
How to open up your Eustachian tube naturally?
What to do:
- Pinching your nostrils together, open your mouth to take in a deep breath.
- Keep your mouth closed and your nostrils pinched while you attempt to blow the air out through your nose.
- If effective, you will hear a popping sound and the tubes will be open again.
How to clear a clogged Eustachian?
Tips for a clogged outer ear
- Mineral oil. Try dripping mineral, olive, or baby oil into your clogged ear. ...
- Hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide otic. Hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide otic can also be dripped into your ear. ...
- Over-the-counter ear drops. You can pick up ear drops online or at your local pharmacy. ...
- Ear irrigation. ...
- Warm compress or steam. ...
Does a human have an Eustachian tube?
In anatomy, the Eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part.In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately 35 mm (1.4 in) long and 3 mm (0.12 in) in diameter. It is named after the sixteenth-century Italian anatomist Bartolomeo Eustachi.
What are Eustachian tubes function?
Your Eustachian tubes have three primary functions. They: Drain excess fluids and secretions from your middle ear. Ventilate your middle ear and equalize air pressure on either side of the eardrum. Protect your middle ear from pathogens (microorganisms that cause disease).
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/6781/salpingopharyngeus.png)
Which causes opening of Eustachian tube?
Most of the time, your eustachian tubes stay closed. But when you yawn, chew or swallow, they open. The eustachian tube is named after Bartolomeo Eustachi, the Italian physician who discovered that the tube connected the middle ear to the nose and throat.
How do you open a blocked Eustachian tube?
You may be able to open the blocked tubes with a simple exercise. Close your mouth, hold your nose, and gently blow as if you are blowing your nose. Yawning and chewing gum also may help. You may hear or feel a "pop" when the tubes open to make the pressure equal between the inside and outside of your ears.
What muscle opens pharyngotympanic tube?
Tensor veli palatiniTensor veli palatini As it also takes some of its origin from the auditory tube, it is the main muscle which opens it upon contraction.
What is Eustachian tube innervated by?
Motor innervation to the muscle attachments of the Eustachian tube is provided by the pharyngeal plexus of the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) and the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V).
How does an ENT unclog ears?
The Valsalva maneuver can help relieve pressure that is blocking the Eustachian tube in the inner ear. During the maneuver, clogged ears can be unblocked by forcing air through the sinuses and Eustachian tube.
How do you remove fluid from the eustachian tube?
Blocked eustachian tubes often get better on their own. For adults, decongestants that you take by mouth or spray into your nose may be helpful. If you have allergies, the doctor may prescribe a steroid medicine that you spray into your nose.
Where is the opening of the eustachian tube located?
Where Is the Eustachian Tube? The eustachian tube is located in a part of the head and neck called the parapharyngeal space. It runs from the front wall of the middle ear to the side wall of the top part of the throat (nasopharynx ).
What muscle is responsible for middle ear function?
The tensor tympani muscle (TTM) (Fig. 1) resides in the middle ear. It arises from the cartilaginous part of the pharyngotympanic tube and inserts on the manubrium of the malleus [1]. It is innervated by the nerve to the tensor tympani, which originates from the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve.
How do you relieve eustachian tube pressure?
To relieve ear pain or discomfort, you can take steps to open the eustachian tube and relieve the pressure, such as:Chew gum.Inhale, and then gently exhale while holding the nostrils closed and the mouth shut.Suck on candy.Yawn.
How do you naturally open eustachian tubes?
Eustachian tube dysfunction treatment You can do exercises to open up the tubes. This includes swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum. You can help relieve the “full ear” feeling by taking a deep breath, pinching your nostrils closed, and “blowing” with your mouth shut.
How long does it take for eustachian tubes to unclog?
Eustachian tube dysfunction usually resolves in a few days to two weeks without treatment. You can take certain actions to open up the tubes, such as swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum.
Will a blocked eustachian tube clear itself?
Eustachian tube dysfunction is a condition where the tubes that connect your middle ears to your upper throat become blocked. This can lead to discomfort, hearing difficulties and a feeling of fullness in your ear. Eustachian tube dysfunction usually resolves itself in a few days.
How do you massage your ears to drain?
With firm, steady pressure slide your finger down until it slips into a groove between the ear lobe and the jaw. Follow that groove down the neck with your finger, sliding down (with same steady pressure) until you reach the collar bone. Repeat three to four times per side, about three times a day.
How many muscles are associated with the Eustachian tube?
There are four muscles associated with the function of the Eustachian tube:
Which structure is the Eustachian tube?
Upper respiratory system, showing entrance to auditory tube near middle. The Eustachian tube has recently been redefined as the fibrocartilaginous structure connecting the air cell system of the temporal bone to the nose. What was thought of as the bony tube is really part of the air cell system of the temporal bone.
What is the purpose of the Eustachian tube?
Active opening of the Eustachian tube (through actions like swallowing or the Valsalva maneuver) is required to equalize the pressure between the middle ear and the ambient atmosphere as the plane descends.
Why do Eustachian tubes open?
Under normal circumstances, the human Eustachian tube is closed, but it can open to let a small amount of air through to prevent damage by equalizing pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. Pressure differences cause temporary conductive hearing loss by decreased motion of the tympanic membrane and ossicles of the ear. Various methods of ear clearing such as yawning, swallowing, or chewing gum may be used to intentionally open the tube and equalize pressures. When this happens, humans hear a small popping sound, an event familiar to aircraft passengers, scuba divers, or drivers in mountainous regions. Devices assisting in pressure equalization include an ad hoc balloon applied to the nose, creating inflation by positive air pressure. Some people learn to voluntarily 'click' their ears, together or separately, performing a pressure equalizing routine by opening their Eustachian tubes when pressure changes are experienced, as in ascending/descending in aircraft, mountain driving, elevator lift/drops, etc. Some are even able to deliberately keep their Eustachian tubes open for a brief period, and even increase or decrease air pressure in the middle ear. The 'clicking' can actually be heard by putting one's ear to another's while performing the clicking sound. This voluntary control may be first discovered when yawning or swallowing, or by other means (above). Those who develop this ability may discover that it can be done deliberately without force even when there are no pressure issues involved.
What happens when the Eustachian tube collapses?
Normally, the Eustachian tube is collapsed, but it gapes open with swallowing and with positive pressure, allowing the middle ear's pressure to adjust to the atmospheric pressure. When taking off in an aircraft, the ambient air pressure goes from higher (on the ground) to lower (in the sky).
How big is the Eustachian tube?
In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately 35 mm (1.4 in) long and 3 mm (0.12 in) in diameter. It is named after the sixteenth-century Italian anatomist Bartolomeo ...
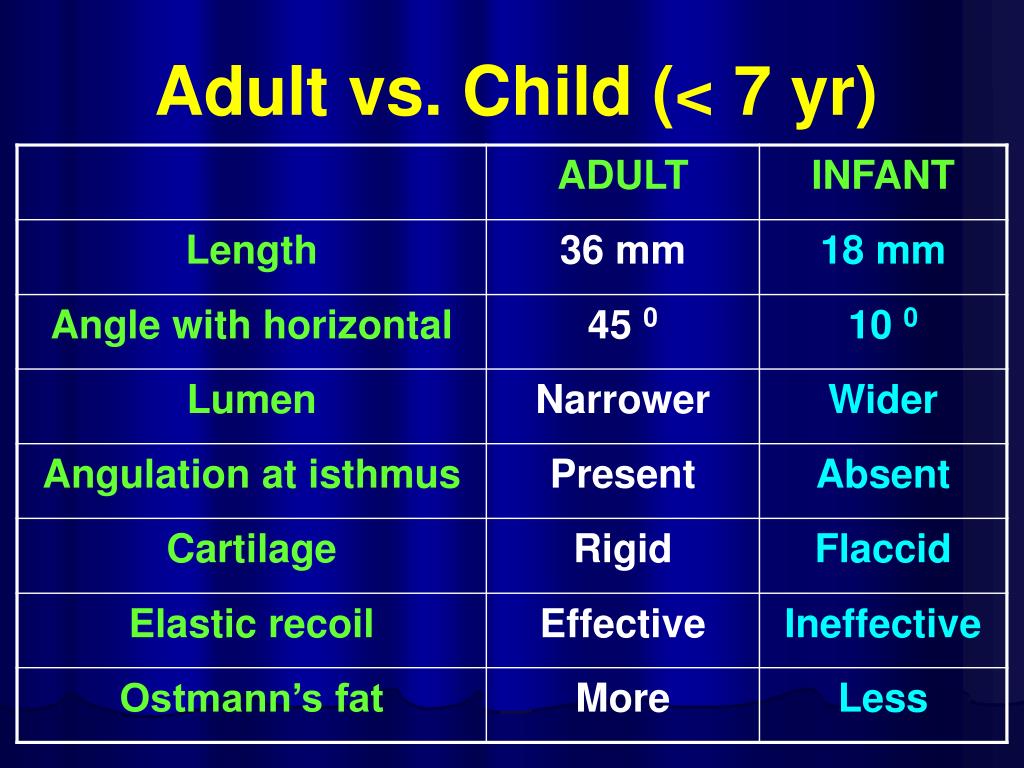
Why do children have ear infections?
This swelling can be reduced through the use of decongestants such as pseudoephedrine, oxymetazoline, and phenylephrine. Ear infections are more common in children because the tube is horizontal and shorter, making bacterial entry easier, and it also has a smaller diameter, making the movement of fluid more difficult. In addition, children's developing immune systems and poor hygiene habits make them more prone to upper respiratory infections.
What is the Eustachian tube?
The Eustachian tube is also known as the pharyngotympanic tube or the auditory tube.[1][2] The Eustachian tube is named after the Italian anatomist, Bartolomeo Eustachi, who observed that it was a canal that connected the nasopharynx to the middle ear.
Where is the Eustachian tube located?
The Eustachian tube is located in the para-pharyngeal space and is closely linked to the infratemporal fossa. The Eustachian tube continues from the front wall of the middle ear to the sidewall of the nasopharynx, progressing along the posterior edge of the medial pterygoid plate.
How does the Eustachian tube affect sound waves?
In doing so, the Eustachian tube allows for regulation of the pressure across the tympanic membrane. It thus influences the tension in this structure and the attached ossicles, and in this way indirectly affects the effectiveness of sound wa ve transmission.
How does the Valsalva maneuver help the Eustachian tube?
The Valsalva maneuver can help in opening the Eustachian tube by insufflating air inside of it.
What is the name of the tube that connects the nasopharynx to the middle ear?
The Eustachian tube is named after the Italian anatomist, Bartolomeo Eustachi, who observed that it was a canal that connected the nasopharynx to the middle ear. The Eustachian tube is also known as the pharyngotympanic tube or the auditory tube. [1][2] Structure and Function. The Eustachian tube plays a role in equalization, oxygenation, ...
Why does otitis media develop in children?
This is believed to be a contributing factor in the development of acute otitis media in children due to impaired middle ear drainage and even reflux of nasopharyngeal contents into the middle ear through the Eustachian tube. Mucus cannot drain as readily with the smaller slope.
Which cranial nerve innervates the levator veli palatini?
Specifically, the levator veli palatini and salpingopharyngeus muscles are innervated by cranial nerve X, and the tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini muscles are supplied by the mandibular branch of cranial nerve V. Sensory innervation to the Eustachian tube, middle ear, and the trigeminal nerve governs pharynx.
What is the Eustachian tube?
Overview. The Eustachian tube is an opening that connects the middle ear with the nasal-sinus cavity. This tube helps to: Balance pressure in the middle ear (commonly felt as your ears popping) Drain fluid from the middle ear. Protect the ear from both hearing sounds your body causes and nasal drainage. This tube contains a valve that opens and ...
What causes the eustachian tube to remain open?
Pa tulous Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction is a disorder of the valve of the Eustachian tube that causes it to remain open. When this valve remains open, sound can travel from the nasal-sinus cavity to the ears, allowing you to hear your own voice or your own breathing too loudly, or even the sound of blood pumping.
What is a obstructed eustachian tube?
Obstructive Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Obstructive dysfunction occurs when the valve of the Eustachian tube does not open properly. This prevents pressure from balancing and fluids from draining out of the ear.
What causes otitis media in the ear?
Eustachian tube disorders are common and one of the leading causes of ear infections (otitis media). Common Eustachian tube disorders include: Baro-challenge-induced Eustachian tube dysfunction (obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction when on airplanes or when SCUBA diving)
How to treat Eustachian tube dysfunction?
A common course of treatment for Eustachian tube dysfunction is the use of decongestants or antihistamines. In some cases, this treatment may make the condition worse. If decongestants or antihistamines do not provide relief, contact your doctor. You may need to see an ear, nose and throat specialist for treatment.
What is the Johns Hopkins Eustachian Tube Health Center?
The Johns Hopkins Eustachian Tube Health Center provides comprehensive evaluation, diagnosis and management of Eustachian tube dysfunction that include medical, multidisciplinary and surgical approaches.
When obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction is only felt during airplane flights or SCUBA diving,?
When obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction is only felt during airplane flights or SCUBA diving , this is known as baro-challenge-induced Eustachian tube dysfunction.
How often does the eustachian tube open?
In order to equalize pressure and drain any fluid inside the inner ear, your eustachian tube opens once or twice every hour.
What is a patulous eustachian tube?
Patulous eustachian tube (PET) occurs when the eustachian tube remains open (patulous). It is an uncommon condition affecting only around 1 of every 10,000 people. 1 The eustachian tubes, also called auditory tubes, run from the inner ear to the back of the throat. Typically, your eustachian tube is in a closed position, ...
What are some invasive treatments for eustachian tube narrowing?
Other more invasive therapies that are being studied, and are not available in all areas, include: Inserting a catheter inside the eustachian tube, injecting the eustachian tube, or musculature manipulation all allow for a narrowing of the eustachian tube.
What is the best treatment for patulous eustachian tube?
The most common treatment for a patulous eustachian tube is nasal sprays. Saline is the most common choice in the United States. While many inner ear conditions can benefit from nasal decongestants or steroids, the practice will likely worsen your symptoms of PET. If this occurs, treatment should be stopped.
When less invasive methods prove insufficient to resolve symptoms of a patulous eustachian tube?
When less invasive methods prove insufficient to resolve symptoms of a patulous eustachian tube, surgical treatments may be more effective .
Can you remove ear tubes?
Unfortunately, there is not enough evidence to predict which patients will respond positively to the surgical placement of ear tubes. However, ear tube placement is a fairly simple procedure with few side effects and the synthetic tubes can be removed if they do not provide relief for you.
Can you insert a catheter inside an eustachian tube?
Inserting a catheter inside the eustachian tube, injecting the eustachian tube, or musculature manipulation all allow for a narrowing of the eustachian tube. While this does not return the normal function of the tube, it reduces the amount of airflow into the middle ear, which helps to reduce the symptoms of autophony.
Overview
In anatomy, the Eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately 35 mm (1.4 in) long and 3 mm (0.12 in) in diameter. It is named after the sixteenth-century Italian anatomist Bartolomeo Eustachi.
In humans and other tetrapods, both the middle ear and the ear canal are normally filled with air. …
Structure
The Eustachian tube extends from the anterior wall of the middle ear to the lateral wall of the nasopharynx, approximately at the level of the inferior nasal concha. It consists of a bony part and a cartilaginous part.
The bony part (1⁄3) nearest to the middle ear is made of bone and is about 12 mm in length. It begins in the anterior wall of the tympanic cavity, below the septum canalis musculotubarius, and…
Development
The Eustachian tube is derived from the dorsal part of the first pharyngeal pouch and second endodermal pouch, which during embryogenesis forms the tubotympanic recess. The distal part of the tubotympanic sulcus gives rise to the tympanic cavity, while the proximal tubular structure becomes the Eustachian tube. It helps transformation of sound waves.
• Frontal section through left ear; upper half of section
Function
Under normal circumstances, the human Eustachian tube is closed, but it can open to let a small amount of air through to prevent damage by equalizing pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. Pressure differences cause temporary conductive hearing loss by decreased motion of the tympanic membrane and ossicles of the ear. Various methods of ear clearing such as yawning, swallowing, or chewing gum may be used to intentionally open the tube and equalize p…
Clinical significance
Otitis media, or inflammation of the middle ear, commonly affects the Eustachian tube. Children under 7 are more susceptible to this condition, one theory being that this is because the Eustachian tube is shorter and at more of a horizontal angle than in the adult ear. Others argue that susceptibility in this age group is related to immunological factors and not Eustachian tube anatomy.
Other animals
In the equids (horses) and some rodent-like species such as the desert hyrax, an evagination of the Eustachian tube is known as the guttural pouch and is divided into medial and lateral compartments by the stylohyoid bone of the hyoid apparatus. This is of great importance in equine medicine as the pouches are prone to infections, and, due to their intimate relationship to the cranial nerves (VII, IX, X, XI) and the internal and external carotid artery, various syndromes may …