What enzymes break down fibrin in the body?
Some of the important Systemic enzymes include Fibrinolytic enzymes, Proteases, and Catalases. Among them, Serrapeptase and Nattokinase are the essential Fibrinolytic enzymes, which act to break down excess fibrin in the body.
What are fibrinolytic enzymes?
Among them, Serrapeptase and Nattokinase are the essential Fibrinolytic enzymes, which act to break down excess fibrin in the body. These enzymes fight inflammation, fibrosis (scar tissues), and viruses; modulate the immune system; and cleanse the blood.* Why are Fibrinolytic Enzymes so important?
What is the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin?
The conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is the final stage in blood clotting. Platelets, a type of cell found in blood, release the enzyme thrombin when they come into contact with damaged tissue, and the formation of fibrin then occurs.
How does fibrin form in a wound?
Platelets, a type of cell found in blood, release the enzyme thrombin when they come into contact with damaged tissue, and the formation of fibrin then occurs. Fibrin is essential for wound healing, as it lays down the framework for the new tissue to grow.

What are fibrin enzymes?
Fibrinolytic enzymes are involved in the degradation of fibrin clots, by either catalyzing fibrin degradation process or by transforming the inactive plasminogen into active plasmin, thus re-establishing the normal blood vascular architecture (Krishnamurthy et al., 2018).
Which enzyme destroy fibrin clots?
Fibrinolysis is the breakdown of a fibrin clot. Plasmin is the enzyme that breaks down fibrin. It is activated from inactive plasminogen by tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and urokinase.
How do you break up fibrin?
Look for enzyme supplements containing nattokinase and serrapeptase, two powerful enzymes that have been directly studied for their fibrinolytic properties. This powerful enzyme directly dissolves fibrin and may also improve the ability of your body to produce its own fibrinolytic enzymes.
Which enzyme converts fibrinogen to fibrin?
Fibrinogen is a soluble macromolecule, but forms an insoluble clot or gel on conversion to fibrin by the action of the serine protease thrombin, which is activated by a cascade of enzymatic reactions triggered by vessel wall injury, activated blood cells, or a foreign surface (Fig. 13.1).
What enzyme destroys fibrin clots quizlet?
The bacterial enzyme streptokinase is used to digest fibrin (blood clots) in patients with atherosclerosis.
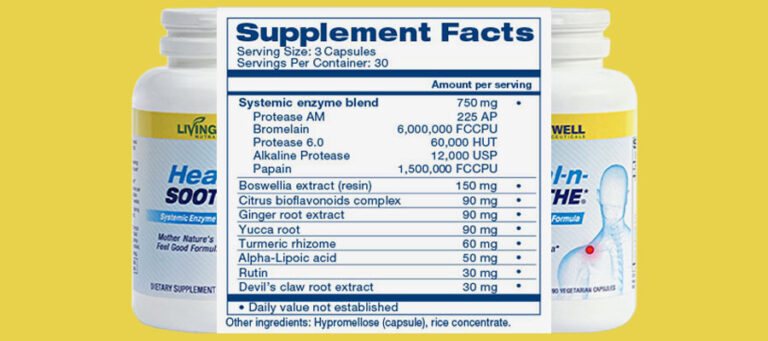
Does bromelain dissolve fibrin?
In vitro and in vivo studies have suggested that bromelain is an effective fibrinolytic agent as it stimulates the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, resulting in increased fibrinolysis by degrading fibrin [49, 50].
Can bromelain dissolve blood clots?
Bromelain is able to dissolve the clots because of its fibrinolytic properties.
How do you remove fibrin from blood?
Therefore, eating more fruits and vegetables, and avoiding sugary, processed, and fast foods can help lower fibrinogen levels [39, 40]. Diets rich in healthy fats and fiber can help decrease fibrinogen levels. Avoid sugary, processed, and fast foods.
What enzymes break down fibrin?
Among them, Serrapeptase and Nattokinase are the essential Fibrinolytic enzymes, which act to break down excess fibrin in the body. These enzymes fight inflammation, fibrosis (scar tissues), and viruses; modulate the immune system; and cleanse the blood.*.
What is the strongest fibrinolytic enzyme?
Serrapeptase is known as the strongest fibrinolytic enzyme. Our body system produces certain chemicals called prostaglandins in response to injury. A certain type of prostaglandin causes inflammation, leading to redness, swelling, constriction of blood vessels and decreased tissue permeability.*
What is Enzyme?
Enzymes are energized protein molecules found in all living cells which catalyze and regulate all biochemical reactions that occur within the human body. They break down proteins, fats, carbohydrates and fiber making it possible to benefit from the nutrients found in those foods while removing the toxins.
What is Fibrin?
Fibrin is an insoluble protein involved in blood clotting. It is deposited around the wound in the form of a mesh, when an injury occurs. It becomes dry and hard which leads to stop bleeding.
What is the difference between digestive enzymes and systemic enzymes?
Enzymes are mainly categorized as Digestive Enzymes and Systemic Enzymes.
Why are Fibrinolytic Enzymes so important?
Fibrinolytic enzymes are systemic enzymes that eat away the excess fibrin that forms scar tissue, adhesions, and growths.
What is the purpose of nattokinase?
Nattokinase may prove to be a defibrinogenating enzyme that drastically decreases blood viscosity. Decreasing blood viscosity strikes at the root of arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis as well as hypertension, peripheral vascular disease and congestive heart failure.* The fibrinolytic activity of Nattokinase resolves the active process of atherosclerosis and lyses thrombi.
How is fibrin formed?
Fibrin formation is regulated by the process of fibrinolysis, which involves the enzymatic degradation of fibrin and fibrinogen by plasmin (9 ). Plasmin is formed from plasminogen, a β-globulin synthesized by the liver ( 25 ). The biologic activity of plasmin, and hence fibrinolysis, is determined by activators and inactivators of plasminogen and plasmin inhibitors (see Fig. 35.1 ). Fibrinolysis is initiated by either factor XIIa or urokinase plasminogen activator (intrinsic pathway) or tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA), the extrinsic pathway ( 31 ). Tissue plasminogen activator, which is produced by the endothelial cells and released into the circulation, in the presence of fibrin binds together with plasminogen to generate plasmin, and thus fibrinolysis ( 17 ). Fibrin acts both as a substrate and a cofactor to plasminogen activity.
How is fibrinogen converted to fibrin?
Because fibrinogen to fibrin formation is catalyzed by thrombin, investigations have centered on the regulation of thrombin activity in diabetes and on an in vivo index of thrombin activity, fibrinopeptide A (FPA). 279 FPA is cleaved from the α-chain of fibrinogen by the action of thrombin. This forms the first step in the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. FPA levels tend to be elevated in diabetes, especially when control is poor or vascular problems exist. Furthermore, recent studies have indicated that elevated FPA levels might be seen in diabetic individuals before vascular complications are present. A relation between plasma and urinary FPA and hyperglycemia in diabetes has been reported.
How does antiplasmin inhibitor work?
It acts in two ways: direct inactivation of plasmin and blockage of plasminogen binding to fibrin.
What is the chain of reactions that leads to the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin?
First, the chain of reactions that leads to conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is restricted to a surface , such as platelet phospholipids. Second, a series of inhibitors constrains the reaction to the site of injury and platelet deposition. Historically the blood coagulation system is divided into two initiating pathways: the tissue factor ...
What is the mechanism of thrombin and fibrin?
Mechanisms of Thrombin and Fibrin Generation. The coagulation phase of hemostasis involves generation by thrombin of fibrin, which binds and stabilizes the weak platelet hemostatic plug. Thrombin is highly specific in cleaving fibrinogen at only two arginine sites.
What are the two pathways of blood coagulation?
Historically the blood coagulation system is divided into two initiating pathways: the tissue factor (extrinsic) pathway and the contact factor (intrinsic) pathway. These pathways meet in a final common pathway whereby factor Xa converts prothrombin to thrombin, which then cleaves fibrinogen to fibrin.
Where does plasminogen activator take place?
The activity of tissue-type plasminogen activator, released by endothelial cells, is increased by thrombin, and thus tissue plasminogen activation takes place in the fibrin clot. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is found in plasma as a proenzyme and is converted to a two-chain molecule upon activation.
