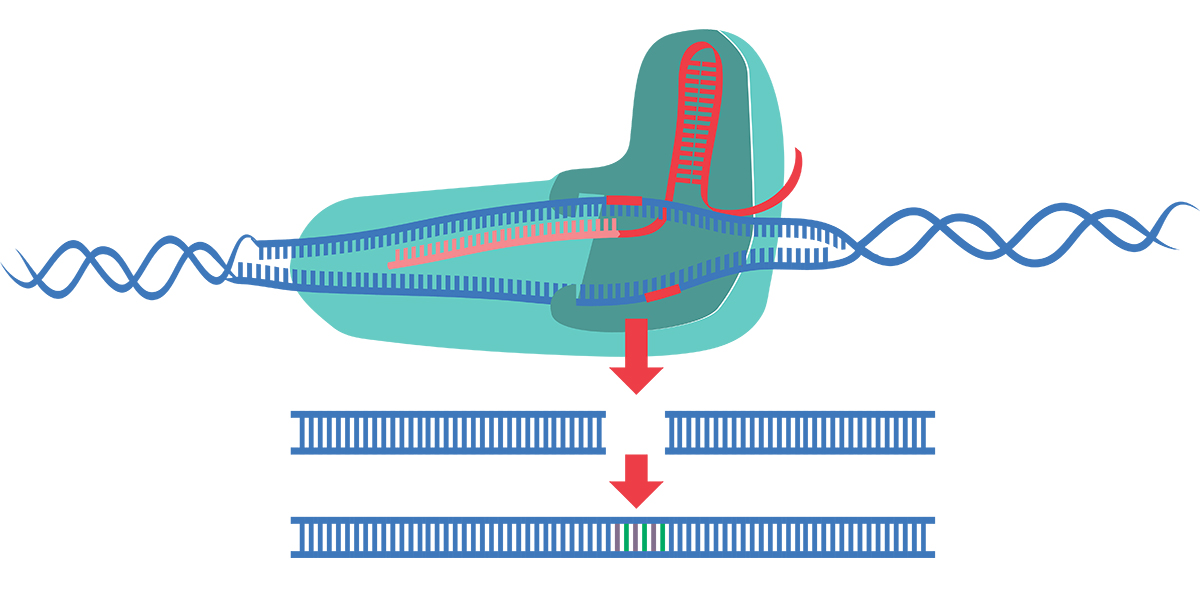
What is the enzyme critical to cutting and pasting DNA?
Restriction enzymes are a group of proteins that bacteria produce to cut up the DNA of invading viruses. Electron micrograph of Escherichia coli, close-up. Such bacteria are an important source for restriction enzymes. Credit: David Gregory and Debbie Marshall, Wellcome Images. Connections Herbert Boyer.
What is the enzyme for untwist the DNA?
DNA helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds down the center of the strand. It begins at a site called the origin of replication, and it creates a replication fork by separating the two sides of the parental DNA. ... What causes the double helix to untwist and separate during replication?
Which enzyme is used to digest DNA?
- DNA
- Restriction Enzyme (s)
- Buffer
- BSA (if recommended by manufacturer)
- dH 2 O up to total volume
What enzyme cuts DNA at specific nucleotide sequences?
Restriction enzymes are enzymes that cut DNA into fragments based upon recognizing a specific sequence of nucleotides. Restriction enzymes are also known as restriction endonucleases. Regina Bailey is a board-certified registered nurse, science writer and educator.

What enzymes dismantle DNA?
Restriction enzymes dismantle foreign DNA by cutting it into fragments. This disassembling process is called restriction.
What Is DNA Ligase?
The sticky ends of the fragments produced by restriction enzymes are useful in a laboratory setting. They can be used to join DNA fragments from both different sources and different organisms. The fragments are held together by hydrogen bonds. From a chemical perspective, hydrogen bonds are weak attractions and are not permanent. Using another type of enzyme however, the bonds can be made permanent.
What sequences do restriction enzymes recognize?
For example, a restriction enzyme may recognize a specific sequence of guanine, adenine, adenine, thymine, thymine, cytosine. When this sequence is present, the enzyme can make staggered cuts in the sugar-phosphate backbone in the sequence. But if restriction enzymes cut based on a certain sequence, how do cells like bacteria protect their own DNA ...
What happens when restriction enzyme cuts DNA?
Since the DNA is cut on both strands, there will be complementary ends that can hydrogen bond to one another. These ends are often called "sticky ends."
What is restriction enzyme?
Restriction enzymes are enzymes that cut DNA into fragments based upon recognizing a specific sequence of nucleotides. Restriction enzymes are also known as restriction endonucleases. Regina Bailey is a board-certified registered nurse, science writer and educator. Her work has been featured in "Kaplan AP Biology" and "The Internet for Cellular ...
Why are restriction enzymes important?
Restriction enzymes have been used to help produce vaccines, pharmaceutical products, insect resistant crops, and a host of other products.
Why are methyl groups added to DNA?
In a typical cell, methyl groups (CH 3) are added to the bases in the sequence to prevent recognition by the restriction enzymes. This process is carried out by complementary enzymes that recognize the same sequence of nucleotide bases as restriction enzymes. The methylation of DNA is known as modification. With the processes of modification and ...
What is the enzyme that seals the gap between two DNA molecules?
If two DNA molecules have matching ends, they can be joined by the enzyme DNA ligase. DNA ligase seals the gap between the molecules, forming a single piece of DNA. Restriction enzymes and DNA ligase are often used to insert genes and other pieces of DNA into plasmids during DNA cloning.
How is recombinant plasmid produced?
Right: recombinant plasmid produced when gene goes in backwards ("pointing" back towards the promoter that is already in the plasmid). Restriction digests and ligations like this one are performed using many copies of plasmid and gene DNA. In fact, billions of molecules of DNA are used in a single ligation!
Why are blunt-ended fragments harder to ligate together?
However, blunt-ended fragments are harder to ligate together (the ligation reaction is less efficient and more likely to fail) because there are no single-stranded overhangs to hold the DNA molecules in position.
How does DNA ligase work?
How does DNA ligase do this? Using ATP as an energy source, ligase catalyzes a reaction in which the phosphate group sticking off the 5’ end of one DNA strand is linked to the hydroxyl group sticking off the 3’ end of the other. This reaction produces an intact sugar-phosphate backbone.
Why do enzymes leave sticky ends?
Sticky ends are helpful in cloning because they hold two pieces of DNA together so they can be linked by DNA ligase. Not all restriction enzymes produce sticky ends.
What is the purpose of DNA ligase?
In DNA cloning, restriction enzymes and DNA ligase are used to insert genes and other pieces of DNA into plasmids.
How can we avoid the bad plasmids?
How can we avoid the "bad" plasmids? When we transform bacteria with DNA from a ligation, each one takes up a different piece of DNA. We can check the bacteria after transformation and use only the ones with the correct plasmid. In many cases, plasmid from transformed bacteria is analyzed using another restriction digest to see if it contains the right insert in the right orientation.