
Primary and Secondary Ecological Succession Facts
- Primary succession is a series of community changes that occurs in an entirely new habitat and has never been colonized before. ...
- Secondary succession occurs in an area that is previously colonized but disturbed or damaged habitat. ...
- Succession will not move further than the climax community. ...
Full Answer
What are the steps of secondary succession?
what are the steps of secondary succession
- Growth exists.
- Existing growth is destroyed.
- Destruction stops. …
- The soil remains.
- Time goes by.
- Regrowth begins.
- Fast-growing plants and/or trees are dominant for a while.
- Slower growing plants and/or trees come back and begin growing.
What are facts about secondary succession?
The stages of secondary succession are similar to those of primary succession; however, primary succession always begins on a barren surface, whereas secondary succession begins in environments that already possess soil. In addition, through a process called old-field succession, farmland that has been abandoned may undergo secondary succession.
Where is primary succession most likely to occur?
Where has primary succession occur?
- Volcanic eruptions.
- Retreat of glaciers.
- Flooding accompanied by severe soil erosion.
- Landslides.
- Nuclear explosions.
- Oil spills.
- Abandonment of a manmade structure, such as a paved parking lot.
Which of these is the final result of secondary succession?
What is the end result of secondary succession? When a natural disturbance or a human activity destroys an ecosystem, the existing community will undergo a secondary succession. In this succession, the remaining life-forms will restore the community. The end result is called a climax community. ….
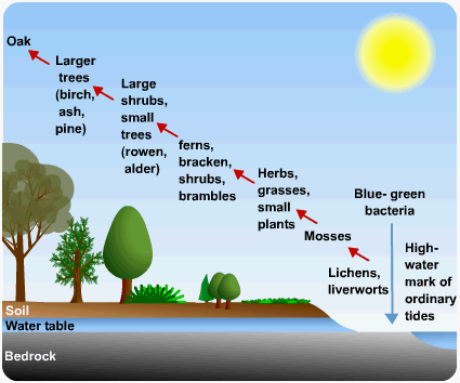
What are the factors that occur during secondary succession?
The factors that occur in secondary succession are tropical interaction, initial composition, and competition colonization trade-offs. The factors that prevent an increase in an abundance of species during succession may be identified mainly by microclimate, seed production and dispersal, bulk density, ph, soil textures (sand and clay, etc.)
Why is secondary succession faster than primary succession?
The secondary succession is usually faster than the primary succession because of the following reasons: The soil is already present. Seeds, roots, and underground vegetative organs may still exist in the soil.
What is Primary Succession?
Primary succession is defined as a change in vegetation that takes place on previously unvegetated terrain. A few examples where primary succession comes about include the formation of new islands, new volcanic rock, and on land formed from glacier retreats. The initial conditions in primary succession are often harsh, with little or no soil present. The site condition changes slowly in response to the vegetation as soil grows.
What are the initial conditions of primary succession?
The initial conditions in primary succession are often harsh, with little or no soil present. The site condition changes slowly in response to the vegetation as soil grows. The problem here is that primary succession occurs only on previously unvegetated terrain.
How long does ecological succession last?
The time duration of ecological succession can be decades (for example, after a wildfire) or even millions of years after the mass extinction. There are two types of ecological succession namely primary succession and secondary succession. 2.
What is ecological succession?
Ans. Ecological succession is the process of changing the structure of the species of an ecological community over time. These changes result in some species becoming more abundant while others may go into decline. The time duration of ecological succession can be decades (for example, after a wildfire) or even millions of years after the mass extinction. There are two types of ecological succession namely primary succession and secondary succession
What is the most renowned example of succession?
The most renowned example of succession deals with plant succession. It is worth remembering that as the plant community changes so will the associated microorganisms, fungus, and animal species. Succession includes the whole community rather than just the plant community.
What is secondary succession?
The ecosystem is now back to a similar state to where it began. Secondary succession is one of the two types ecological succession of a plant's life. As opposed to the first, primary succession, secondary succession is a process started by an event (e.g. forest fire, harvesting, hurricane, etc.) that reduces an already established ecosystem (e.g.
How does secondary succession affect soil?
The effects of secondary succession on soil are strongest in the A-horizon (0–10 cm), where an increase in carbon stock, N, and C/N ratio, and a decrease in bulk density and pH are observed. Soil carbon stocks also increase upon secondary succession from Imperata grassland to secondary forest.
How does fire affect secondary succession?
Generation of carbonates from burnt plant material following fire disturbance causes an initial increase in soil pH that can affect the rate of secondary succession, as well as what types of organisms will be able to thrive. Soil composition prior to fire disturbance also influences secondary succession, both in rate and type of dominant species growth. For example, high sand concentration was found to increase the chances of primary Pteridium over Imperata growth in Imperata grassland. The byproducts of combustion have been shown to affect secondary succession by soil microorganisms. For example, certain fungal species such as Trichoderma polysporum and Penicillium janthinellum have a significantly decreased success rate in spore germination within fire-affected areas, reducing their ability to recolonize.
What is the effect of soil composition on secondary succession?
Soil composition prior to fire disturbance also influences secondary succession, both in rate and type of dominant species growth. For example, high sand concentration was found to increase the chances of primary Pteridium over Imperata growth in Imperata grassland.
What factors control the increase in abundance of a species during succession?
The factors that control the increase in abundance of a species during succession may be determined mainly by seed production and dispersal, micro climate; landscape structure (habitat patch size and distance to outside seed sources); bulk density, pH, and soil texture (sand and clay).
What is secondary succession?
One of the two main forms of ecological succession, secondary succession is the process relating to community growth or change that takes place when a habitat is disturbed or damaged.
Why is secondary succession faster than primary succession?
Secondary succession is usually faster than primary succession because soil and nutrients are already present due to ‘normalization’ by previous pioneer species, and because roots, seeds and other biotic organisms may still be present within the substrate.
What happens to vegetation after abandonment?
The abandonment of such land allows plants and animals that were previously unable to inhabit the area to colonize. Early succession of vegetation following the abandonment of farmland is responsible for increases in soil organic content, nutrient density and soil porosity.
Why is fire important in secondary succession?
Fire. Fire is one of the most common causes of secondary succession and is an important component for the renewal and vitality of many types of ecosystem. Fires may either take place naturally, for example when lightning strikes a dry habitat, or may involve controlled, systematic burning of a landscape by humans.
Is secondary succession a large or small scale event?
Although secondary succession can happen on a large scale and have an intense effect on a habitat or ecosystem, it is most common on a small scale. The disturbance and subsequent secondary succession that occurs after a gap is created in a forest canopy, following the death and collapse of a single tree or the loss of a large branch, ...
Does secondary succession affect rainfall?
3. Secondary succession does not directly affect: A. Rainfall. B. Species diversity. C. Soil nutrients. D. Soil moisture content. Answer to Question #3. A is correct. Secondary succession does not directly affect the amount of rain that falls in an area; however, it can affect the moisture retention properties of the soil.
What is secondary succession?
Secondary succession occurs when the severity of disturbance is insufficient to remove all the existing vegetation and soil from a site. Many different kinds of disturbances, such as fire, flooding, windstorms, and human activities (e.g., logging of forests) can initiate secondary succession. Pioneers of secondary successions face quite different conditions from those that accompany primary succession. Secondary successions often start with resource-rich conditions associated with high light availability and reduced competition for nutrients and moisture. Disturbances may also be short-lived; for example, gaps created in forest canopies close as the crowns of surrounding trees expand and as seedlings and saplings in the understory grow up in response to increased light. Pioneers rely on recruitment from propagules present in the soil, or that disperse into the site after disturbance occurs. Pioneers are able to outcompete established vegetation that survived the disturbance by maintaining high juvenile growth rates. Some of the fastest growing trees are pioneers in tropical rain forests. Individuals of the balsa tree Ochroma pyramidale, for example, can grow from seedlings to adults with >30 cm trunk diameter in <10 years.
How is succession used?
Succession has been used in so many different ways and situations that it is almost useless as a precise idea. However, no matter whether succession has been considered a population ( Peet and Christensen, 1980 ), community ( Cooper, 1923a,b; Clements, 1916 ), or ecosystem ( Odum, 1969) phenomenon or process, it has contained certain common ideas. Succession is an orderly unidirectional process of community change in which communities replace each other sequentially until a stable (self-reproducing) community is reached (see definitions in Abercrombie et al., 1973; Small and Witherick, 1986; Allaby, 1994 ). The explanation of why and how succession is directed has changed over its more than hundred-year history, but most arguments share the notion that species are adapted to different stages in succession and in some way make the environment unsuited for themselves and more suited for the species in the next stage. This group selection argument was first instilled into succession in the Lamarckian ideas of Warming, Cowles, and Clements.
How does mycorrhizal colonization affect the successional process?
(1979) who proposed that plants characteristic of a particular stage of succession may have a higher ‘affinity’, through their fungal associates, for nutrients at a particular stage. However, few ecologists have considered mycorrhizas as possibly playing a pivotal role in the successional dynamics. The hypothesis that mycorrhizal colonization might provide hosts with a greater competitive ability and that this leads to acceleration of successional processes was tested by Allen and Allen (1988), who introduced inoculum of AM fungi to a high-altitude soil which had been disturbed by open-cast coal mining and was colonized largely by annual ‘non-host’ species. The presence of inoculum had the effect of reducing the growth of the ruderals and so, in some plots, led to increases in rates of succession. However, in others, loss of cover provided by the ruderals led to exposure-damage to those species, mostly grasses, that had the potential to respond to colonization. Consequently, the rate of succession declined ( Allen, 1989 ). Experiments of this kind demonstrate the complexity of interacting factors that can influence the successional process and emphasize that above ground, as well as below ground, factors can affect plant response (see Chapter 16 ).
What is the response of an ecosystem to changing N status?
A response seen in some ecosystems to changing N status is the appearance, as transient occupants, of N-fixing shrubs and trees ( van Cleve and Viereck, 1981 ). In the succession from grassland to boreal or temperate forest, other trees that appear early are members of the genera Salix and Populus which, in addition to having light-weight propagules that enhance their capacity for dispersal into successional environments, are characterized by a plasticity which enables them to form both VA and ectomycorrhizas. Compatibility with VA mycorrhizal fungi may be a factor facilitating their incorporation into a turf dominated by VA mycorrhizal grasses or herbs, while associations with ectomycorrhizal fungi would be advantageous in the situation where a progressively greater proportion of the soil N is present in organic form.
What are the processes of tree death and regeneration?
The processes of tree death and regeneration described above are intrinsic to all natural forest communities. They provide examples of internal secondary successions that arise because of the uneven-aged structure of most natural forest communities. The heterogeneous nature of forest composition and history creates a mosaic of patches at different stages in the forest growth cycle. Experienced foresters and ecologists have attempted to map the distribution of patches at different stages using species composition and forest structure as indicators of patch status, although these efforts are inherently limited by the low degree of spatial coverage relative to inherent spatial heterogeneity. However, in one well-replicated study of a semideciduous forest in Panama, approximately 0.1% of the ground surface area was covered by canopy gaps (defined as contiguous areas of at least 25 m 2 in which the height of the canopy is <5 m).
What are the stages of secondary succession?
Secondary succession is new growth, but it is not initial growth. Before secondary succession can occur, there has to have been previous growth in the same area. The stages that lead to secondary succession include: 1 Growth exists. 2 Existing growth is destroyed. 3 Destruction stops. (For example, the fire goes out or is put out, the hurricane ends or the pest overpopulation problem is solved.) 4 The soil remains. 5 Time goes by. 6 Regrowth begins. 7 Fast-growing plants and/or trees are dominant for a while. 8 Slower growing plants and/or trees come back and begin growing. 9 Eventually, the area is fully populated with plant life again, though it may be more diverse or otherwise different than it was prior to being destroyed.
Why is secondary succession more rapid than primary succession?
Secondary succession is a much more rapid process than primary succession because the soil and nutrients are already available. Because life previously existed in the soil, regrowth can occur without the need for new seeds or soil. The renewal of a forest after a fire: The fire itself destroys a majority of different types of trees and plant life.
What happens to a plant population after a disease?
Renewal after plant diseases: A plant population can be very negatively affected by a variety of infectious plant diseases. If the entire population dies, but the soil and roots remain, it is possible for secondary succession to occur and for the population of those plants to return.
How does a forest return to its original state?
A forest renews after logging: A large number of trees were chopped down by loggers in order to create building materials. Over time, trees grow in the area that was deforested. Eventually, the area returns to being similar to its previous state.
Does secondary succession increase tree diversity?
Scientists have found that secondary succession can lead to an increase in tree diversity. Plant and vegetation regrowth after a fire: On the island of Lawahii, several centuries ago, a fire erupted that caused the destruction of all plants and vegetation. Many years later, the plants and vegetation had grown back in, as the nutrients, ...
What is Secondary Succession?
Ecological succession refers to changes that occur in an ecosystem over time.
Why is secondary succession called secondary succession?
Secondary succession is called secondary because it comes after primary succession. Primary succession occurs when an ecological community first enters the barren habitat. Secondary succession occurs after the initial community is established and has become disturbed in some way.
How does primary succession happen?
Primary succession occurs when this area first becomes colonized with living plants or organisms. Plants will come first and, as that population grows, animals will flock to that area as well and make it their home. This process is very time-consuming and it can take decades or even millions of years for primary succession to complete. An example of primary succession could be the colonization of a barren area following a severe landslide or a recently exposed land from retreating glaciers.
How long does it take for primary succession to occur?
This process is very time-consuming and it can take decades or even millions of years for primary succession to complete. An example of primary succession could be the colonization of a barren area following a severe landslide or a recently exposed land from retreating glaciers.
How many stages are there in succession?
Basically, there are really three main stages. These stages are basically the same for primary and secondary succession with the only difference being that primary succession has no preexisting forms of life. The stages are:
What are the two types of ecological succession?
There are two types of ecological succession: Primary ecological succession, and. Secondary ecological succession. Primary succession is the succession that occurs in areas that have no living things such as areas without soil or areas where the soil cannot really sustain living things.
What is an example of an event that can cause secondary succession?
A flood is an example of an event that can cause secondary succession.
