
Common Causes
The vertebral arteries divide into four segments based on where they are within the spinal column:
- V1 (pre-foraminal) arises from the subclavian artery. It runs behind the carotid artery, which is also in the neck.
- V2 (foraminal) travels alongside vertebral veins and nerves. ...
- V3 (extradural or extraspinal) curves and twists across the top of the C1 vertebra (the atlas) until it enters the skull.
- V4 (intradural or intracranial) enters the skull. ...
Related Conditions
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the face or body
- Trouble seeing from one eye
- Confusion
- Slurred or slow speech
- Difficulty using or understanding words
- Dizziness, and loss of balance or coordination
What artery is on the left side of the neck?
The carotid arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the head and brain. Located on each side of the neck, these arteries can easily be felt pulsating by placing your fingers gently on either side of your windpipe. The carotid arteries are essential as they supply blood to the large front part of the brain.
What are the symptoms of a neck artery blockage?
This is an invasive procedure and can be performed under local or general anaesthesia. It should be remembered that carotid artery surgery is not dangerous because it is always performed by a team of skilled surgeons and is aimed at improving the quality of life for patients suffering from carotid artery disease.
Where are your carotid arteries located?
Is carotid artery surgery dangerous?

What does carotid artery pain feel like?
Carotidynia is a pain that you feel in your neck or face. It is linked with physical changes that can happen in a carotid artery in your neck. Your neck may feel tender in the area of the artery. The pain often goes up the neck to the jaw, ear, or forehead.
Which side of the neck is the carotid artery on?
There are two carotid arteries, one on the right and one on the left. In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions: The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck.
What are the symptoms of a blocked artery in the neck?
Carotid Artery Blockage SymptomsBlurred vision or vision loss.Confusion.Memory loss.Numbness or weakness in part of your body or one side of your body.Problems with thinking, reasoning, memory and speech.
How do you check for blocked carotid arteries?
Carotid ultrasound (standard or Doppler). This noninvasive, painless screening test uses high-frequency sound waves to view the carotid arteries. It looks for plaques and blood clots and determines whether the arteries are narrowed or blocked. A Doppler ultrasound shows the movement of blood through the blood vessels.
Can you live with a blocked carotid artery?
In other words, most patients who have carotid stenosis without symptoms will not have a stroke and this risk can be further reduced by surgery. To benefit from surgery, asymptomatic patients should have a narrowing of more than 70% and a life expectancy of at least 3-5 years.
What vitamin removes plaque from arteries?
Niacin, or Vitamin B3, is the best agent known to raise blood levels of HDL, which helps remove cholesterol deposits from the artery walls.
How do you clear a blocked carotid artery without surgery?
Balloon angioplasty appears to be just as good as surgery to unblock carotid arteries. Date of last review, March 25, 2020Opening a blocked heart artery with a balloon and then propping it open with a wire-mesh stent is more commonly used than bypass surgery for restoring blood flow to the heart.
What is the treatment for a blockage in the carotid artery?
Carotid endarterectomy, the most common treatment for severe carotid artery disease. After making an incision along the front of your neck, the surgeon opens the affected carotid artery and removes the plaques. The artery is repaired with either stitches or a graft.
What is the survival rate for carotid artery surgery?
In the present study the 5-year survival was 78.2% and the 10-year survival was 45.5% for the asymptomatic cohort.
What does a blocked artery feel like?
The symptoms of an artery blockage include chest pain and tightness, and shortness of breath. Imagine driving through a tunnel. On Monday, you encounter a pile of rubble. There is a narrow gap, big enough to drive through.
Does aspirin reduce plaque in arteries?
Now, a team led by a University of Florida Health researcher has found that aspirin may provide little or no benefit for certain patients who have plaque buildup in their arteries. Aspirin is effective in treating strokes and heart attacks by reducing blood clots.
What is the best test for a carotid artery?
A carotid ultrasound is performed to test for narrowed carotid arteries, which increase the risk of stroke. Carotid arteries are usually narrowed by a buildup of plaque — made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium and other substances that circulate in the bloodstream.
Is the carotid artery on both sides of the neck?
The carotid arteries are a pair of blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head. Carotid artery disease occurs when fatty deposits (plaques) clog the blood vessels that deliver blood to your brain and head (carotid arteries).
How deep in the neck is the carotid artery?
4.2 cm to 7.5 cmBecause the depth of the carotid artery in a human neck varies significantly along the length of the neck (9), the corresponding SNR line plots from a single sagittal plane resulted in a depth ranging from 4.2 cm to 7.5 cm along an S/I length of 10 cm centered at the middle of the neck.
What percentage of carotid artery blockage requires surgery?
If a carotid artery is narrowed from 50% to 69%, you may need more aggressive treatment, especially if you have symptoms. Surgery is usually advised for carotid narrowing of more than 70%. Surgical treatment decreases the risk for stroke after symptoms such as TIA or minor stroke.
What causes a carotid artery to narrow?
A carotid artery may become so narrowed by atherosclerosis that not enough blood is able to reach portions of your brain. Ruptured plaques. A piece of a plaque may break off and flow to smaller arteries in your brain.
How to treat carotid artery disease?
Treatment of carotid artery disease usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication and sometimes surgery.
What causes a buildup of plaque in the arteries?
Causes. Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. Plaques are clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery. This process is called atherosclerosis.
How many strokes are caused by carotid artery disease?
Carotid artery disease causes about 10 to 20 percent of strokes. A stroke is a medical emergency that can leave you with permanent brain damage and muscle weakness. In severe cases, a stroke can be fatal. Carotid artery disease can lead to stroke through: Reduced blood flow.
What is the name of the blood vessel that delivers blood to the brain?
Carotid artery. Carotid artery. The carotid arteries are a pair of blood vessels located on both sides of your neck that deliver blood to your brain and head. Carotid artery disease occurs when fatty deposits (plaques) clog the blood vessels that deliver blood to your brain and head (carotid arteries).
What is the process of clogging the carotid arteries?
This process is called atherosclerosis. Carotid arteries that are clogged with plaques are stiff and narrow. Clogged carotid arteries have trouble delivering oxygen and nutrients to vital brain structures that are responsible for your day-to-day functioning.
What is the term for a stroke that occurs when a blood clot blocks or plugs an artery?
Ischemic stroke. Ischemic stroke. Ischemic stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks or plugs an artery leading to the brain. A blood clot often forms in arteries damaged by the buildup of plaques (atherosclerosis).
Which layer of the carotid artery is the smooth innermost layer?
Intima, the smooth innermost layer. Media, the muscular middle layer. Adventitia, the outer layer. The carotid sinus, or carotid bulb, is a widening of a carotid artery at its main branch point. The carotid sinus contains sensors that help regulate blood pressure.
What are the two divisions of the carotid artery?
In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions: The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. Like all arteries, the carotid arteries are made of three layers of tissue: Intima, the smooth innermost layer. Media, the muscular middle layer.
What is the procedure to open a narrowing carotid artery?
Carotid endarterectomy: A surgery to open a narrowing, or stenosis, caused by cholesterol plaque in the carotid artery. A vascular surgeon cuts open the carotid artery, removes the plaque, and sews the artery closed. Statins: Cholesterol-lowering medicines taken in pill form daily.
What causes a sudden blood clot in the carotid artery?
Stroke: A sudden blood clot in the carotid artery can interrupt blood flow to the brain, causing a stroke. Fragments of cholesterol plaque in the carotid artery may also travel into the brain to cause a stroke.
What is the cause of vasculitis in the carotid artery?
Carotid artery vasculitis: Inflammation of the carotid artery, due to an autoimmune condition or an infection.
What is the name of the blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, neck, and face?
All rights reserved. The carotid arteries are major blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, neck, and face. There are two carotid arteries, one on the right and one on the left. In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions: The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain.
How many layers are there in the carotid artery?
Like all arteries, the carotid arteries are made of three layers of tissue:
How many carotid arteries are there on each side of the neck?
On each side of the neck and head, there are three carotid arteries with a Y-shaped relationship.
Where is the inominate artery in the neck?
In one’s neck between the chest (arising from the aorta on the left, and the inominate artery to the right) and the head:
How to cut a carotid artery?
If your own, just cut from the outside, low down, and don’t go too deep. Oh, and do it standing up. Where you’d want to cut is below your mouth, so gravity will help keep you from choking. As long as you don’t get the trachea when you cut the carotid (stay lateral!), your airway will stay nice and clear while your blood volume drops. Once you faint from blood loss, though, you may lose those protective airway reflexes and aspirate some. Thus, I’d recommend wearing some kind of respirator just to be sure no blood gets in there once you’re unconscious.
What would happen if your left carotid artery was completely transected?
If your left carotid artery were completely transected and you were nowhere near a hospital, you would die pretty quickly. Here is a rough calculation. Your cardiac output is about 5L/min. Roughly 20% of that goes to your carotids, so 10% each. So your left carotid sees a flow of about 500mL/min. At that rate, you would have no blood left in 10 minutes. Obviously that flow would not stay constant as you continued to lose blood, but it’s a good starting point.
Which artery splits in two?
Then at the angle of the jaw, the common carotid artery splits in two. One branch, the external carotid artery, gives off smaller branches that supply the face and scalp. The other one, the internal caroti
Which arteries are felt by feeling for pulsations left and right of your airway?
Your own? Only the (common carotid) arteries by feeling for pulsations left and right of your airway.
Is the carotid artery unconsciously severed?
However, most importantly, assuming that the carotid artery is severed completely, an unconsci
What is the sound of carotid artery?
During a physical exam, your doctor will listen to the arteries in your neck with a stethoscope for a swishing sound called a bruit.
What causes carotid artery disease?
Carotid artery disease is typically caused by atherosclerosis, a disease in which plaque builds up in the arteries. A similar buildup occurs in the heart’s blood vessels when someone has coronary artery disease. Plaque contains clumps of:
What is the most common form of surgery for carotid artery disease?
Carotid endarterectomy is the most common form of surgery for severe carotid artery disease. After your anesthesiologist gives you local or general anesthesia, your doctor will make an incision on the front of your neck. They’ll open your carotid artery and remove any blockages.
What does it mean when your doctor puts your hands on your neck?
When your doctor puts their hands on your neck to detect a pulse, they’re feeling one of your carotid arteries. Carotid artery disease occurs when a blockage in one or both of these arteries decreases the amount of blood flow to your brain. This can lead to a stroke.
Can a stroke cause a narrowed carotid artery?
There are several ways that carotid artery disease can cause a stroke: Narrowed carotid arteries may not supply enough blood to the brain. A piece of plaque can break off and lodge in one of the smaller arteries of your brain, blocking blood flow. Blood clots can form in your carotid artery, blocking blood flow.
Can a carotid artery be caused by other diseases?
Carotid artery disease can also be the result of other diseases that cause arterial damage.
Does smoking cause a stiff heart?
Smoking can irritate the lining of your arteries. It can also increase your heart rate and blood pressure. Older age makes your arteries stiffer and more susceptible to damage. A family history of atherosclerosis is associated with increased risk of carotid artery disease.
Where is the incision for carotid artery blockage?
During the procedure, an incision is made in the neck at the site of the carotid artery blockage. The surgeon removes the plaque from the artery and when the plaque removal is complete, the surgeon stitches the vessel closed. Blood flow to the brain is restored through its normal path.
Why do we need to open the carotid artery?
If there is severe narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery, a procedure may be necessary to open the artery and increase blood flow to the brain, to prevent a future stroke.
What happens when plaque builds up in the carotid artery?
Plaque buildup can lead to narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery which, when significant, can put an individual at increased risk for stroke.
What is the best treatment for carotid stenosis?
Carotid endarterectomy is the traditional surgical treatment for carotid artery disease. Carotid endarterectomy has been proven to be beneficial for symptomatic patients with a 50 percent or greater carotid stenosis (blockage) and for asymptomatic patients with a 60 percent or greater carotid stenosis.
What causes a narrowing of the carotid artery?
Carotid artery disease, also called carotid artery stenosis, is the narrowing of the carotid arteries, usually caused by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of cholestero l, fat and other substances traveling through the bloodstream, such as inflammatory cells, cellular waste products, proteins and calcium. These substances stick to the blood vessel walls over time as people age, and combine to form a material called plaque.
How to prevent carotid artery disease?
Lifestyle changes. To prevent carotid artery disease from progressing, these lifestyle changes are recommended by your doctor and the National Stroke Association: Quit smoking and using tobacco products. Control high blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, and heart disease. Have regular checkups with your doctor.
Can a carotid artery be a sign of a stroke?
There may not be any symptoms of carotid artery disease. However, there are warning signs of a stroke. A transient ischemic attack (also called TIA or "mini-stroke") is one of the most important warning signs of a stroke. A TIA occurs when a blood clot briefly blocks an artery that supplies blood to the brain.
What is the name of the narrowing of the carotid arteries?
What Is Carotid Stenosis? Carotid stenosis, or carotid artery disease, is a narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries. Located in the side of your neck, your left and right carotids are two large arteries that carry oxygen-rich blood to your brain.
What happens when plaque deposits in the carotid artery increase?
As plaque deposits in the carotids increase in size, the opening of your carotid artery becomes narrower, and your risk for stroke increases. Plaque makes the inside surface of your carotids rough, and this roughness attracts platelets, the blood cells that help your blood clot. Sometimes small pieces of clot or plaque can break off, ...
What is the purpose of a CT scan for carotid stenosis?
A dye is injected into a vein in your arm, and the CT scan is used to take pictures of your carotids . The dye makes the area of stenosis visible and allows doctors to tell how severe the stenosis is.
What causes carotid stenosis?
A buildup of deposits of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances (collectively referred to as plaque) along the lining of the carotid artery is the most common cause of carotid stenosis. This buildup or hardening of the arteries is called atherosclerosis. As plaque deposits in the carotids increase in size, ...
What is the best treatment for carotid stenosis?
Mild carotid stenosis without severe symptoms can be treated with aspirin. Antiplatelet medications, such as aspirin and clopidogrel (Plavix), decrease the ability of platelets to form blood clots. Sometimes blood thinners, such as coumadin, are used to reduce stroke risk. Severe blockage can be treated surgically by removing the plaque.
What is the procedure called for a vascular surgeon to remove a stenosis of the carot?
A vascular surgeon who specializes in operating on blood vessels will perform this kind of surgery. The procedure is called carotid endarterectomy. Treatment for the underlying cause for carotid stenosis is essential. People with carotid stenosis who smoke should quit immediately.
Why is carotid stenosis dangerous?
Carotid stenosis is dangerous because it can decrease blood flow to your brain. If blood flow to your brain is interrupted, you can have a stroke. About 800,000 Americans. Trusted Source. have strokes every year.
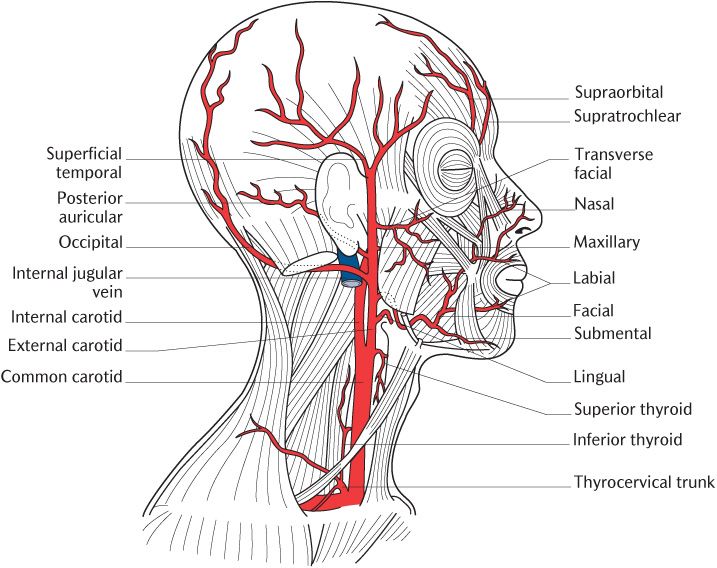
Where does the external carotid artery travel?
The external carotid artery supplies the areas of the head and neck external to the cranium. After arising from the common carotid artery, it travels up the neck, passing posteriorly to the mandibular neck and anteriorly to the lobule of the ear.
Where does the right common carotid artery originate?
We shall start at the origin of the carotid arteries. The right common carotid artery arises from a bifurcation of the brachiocephalic trunk (the right subclavian artery is the other branch). This bifurcation occurs roughly at the level of the right sternoclavicular joint.
What is the carotid sinus?
The carotid sinus is a dilated portion of the common carotid artery and proximal internal carotid artery. It contains baroreceptors: specialised sensory cells. The baroreceptors detect stretch as a measure of blood pressure. The glossopharyngeal nerve feeds this information to the brain, and this is used to regulate blood pressure.
How many branches does the parotid artery have?
The artery ends within the parotid gland by dividing into the superficial temporal artery and the maxillary artery. It gives rise to six branches in total:
What is the function of the carotid body?
These cells act as peripheral chemoreceptors; detecting the O2 content of the blood and relaying this information to the brain to regulate breathing rate.
Which artery supplies the deep structures of the face?
Posterior auricular artery. The facial, maxillary and superficial temporal arteries are the major branches of note. The maxillary artery supplies the deep structures of the face, while the facial and superficial temporal arteries generally supply superficial areas of the face.
What nerve is responsible for blood pressure?
The glossopharyngeal nerve feeds this information to the brain, and this is used to regulate blood pressure. In some individuals, the baroreceptors are hypersensitive to stretch. External pressure on the carotid sinus can cause slowing of the heart rate and a decrease in blood pressure.
Overview
A vascular murmur sound heard with a stethoscope over the carotid artery.
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- In its early stages, carotid artery disease often doesn't produce any signs or symptoms. The condition may go unnoticed until it's serious enough to deprive your brain of blood, causing a stroke or TIA. Signs and symptoms of a stroke or TIA include: 1. Sudden numbness or weaknessin the face or limbs, often on only one side of the body 2. Sudden trouble speakingand understandi…
Prevention
- Carotid artery disease is caused by a buildup of plaques in arteries that deliver blood to your brain. Plaques are clumps of cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue and other cellular debris that gather at microscopic injury sites within the artery. This process is called atherosclerosis. Carotid arteries that are clogged with plaques are stiff and narrow. Clogged carotid arteries have trouble deliveri…