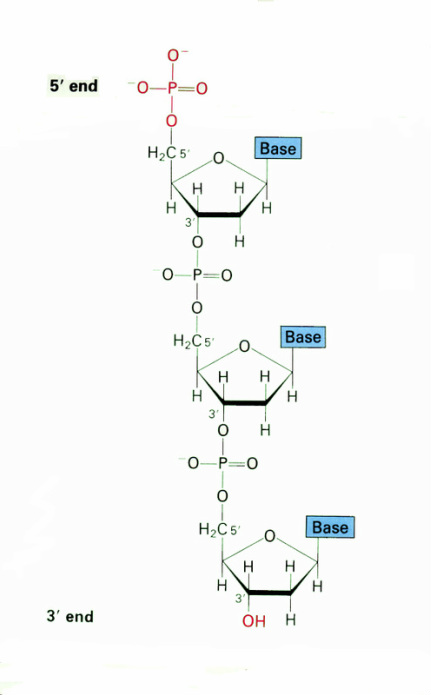
Which are the basic units of a DNA nucleotide? The basic repeating unit of nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of three distinct chemical groups, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose
Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, or more precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H₃−H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom. Since the pentose sugars arabinose and ribose only differ by the stereoche…
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached. The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrog…
What is nucleotide and what three units make it up?
They are:
- Nitrogenous bases – Purine and Pyrimidine
- Pentose Sugar – Ribose and Deoxyribose
- Phosphate – monophosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate
What are the three components that make up a nucleotide?
- nucleotide. consists of three parts: a five carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- deoxyribose. the five carbon sugar in a DNA nucleotide.
- what does the phosphate group consist of?
- nitrogenous base.
- purines.
- pyrimidines.
- base-pairing rules.
- complementary base pairs.
What are three subunits that make up a nucleotide?
what are the subunits of dna and their function
- Structure of DNA polymerase III enzyme I Subunits of DNA polymerase III and their functions. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. ...
- (OLD VIDEO) DNA Structure and Function. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. ...
- The Structure of DNA. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. ...
What three things that make up nucleotides?
Nucleotides each have three parts: phosphate, sugar molecule, and one of four bases. The bases include: A, (adenine), g (guanine), t (thymine), c (cytosine). The phosphate and sugar molecule bonds form the backbone or hand rail of the DNA (staircase), but the genetic key is in the steps (of the stairs): the bases.
What is the basic unit of DNA?
What is the basic repeating unit of nucleic acids?
What is the basic building block of DNA?
What are the 5 carbon sugars found in DNA?
What is the backbone of DNA?
What is DNA made of?
Why is DNA important?
See more
Which are the basic units of a DNA nucleotide quizlet?
The basic structural unit of DNA is called a nucleotide, which is composed of a deoxyribose sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The nucleotides link together in a series spiraling clockwise around a central axis forming a twisted ladder called a double helix.
What are 3 basic units for DNA?
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (Figure 9.3). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Which are the basic units parts of a DNA nucleotide?
Nucleotide A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
What is the basic molecular unit of DNA?
nucleotidesEach strand of DNA is a polynucleotide composed of units called nucleotides. A nucleotide has three components: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
Each nucleotide, in turn, is made up of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate.
What nucleotides make up a nucleotide?
Listen to pronunciation. (NOO-klee-oh-tide) A molecule consisting of a nitrogen-containing base (adenine, guanine, thymine, or cytosine in DNA; adenine, guanine, uracil, or cytosine in RNA), a phosphate group, and a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA; ribose in RNA).
What are the bases in DNA?
There are four nucleotides, or bases, in DNA: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases form specific pairs (A with T, and G with C).
Which is not a nucleotide base in DNA?
So, the correct option is 'Uracil'.
What is the basic unit of DNA and how are these units arranged?
DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs. Each base is also attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule. Together, a base, sugar, and phosphate are called a nucleotide. Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix.
How many nucleotides are in DNA?
DNA molecules are composed of four nucleotides, and these nucleotides are linked together much like the words in a sentence. Together, all of the DNA "sentences" within a cell contain the instructions for building the proteins and other molecules that the cell needs to carry out its daily work.
What is a DNA molecule made of?
A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain, or a DNA strand. Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together (Figure 4-3).
Answer
The basic repeating unit of nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of three distinct chemical groups, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a nitrogen-rich base - (cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), thymine (T) in DNA or uracil (U) instead of T (in RNA), and phosphate.
Answer
Nucleotides are the subunits of DNA. The four nucleotides are adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. Each of the four bases has three components, a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar and a nitrogen-containing base. The nitrogenous base attached to the bases may be a double-ringed purine or a single-ringed pyrimidine.
How many nucleotides are in DNA?
There's an A, C, G, and T in DNA, and in RNA there's the same three nucleotides as DNA, and then the T is replaced with a uracil. The nucleotide is the basic building block of these molecules, and is essentially are assembled by the cell one at a time and then strung together by the process of either replication, in the form of DNA, ...
What is the building block of nucleic acids?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids. RNA and DNA are polymers made of long chains of nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base.
How many units are in a nucleotide?
A nucleotide consists of three units, which are covalently linked. They are:
What are the names of the nucleotides?
Nucleotides are named as Adenylic acid, Guanylic acid, Thymidylic acid, Cytidylic acid and Uridylic acid. Nucleotides are also named as nucleoside mono, di or triphosphate, based on the number of phosphate groups attached to it, e.g. Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ...
What is a NAD?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD): NAD is a dinucleotide. It contains two nucleotides joined by phosphate groups. One of the nucleotides contains adenine base and the other nucleotide has nicotinamide. They play an important role in metabolic processes and act as an electron carrier.
What is the energy currency of the cell?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP): ATP is the energy currency of the cell. The energy required for metabolic processes is derived from ATP. It also acts as a coenzyme and is a precursor of DNA and RNA synthesis.
What is a nucleotide?
What is Nucleotide? A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases.
Which nucleotide has a phosphate group?
Nucleotides at least contain one phosphate group. Phosphate of one nucleotide attaches to the 3 rd C-OH group of the sugar of the 2 nd nucleotide, thereby forming 5’ → 3’ linkage.
What are the building blocks of DNA and RNA?
Nucleotides are the building block of DNA and RNA. They contain genetic information
What are the three basic units of DNA?
Each nucleotide consists of three portions: a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base . DNA uses four nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine.... [internet,google) , தமிழன் ! The basic unit used to make a strand of DNA is called a nucleotide.
What are the two nucleotides that make up DNA?
Together, these nucleotides make up the DNA (and RNA) nucleobases: thymine (in RNA: uracil) and cytosine are pyrimidines, a denine and guanine are purines.
What is the genetic material of most living organisms?
DNA or Deoxyribonucleic acid is the genetic material for most living organisms including human. Nitogen bases Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine pair up with ribose sugar to form nucleosides which in turn add up a Phosphate group to become nucleotides. These nucleotides are considered as monomers for DNA. 3K views.
Why is DNA called nucleic acid?
DNA or RNA are called nucleic acids because of the acidic nature of the phosphate group attached to them. The phosphodiester bond can easily lose the proton in the presence of nucleophile group subsequently masking the basic nature of nitrogenous bases. Figure 1. Phosphoric acid, Figure 2. short DNA strand.
How does DNA work in nature?
In a DNA molecule, the two strands are not parallel, but intertwined with each other. Each strand looks like a helix. The two strands form a " double helix " structure, which was first discovered by James Watson and Crick in 1953. In this structure, also known as the B form, the helix makes a turn every 3.4 nm, and the distance between two neighbouring base pairs is 0.34 nm. Hence, there are about 10 pairs per turn. The intertwined strands make two grooves of different widths, referred to as the major groove and the minor groove, which may facilitate binding with specific proteins.
Which protein has the information of amino acids?
Thus, it is said that DNA has the “information” of the amino acid sequences in proteins. As Emily Czinege pointed out, there are other levels of information. RNA. DNA also contains the sequences of nucleotides that become the ribosomal RNA and the transfer RNA.
How many chromosomes are there in a human body?
You have 46 chromosomes (23 from mom and 23 from dad). Each chromosome is basically a strand of DNA wrapped around small proteins called histones (imagine a beaded string of pearls). Collectively we call this unit a chromatid. Right before cell division these chromatids that contain your DNA get
What is the basic unit of DNA?
The basic unit used to make a strand of DNA is called a nucleotide. A single basic unit or "building block" of DNA consists of a sugar , a phosphate group and a base. Sugars are rings of carbon and oxygen atoms.
What is the basic repeating unit of nucleic acids?
The basic repeating unit of nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. A nucleotide consists of three distinct chemical groups, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a nitrogen-rich base - (cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), thymine (T) in DNA or uracil (U) instead of T (in RNA), and phosphate.
What is the basic building block of DNA?
Nucleotide Structure. The basic building block of DNA is the nucleotide. The nucleotide in DNA consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), one of four bases (cytosine (C), thymine (T), adenine (A), guanine (G)), and a phosphate. Cytosine and thymine are pyrimidine bases, while adenine and guanine are purine bases.
What are the 5 carbon sugars found in DNA?
Ribose and Deoxyribose. The 5-carbon sugars ribose and deoxyribose are important components of nucleotides, and are found in RNA and DNA, respectively. The sugars found in nucleic acids are pentose sugars; a pentose sugar has five carbon atoms. A combination of a base and a sugar is called a nucleoside.
What is the backbone of DNA?
The sugar-phosphate backbone forms the structural framework of nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA. This backbone is composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups, and defines directionality of the molecule.
What is DNA made of?
DNA is made up of the sugar-phosphate backbone. It consists of 5-carbon deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups. These sugars are linked together by a phosphodiester bond, between carbon 4 of their chain, and a CH2 group that is attached to a phosphate ion.
Why is DNA important?
DNA is vital for all living beings – even plants. It is important for inheritance, coding for proteins and the genetic instruction guide for life and its processes. DNA holds the instructions for an organism's or each cell's development and reproduction and ultimately death.