lodged based on medical imaging did not show many stones at the place where the iliac blood vessels cross.
What is the connection between the arteries of the ureter and the blood supply?
The arteries that supply the ureters end in a network of vessels within the adventitia of the ureters. There are many connections ( anastamoses) between the arteries of the ureter, particularly in the adventitia, which means damage to a single vessel does not compromise the blood supply of the ureter.
What is the name of the tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder?
Ureter. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Jump to navigation Jump to search. Tubes used in the urinary system in most animals. Not to be confused with urethra. Ureter . The ureters are tubes that carry urine and connect the kidneys to the bladder. Details.
How to diagnose cancer in the kidney?
Investigations performed usually include collecting a sample of urine for an inspection for malignant cells under a microscope, called cytology, as well as medical imaging by a CT urogram or ultrasound. If a concerning lesion is seen, a flexible camera may be inserted into the ureters, called ureteroscopy, in order to view the lesion and take a biopsy, and a CT scan will be performed of other body parts (a CT scan of the chest, abdomen and pelvis) to look for additional metastatic lesions. After the cancer is staged, treatment may involve open surgery to remove the affected ureter and kidney if it is involved; or, if the lesion is small, it may be removed via ureteroscopy. Prognosis can vary markedly depending on the tumour grade, with a worse prognosis associated with an ulcerating lesion.
Which arteries supply the ureter?
The upper third of the ureter, closest to the kidney, is supplied by the renal arteries. The middle part of the ureter is supplied by the common iliac arteries, direct branches from the abdominal aorta, and gonadal arteries; the gonadal arteries being the testicular artery in men and the ovarian artery in women.
Where does urine go in the ureter?
The arterial supply to the ureters comes directly and indirectly from the abdominal aorta.
How long are the ureters?
The ureters are collapsible S-shaped channels, each about 25 cm in length. They are widest at the renal pelvis and narrow progressively as they enter the urinary bladder in the concavity of the true pelvis.
How is urine propelled along the ureters?
Also interesting to note is that urine is propelled along the ureters by peristaltic motions initiated by pacemaker cells in the proximal renal pelvis. The whitish, non-pulsatile exterior along with the peristaltic waves helps to distinguish between ureters and blood vessels in vivo.
What is the layer of the ureter that is lined with the ureter?
The lumen of each ureter is lined by a mucosal layer of transitional epithelium, which accommodates the increase in pressure that accompanies increases in the volume of urine leaving the kidney; thereby aiding to minimize the risk of rupturing the ureters.
What is the function of the ureters?
The ureters are bilateral, muscular, tubular structures, responsible for taking urine from one kidney to the urinary bladder for storage, prior to excretion. After blood has been filtered in the kidneys, the filtrate undergoes a series of reabsorptions and exudation throughout the length of the convoluted tubules.
Where do the ureters leave the kidneys?
The ureters leave the kidneys posterior to the renal vessels. Both ureters pass inferiorly over the abdominal surface of the psoas major, with the genitofemoral nerve behind it and the vessels of the gonads in front. As the right ureter travels towards the bladder, it travels posterior to the duodenum and further down it is crossed by branches of the superior mesenteric vessels.
Which artery receives blood supply from the ureteric branch?
The proximal end receives arterial supply from the ureteric branch of the renal artery.
Where is the urethra located?
Anatomy and function of the female urethra. The female urethra begins at the bottom of the bladder, known as the neck. It extends downward, through the muscular area of the pelvic floor. Before reaching the urethral opening, urine passes through the urethral sphincter. This is a muscular structure in the urethra that helps hold urine inside ...
What is the urethra?
The urethra transports urine that’s stored in the bladder out of the body. The urethra is closely linked with the reproductive organs, so the anatomy of the urethra is different between males and females.
What is a benign mass in the urethra?
A urethral caruncle is a benign mass found in the urethra, usually occurring after menopause. It usually doesn’t cause any symptoms. However, some people might notice pain when urinating or bleeding from the urethra.
Why does urine have blood in it?
blood in urine. pelvic pain. Urethritis sometimes develops in response to a recent urinary procedure or placement of a catheter. In other cases, it’s due to an infection. Bacteria can spread from the anus to the urethra, especially if you wipe back to front after going to the bathroom.
Why is the female urethra shorter than the male?
The female urethra is significantly shorter than the male urethra. This means that females often have a higher risk of developing urinary tract infections (UTIs).
What causes a burning sensation when you pee?
Urethritis. Urethritis refers to inflammation of the urethra. This can cause a range of symptoms, including: increased urge to urinate. burning sensation while urinating. releasing small amounts of urine at a time. cloudy or foul-smelling urine. blood in urine. pelvic pain.
What is the treatment for bladder cancer?
Treatment for urethral cancer includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or a combination of all three.
What is a duplicated ureter?
A duplicated ureter occurs when two ureters form on the same kidney. A ureterocele is a small bulge in the ureter, usually in the end closest to the bladder. Both conditions may lead to ureteral obstruction. Different types of ureteral obstruction have different causes, some of them present at birth (congenital).
Why does the ureter block?
Various causes inside (intrinsic) or outside (extrinsic) the ureter can lead to ureteral obstruction, including: Long-term swelling of the ureter wall, usually due to diseases such as tuberculosis or a parasite infection called schistosomiasis.
What happens if your ureter is too narrow?
If the ureter is too narrow and doesn't allow urine to flow normally, a tiny bulge in the ureter (ureterocele) may develop, usually in the section of the ureter closest to the bladder. This can block urine flow and cause urine to back up into the kidney, possibly leading to kidney damage.
How do you know if you have ureteral obstruction?
Symptoms. Ureteral obstruction might have no signs or symptoms. Signs and symptoms depend on where the obstruction occurs, whether it's partial or complete, how quickly it develops, and whether it affects one or both kidneys. Signs and symptoms might include: Pain. Changes in the amount of urine produced. Difficulty urinating. Blood in the urine.
Why does urine back up into the kidney?
The fibers may grow due to cancers or may result from taking certain medicines used to treat migraines. The fibers encircle and block the ureters, causing urine to back up into the kidneys.
Where is the kidney located?
Your kidneys, located in the rear portion of your upper abdomen , produce urine by filtering waste and fluid from your blood. A ureteral obstruction is a blockage in one or both of the tubes (ureters) that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder. Ureteral obstruction can be curable.
Can a kidney have two ureters?
This common condition, which is present at birth (congential), causes two ureters to form on the same kidney. The second ureter can be normal or only partially developed. If either ureter doesn't function properly, urine can back up into the kidney and cause damage.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/brachial-artery/m0zfQyREwwkSdtVao7lw_HJ1ycVnnxtfiI95LEYumYg_A4KbP4mxEp_Arteria_brachialis_1.png)
Overview
Other animals
Structure
Function
Clinical significance
All vertebrates have two kidneys located behind the abdomen that produce urine, and have a way of excreting it, so that waste products within the urine can be removed from the body. The structure specifically called the ureter is present in amniotes, meaning mammals, birds and reptiles. These animals possess an adult kidney derived from the metanephros. The duct that connects the kidney to excrete urine in these animals is the ureter. It connects to the urinary bladder, from whe…
History
The ureters are tubular structures, approximately 20–30 cm (7.9–11.8 in) in adults, that pass from the pelvis of each kidney into the bladder. From the renal pelvis, they descend on top of the psoas major muscle to reach the brim of the pelvis. Here, they cross in front of the common iliac arteries. They then pass down along the sides of the pelvis and finally curve forward and enter the bladder from its left and right sides at the back of the bladder. The ureters are 1.5–6 mm (0.059–0.236 i…