
Where is the largest bone in the human body located?
Your femur, or thighbone, is the largest bone in your body. The head of your femur fits into your hip socket and the bottom end connects to your knee. The two bones beneath your knee that make up your shin are your tibia and fibula.
What is the largest bone and where is it located?
The strongest, longest, and largest bone in the human body is the femur, or thigh bone, which is a bone in the leg that runs from the knee to the hip. Structure. Parts of the femur include the upper part, the body, and the lower part.
Where is a bimalleolar bone located?
The typical bimalleolar fracture involves bone injury to the inner and outer side of the ankle. People who sustain a trimalleolar ankle fracture also have a bone injury at the back of the tibia (posterior malleolus fracture) near the ankle joint. Often this does not change the treatment from that of a bimalleolar ankle fracture.
Where are the phalanges bones located?
Where are the Phalanges Located. Located within each digit, above the metacarpals, these are the terminal bones (located farthest from the center of the body) of the upper limbs in humans [6] You can feel the phalanges within your fingers and thumb, with each section of a finger having one phalanx.
What area is zygomatic?
The zygomatic bone (or zygoma) is a paired, irregular bone that defines the anterior and lateral portions of the face. The zygomatic complex is involved in the protection of the contents of the orbit and the contour of the face and cheeks.[1]
What type of bone is the zygomatic?
irregular boneIn the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from Ancient Greek: ζῠγόν, romanized: zugón, lit. 'yoke'), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone.
Is the zygomatic bone part of the skull?
The zygomatic bone (zygoma) is an irregularly shaped bone of the skull. It is often referred to as the cheekbone, and it comprises the prominence just below the lateral side of the orbit. The zygomatic bone is nearly quadrangular in shape and it features three surfaces, five borders and two processes.
What is the function of zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone is a paired facial bone. Both zygoma or cheek bones are irregular and articulate with other bones of the cranium and face. They are important contributors to mastication or chewing, providing an attachment point for the masseter muscle – a jaw adductor that closes the jaw.
Why is it called the zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone is also known as the zygomatic arch, the zygoma, the malar bone, the cheek bone and the yoke bone. The word "zygomatic" comes from the Greek "zygon" meaning a yoke or crossbar by which two draft animals such as oxen could be hitched to a plow or wagon.
How do you remember the zygomatic bone?
0:357:45Facial Bones of the Skull Mnemonic [Anatomy Animation] - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThere are 14 facial bones and i came up with a simple mnemonic that will help you remember the namesMoreThere are 14 facial bones and i came up with a simple mnemonic that will help you remember the names of each one the mnemonic is my mandible choose nine very large zucchini pizzas.
What bone is located on top of the skull?
The frontal bone forms the forehead. The two parietal bones form the upper sides of the skull; the two temporal bones form the lower sides.
What bone is located in the skull?
In the neurocranium these are the occipital bone, two temporal bones, two parietal bones, the sphenoid, ethmoid and frontal bones.
What is the bone directly under the eye?
The zygomatic bones are more commonly known as the cheekbones. These bones are located just below each eye and extend upward to the outer side of each eye.
What bone is hardest to break?
The thigh bone is called a femur and not only is it the strongest bone in the body, it is also the longest. Because the femur is so strong, it takes a large force to break or fracture it – usually a car accident or a fall from high up.
What is another name for the zygomatic bone?
zygomatic bone, also called cheekbone, or malar bone, diamond-shaped bone below and lateral to the orbit, or eye socket, at the widest part of the cheek. It adjoins the frontal bone at the outer edge of the orbit and the sphenoid and maxilla within the orbit.
What happens if you break your zygomatic bone?
Fractures of the ZMC or zygomatic arch can often lead to unsightly malar depression, which should be corrected to restore a normal facial contour. ZMC fractures can also cause significant functional issues, including trismus, enophthalmos and/or diplopia, and paresthesias of the infraorbital nerve.
What type of bone is the parietal bone?
quadrilateral skull boneThe parietal bone is a paired, irregular, quadrilateral skull bone that forms the sides and roof of the cranium.
What bones make up the zygomatic arch?
The cranial portion of the zygomatic arch is formed by the zygomatic bone, and the caudal portion is formed by the zygomatic process of the temporal bone.
What is zygomatic arch bones?
zygomatic arch, bridge of bone extending from the temporal bone at the side of the head around to the maxilla (upper jawbone) in front and including the zygomatic (cheek) bone as a major portion.
Which bone belongs to the axial skeleton?
Your axial skeleton is made up of the 80 bones within the central core of your body. This includes bones in your skull (cranial and facial bones), ears, neck, back (vertebrae, sacrum and tailbone) and ribcage (sternum and ribs).
What is the zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone (zygoma) is an irregularly shaped bone of the skull. It is often referred to as the cheekbone, and it comprises the prominence just below the lateral side of the orbit. The zygomatic bone is nearly quadrangular in shape and it features three surfaces, five borders and two processes. Besides forming the prominence of the cheek, ...
What bone forms the zygomatic arch?
Besides forming the prominence of the cheek, the zygomatic bone also contributes to the formation of the zygomatic arch, the walls of the temporal and infratemporal fossae, and the floor and lateral wall of the bony orbit. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the zygomatic bone. Key facts about the zygomatic bone.
What are the three surfaces of the zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone has three surfaces: lateral, posteromedial and orbital. The lateral (facial) surface faces towards the outside. It is smooth and convex, and it features a small opening called the zygomaticofacial foramen. This foramen transmits the zygomaticofacial nerve, artery and vein between the orbit and the face.
What is the border between the lateral and orbital surfaces of the zygomatic bone?
It is the border between the lateral and orbital surfaces of the zygomatic bone. The anteroinferior (maxillary) border is the articular surface for the zygomaticomaxillary suture. It also serves as an attachment site for the levator labii superioris muscle.
Which surface faces the temporal and infratemporal fossae?
The posteromedial (temporal) surface faces towards the temporal and infratemporal fossae. Its anteriormost portion is rough and serves for the articulation with the zygomatic (malar) process of maxilla via the zygomaticomaxillary suture. The posteromedial surface spreads over the medial side of the temporal process, comprising a part of the lateral wall of the infratemporal fossa. Near the base of the frontal process, the posteromedial surface features the zygomaticotemporal foramen which transmits the zygomaticotemporal nerve from the orbit to the temporal fossa.
Which border is serrated and articulates with the greater wing of sphenoid bone superiorly via?
The posteroinferior border is rough and serves as the attachment site for the masseter muscle. The posteromedial border is serrated and articulates with the greater wing of sphenoid bone superiorly via the sphenozygomatic suture, and with the orbital surface of maxilla inferiorly.
What is the second most common area of fracture in the face?
Fractures. The second most common area of fracture in the face is the fracture of the zygomatic bone , especially of the left frontal process. This kind of injury often happens during a car accident or due to being punched in the face with a fist.
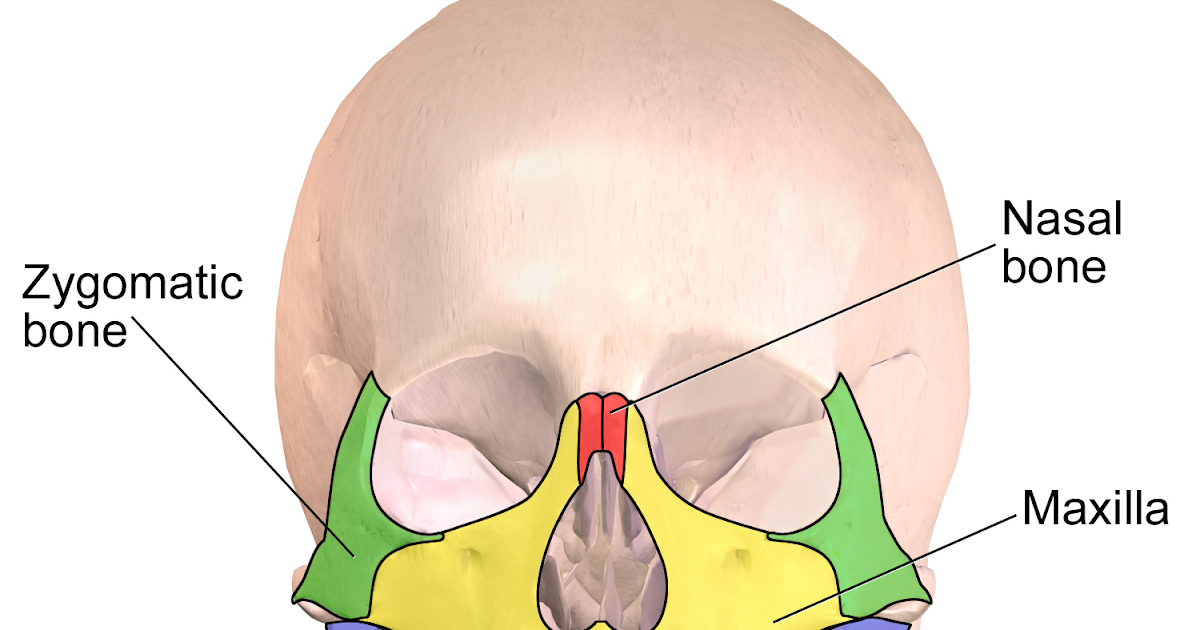
Where is the Zygomatic Bone Located?
Zygomatic bone location can easily be felt as it forms the ridge above the fleshy area of the cheeks, along the outer rim of the eyes .
What is the zygomatic bone?
The zygomatic bone is a paired facial bone. Both zygoma or cheek bones are irregular and articulate with other bones of the cranium and face. They are important contributors to mastication or chewing, providing an attachment point for the masseter muscle – a jaw adductor that closes the jaw.
What is the lateral surface of the zygoma?
From a lateral view, the zygoma are rectangular in form. The lateral surface provides a point of attachment for the zygomaticus major and minor muscles.
What is the function of zygomatic bone?
Zygomatic bone anatomy is not over-complex; its main function is to provide structure and strength to the mid-face. The cheekbones have three surfaces, four processes, three foramina, and three articulations. Processes are projecting pieces of bone that insert into other bones.
How many processes are there in the zygomatic bone?
There are four processes of the zygomatic bone, but these are not zygomatic processes! A process is named after the bone it meets with. In the zygoma, these four processes are the: Orbital process of the zygomatic bone. Maxillary process of the zygomatic bone. Temporal process of the zygomatic bone.
Which process of the cheekbone forms the zygomatic arch?
Together with the temporal process of the cheekbone, the zygomatic process of the temporal bone forms the zygomatic arch. This arch surrounds a large hollow that allows the temporal and masseter muscles to pass through to the lower jaw. It is this arch that gives the mid-face its shape.
Where are zygomatic processes found?
Zygomatic processes, however, are found on other bones that extend into the zygoma. There are three zygomatic processes: Zygomatic process of the frontal bone. Zygomatic process of the temporal bone. Zygomatic process of the maxilla bone (or malar process of the maxilla bone) Zygomatic process of the maxilla bone.
What is the hole in the zygomatic bone?
Moreover, it contains tiny holes, also known as foramina, which allow for the passage of important neurovascular structures. The zygomaticotemporal and zygomaticofacial arteries, as well as nerves, pass through the foramina found in the zygomatic bone. These supply sensory innervation to the anterior part of the temple and the cheeks.
What causes zygomatic fractures?
The most common cause of zygomatic fractures is violent altercation. This is then followed by motor vehicle accident (MVA). These fractures can also occur during falls or activities such as cycling or skiing. Fractures in the zygomatic bone can extend through suture lines, namely, the zygomaticofrontal, zygomaticotemporal and zygomaticomaxillary.
What is the second most common fracture of the face?
Zygomatic Fractures. Following fractures of the nasal bone, zygomatic fractures are the second most common fractures of the face and predominantly occur in males during their twenties and thirties. The zygomatic bone, in particular the malar eminence, plays an important part in the appearance of our faces. It is a component of the lateral wall and ...
Why is my cheek bone flattened?
The cheekbone of these patients may be flattened due to the malar eminence being depressed. There is a palpable ‘step defect’ along the infraorbital rim, lateral orbital region or the zygomaticomaxillary buttress. Furthermore, there is what may be referred to as the ‘flame sign’ that arises as a result of the tendon of the lateral canthal being depressed and disrupted. Patients may also report parasthesia in the areas that are supplied by the nerves that are affected by the injury.
What is the point of attachment for the tendons of the lateral canthi of the eyelids?
Also located on the zygomatic bone is the Whitnall tubercle, which is the point of attachment for the tendons of the lateral canthi of the eyelids and is essential for maintaining the contour of the lids. Image Credit: Fotoslaz / Shutterstock.
What is the end objective of a zygomatic fracture?
The end of objective in the treatment of a zygomatic fracture is to ensure normal or near normal functionality. This includes the restoration of normal somato-sensory and masticatory function, as well as the cosmetic features of the face. Surgical intervention is not always necessary. This is especially true for stable and non-displaced zygomatic fractures, which require simple observation during healing. Surgery, if necessary, is done ideally within three weeks of the injury and involves closed or open reduction, and fixation with plates and screws. The prognosis, in general, is good.
What force is required to fracture a zygomatic bone?
In order for a fracture to occur in the zygomatic bone, kinetic force is required. The severity of the injury is directly proportional to force of the impact. The zygomatic bone is quite sturdy as it serves as a buttress between the skull and the maxilla.
What is the zygoma?
Zygoma are a pair of dense bones found on either side of the face, forming the prominence of the cheeks. These bones are located above the jaw bone, and are much sturdier, thus providing adequate support to implants.
When are zygomatic implants used?
This is mainly due to the presence of numerous nerves, blood vessels, and above all, the maxillary sinus on either side of the jaw.
How successful are zygomatic implants?
Many long-term studies have been carried out, and the majority of publications put the success rate of zygomatic implants at more than 95 percent over a 12 year study period.
What are the complications of zygomatic implants?
The most common complications of zygomatic implants are perforation of the sinus wall, infection of the sinus causing sinusitis, communication between the sinus and the oral cavity, and in some cases, paresthesia of the infraorbital nerve.
How long does it take for a zygomatic implant to be fixed?
Since zygomatic implants are fixed into the dense zygoma bone, they can be immediately loaded with a temporary prosthesis, followed by a fixed prosthesis after four to six months. This immediately restores function and aesthetics for the patient.
What is required prior to a zygomatic implant?
Precise treatment planning, 3D bone scans, and CBCT are must prior to a zygomatic implant procedure given the complexity of the procedure and because of the extensive bone drilling involved.
Why are zygomatic implants longer than conventional implants?
Zygomatic implants are much longer than conventional implants, because they are meant to be drilled to reach up to your cheekbone.
Which part of the jaw forms the upper jaw?
A. The maxilla forms the upper jaw.
What bone did Shannon have?
Shannon, a boxer, is informed after a fight that she has a broken ethmoid bone, and that due to its location she may have difficulty with which of these special senses?
