Why do neurons generate an action potential?
When neurons transmit signals through the body, part of the transmission process involves an electrical impulse called an action potential. This process, which occurs during the firing of the neurons, allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon (a portion of the neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body) toward other cells.
What initiates the action potential in a nerve?
An action potential occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body. Neuroscientists use other words, such as a "spike" or an "impulse" for the action potential. The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity that is created by a depolarizing current.
Where in a neuron can an action potential be generated?
They found out that action potentials are typically initiated in the axon initial segment and the propagation of the action potential along the axon allows communication of output from one neuron to its distal synapses. Action potentials are the prime events in a neuron.
What part of the neuron can conduct an action potential?
Which part(s) of the neuron can conduct an action potential? dendrites and cell body cell body and axon dendrites and telodendria dendrites axon and telodendria

What is the resting potential of a neuron?
The resting potential of the neuron refers to the difference between the voltage inside and outside the neuron. The resting potential of the average neuron is around -70 millivolts, indicating that the inside of the cell is 70 millivolts less than the outside of the cell.
What do neurons do when they are firing?
Through this continual process of firing then recharging, the neurons are able to carry the message from the brain to tell the muscles what to do— hold the glass, take a sip, or put it down. Different Parts of a Neuron.
What is the basic building block of the nervous system?
A neuron (a nerve cell) is the basic building block of the nervous system. When neurons transmit signals through the body, part of the transmission process involves an electrical impulse called an action potential. This process, which occurs during the firing of the neurons, allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon ...
What happens when the brain sends a message to the muscles in your hand that you need to pick up the glass?
Your brain starts the chain of events to send a message to the muscles in your hand that you need to pick up the glass. When a nerve impulse (which is how neurons communicate with one another) is sent out from a cell body, the sodium channels in the cell membrane open and the positive sodium cells surge into the cell.
What is the process of sending electrical signals to the muscles?
This process, which occurs during the firing of the neurons, allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon (a portion of the neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body) toward other cells. This sends a message to the muscles to provoke a response.
How long does a neuron's refractory period last?
After the neuron has fired, there is a refractory period in which another action potential is not possible. The refractory period generally lasts one millisecond. During this time, the potassium channels reopen and the sodium channels close, gradually returning the neuron to its resting potential. Once the neuron has "recharged," it is possible ...
Which atoms have a positive charge?
Electrically charged atoms known as ions maintain the positive and negative charge balance. Calcium contains two positive charges, sodium and potassium contain one positive charge, and chloride contains a negative charge. When at rest, the cell membrane of the neuron allows certain ions to pass through while preventing or restricting other ions ...
Where is action potential initiated?
The action potential is initiated at the beginning of the axon, at what is called the initial segment.
What is action potential?
An action potential is a short lasting event in which electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory. This is a type of way that allows neuronal cells to communicate with each other and with other cells.
What is the difference between action potentials and membrane potentials?
Whereas membrane potentials (MPs) are small in their voltage and occur continuously in the background of a neuron, action potentials (APs) are large in voltage and appear only when a neuron is excited. Thus, the resting phase of a neuron is represented by MPs, whereas APs represent its excitation phase (i.e. when signals pass a neuron). Action potentials
What is the depolarizing phase of AP?
The depolarizing phase: All the sodium channels open simultaneously to allow an inward rush of Na+ into the cell, and the electrical charge inside of the neuron reaches to about +40 mV. This produces the ascending phase of AP.
What is an example of compound action potential?
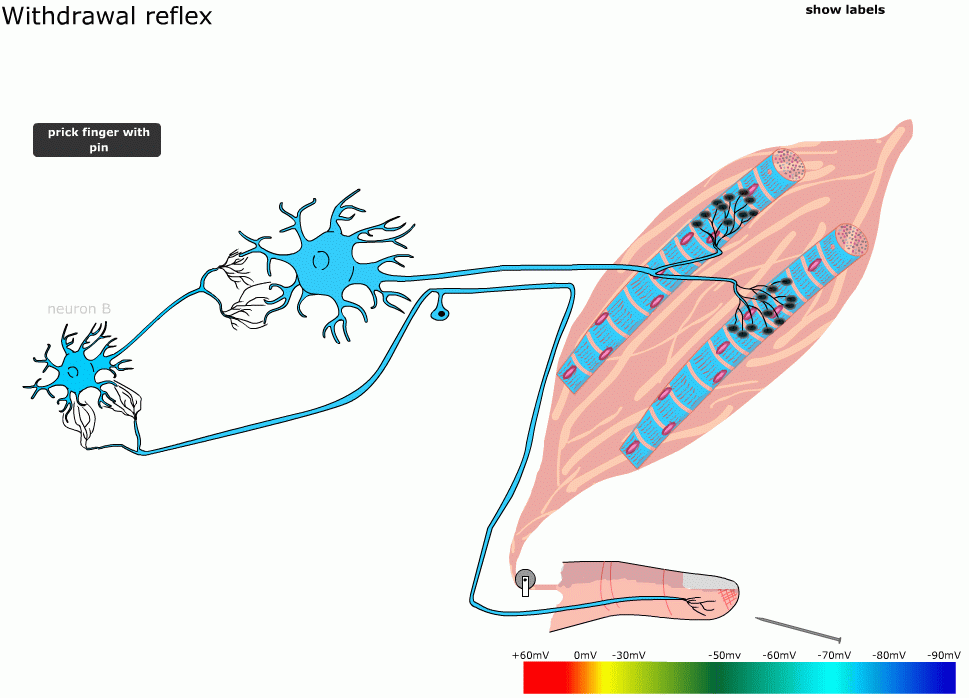
For compound action potential, a very familiar example is the simultaneous firing of muscle fibres excited by one motoneuron. A single motoneuron synapses with hundreds of muscle fibres in hand muscles. When the motoneuron discharges one action potential, it makes all its muscle fibres fire. When you record this activity from the muscle, you are recording superimposed action potential
Where does the trigger zone start?
It usually* begins at the junction between the axon and the neurosoma (cell body), a region called the axon hillock. The hillock and the initial segment of axon before the first Schwann cell (light blue in this figure) are called the trigger zone for this reason.
What happens at the end of an AP?
3. The hyperpolarization phase: At the end of an AP, most neurons show a transient hyperpolarization. This happens because of continued efflux of K+ ions making the inside charge even more negative. This produces the characteristic ‘undershoot’ of AP ( Fig 2.3 ).
What is the repolarization phase of action potential?
The repolarization phase of the action potential involves decreasing sodium influx via inactivation of sodium channels and increasing potassium efflux (exit) via opening potassium channels. Both of these processes begin near the peak of the action potential.
What causes rapid depolarization during action potential?
The influx of sodium ions causes the rapid depolarization during the action potential. The influx of sodium ions through open channels is favored by two factors. (1) The sodium concentration inside the neuron is only about 10% of the sodium concentration outside the neuron. (2) Most of the time, the interior of the cell is electrically negative, which is attractive for the positively charged sodium ions.
What happens when potassium ions flow out of the cell?
Positively charged potassium ions flowing out of the cell makes the transmembrane potential more negative, repolarizing the membrane towards the resting potential.
What happens when potassium exits the cell?
The exit of potassium from the cell causes the cell to become more negative, repolarizing the membrane. The exit of potassium ions through open channels is caused by the large concentration of potassium ions inside the neuron compared to the concentration of potassium ions outside the neuron (the chemical gradient for potassium). Even though the transmembrane potential during most of the repolarization phase is negative, this small electrical gradient (tending to pull potassium ions inward) is not enough to change the overall outward direction of the potassium electrochemical gradient.
How do ions move through channels?
Ions move through channels according to their electrochemical gradient from one side of the membrane to the other. This movement is known as channel-mediated diffusion. The transport rate for channels, unlike that for the carrier proteins involved in facilitated diffusion, does not saturate when the electrochemical gradient for the diffusing ion is increased.
What is the threshold value for membrane potential?
The membrane potential must depolarize from the resting voltage of -70 mV to a threshold value of -55 mV.
When does the plasma membrane repolarize?
The plasma membrane was depolarized to a positive value at the peak of the first phase of the action potential. Thus, it must repolarize back to a negative value.
Which part of the axon can be depolarized?
very narrow unmyelinated spaces between Schwann cells. These nodes are the only part of the axon that can be depolarized
Why is Na+ attracted to the negatively charged interior of a cell?
because the Na+ concentration is much higher outside the cell than it is inside, and the Na+ ions are attracted to the negatively charged interior
What happens at the end of repolarization?
At the end of repolarization when it returns back to resting -70mv, the membranes polarity changes back to normal, which is
Why does the current outward current occur?
this is due to a brief increase in the membrane permeability to k+ that results in the current outward current because that's the direction
Where does action potential begin?
A typical action potential begins at the axon hillock with a sufficiently strong depolarization, e.g., a stimulus that increases Vm. This depolarization is often caused by the injection of extra sodium cations into the cell; these cations can come from a wide variety of sources, such as chemical synapses, sensory neurons or pacemaker potentials .
When an action potential arrives at the end of the pre-synaptic axon (top),?
When an action potential arrives at the end of the pre-synaptic axon (top), it causes the release of neurotransmitter molecules that open ion channels in the post-synaptic neuron (bottom). The combined excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials of such inputs can begin a new action potential in the post-synaptic neuron.
Why are neuronal axons covered with myelin?
In order to enable fast and efficient transduction of electrical signals in the nervous system, certain neuronal axons are covered with myelin sheaths. Myelin is a multilamellar membrane that enwraps the axon in segments separated by intervals known as nodes of Ranvier. It is produced by specialized cells: Schwann cells exclusively in the peripheral nervous system, and oligodendrocytes exclusively in the central nervous system. Myelin sheath reduces membrane capacitance and increases membrane resistance in the inter-node intervals, thus allowing a fast, saltatory movement of action potentials from node to node. Myelination is found mainly in vertebrates, but an analogous system has been discovered in a few invertebrates, such as some species of shrimp. Not all neurons in vertebrates are myelinated; for example, axons of the neurons comprising the autonomous nervous system are not, in general, myelinated.
How do neurons work?
In neurons, the types of ion channels in the membrane usually vary across different parts of the cell, giving the dendrites, axon, and cell body different electrical properties. As a result, some parts of the membrane of a neuron may be excitable (capable of generating action potentials), whereas others are not. Recent studies have shown that the most excitable part of a neuron is the part after the axon hillock (the point where the axon leaves the cell body), which is called the initial segment, but the axon and cell body are also excitable in most cases.
What happens when the K+ channels open?
Na + channels open at the beginning of the action potential, and Na + moves into the axon, causing depolarization. Repolarization occurs when the K + channels open and K + moves out of the axon, creating a change in polarity between the outside of the cell and the inside. The impulse travels down the axon in one direction only, ...
What happens when an action potential travels down an axon?
Action potential. As an action potential (nerve impulse) travels down an axon there is a change in polarity across the membrane of the axon. In response to a signal from another neuron, sodium- (Na +) and potassium- (K +) gated ion channels open and close as the membrane reaches its threshold potential.
Where does the impulse travel?
The impulse travels down the axon in one direction only , to the axon terminal where it signals other neurons. In physiology, an action potential ( AP) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: this depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize.
