What are the barriers to entry for a monopoly?
These barriers include: economies of scale that lead to natural monopoly; control of a physical resource; legal restrictions on competition; patent, trademark and copyright protection; and practices to intimidate the competition like predatory pricing.
Which of the following are common barriers to entry?
Common barriers to entry include special tax benefits to existing firms, patent protections, strong brand identity, customer loyalty, and high customer switching costs. Other barriers include the need for new companies to obtain licenses or regulatory clearance before operation.
What is the barrier to entry in a monopoly quizlet?
There are barriers to entry for monopoly markets. The government may grant a company the sole right to supply a good/service. Also the company may have patent which means only they can manufacture a particular product.
What are the 4 barriers to entry?
There are 4 main types of barriers to entry – legal (patents/licenses), technical (high start-up costs/monopoly/technical knowledge), strategic (predatory pricing/first mover), and brand loyalty.
Which of the following is not a barrier to entry for a monopoly?
Answer and Explanation: A large number of existing firms is not a barrier to entry into a monopoly market as there is only one seller. A monopoly market is characterized by a single seller, lack of substitutes, large economies of scale, high barriers to entry, and profit maximization.
What are the 7 examples of barriers to entry?
There are seven sources of barriers to entry:Economies of scale. ... Product differentiation. ... Capital requirements. ... Switching costs. ... Access to distribution channels. ... Cost disadvantages independent of scale. ... Government policy. ... Read next: Industry competition and threat of substitutes: Porter's five forces.
What is a barrier to entry in a market quizlet?
Barrier to Entry. Any impediment that prevents new firms from entering an industry and competing on an equal basis with existing firms.
What are entry barriers quizlet?
Anything that prevents new competitors from easily entering an industry. If a market has significant economies of scale which have already been exploited by the incumbents, new entrants are deterred.
What do you mean by monopoly market?
Definition: A market structure characterized by a single seller, selling a unique product in the market. In a monopoly market, the seller faces no competition, as he is the sole seller of goods with no close substitute.
What are the 3 barriers to entry?
Three types of barriers to entry exist in the market today. These are natural barriers to entry, artificial barriers to entry, and government barriers to entry.
What is a barrier to entry give some examples quizlet?
Examples include: - Capital inputs that are specific to a particular industry and which have little or no resale value. - Money spent on advertising/marketing/research which cannot be carried forward into another market or industry.
What is a barrier to market entry?
A barrier to market entry is an obstacle (usually high costs) which prevents a product from gaining traction in a new market.
What are the two most common barriers to entry?
There are two types of barriers:Natural (Structural) Barriers to Entry. Economies of scale: If a market has significant economies of scale that have already been exploited by the existing firms to a large extent, new entrants are deterred. ... Artificial (Strategic) Barriers to Entry.
Which of the following is an example of a barrier to entry quizlet?
Copyrights and patents are examples of barriers to entry.
Which of the following is not a common barrier to entry for firms?
The correct answer is 1. differentiated products. This is not a barrier to entry.
In which of the following industry structures is the entry of new firms the most difficult?
Explanation: A market in which entry of a new firm is the most difficult task is known as the pure monopoly market.
What is a monopoly?
Monopoly MonopolyA monopoly is a market with a single seller (called the monopolist) but with many buyers. In a perfectly competitive market, which comprises
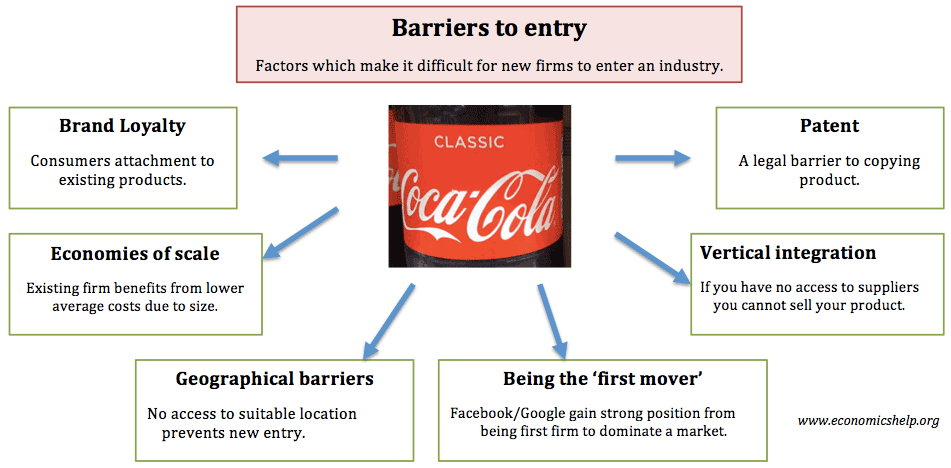
What are the barriers to entry?
What are Barriers to Entry? Barriers to entry are the obstacles or hindrances that make it difficult for new companies to enter a given market. These may include technology challenges, government regulations, Fiscal Policy Fiscal Policy refers to the budgetary policy of the government, which involves the government controlling its level ...
What is an ancillary barrier to entry?
An ancillary barrier to entry refers to the cost that does not include a barrier to entry by itself but reinforces other barriers to entry if they are present. An antitrust barrier to entry is the cost that delays entry and thereby reduces social welfare relative to immediate and costly entry. All barriers to entry are antitrust barriers ...
Why are barriers to entry dysfunctional?
Barriers become dysfunctional when they are so high that incumbents can keep out virtually all competitors, giving rise to monopoly or oligopoly.
What are the two types of barriers?
There are two types of barriers: 1. Natural (Structural) Barriers to Entry. Economie s of scale. Economies of Scale Economies of scale refer to the cost advantage experienced by a firm when it increases its level of output.The advantage arises due to the. : If a market has significant economies of scale that have already been exploited by ...
What is the largest network effect?
The largest and best-known example of a network effect is the Internet. : This refers to the effect that multiple users have on the value of a product or service to other users. If a strong network already exists, it might limit the chances of new entrants to gain a sufficient number of users.
What is predatory pricing?
Predatory pricing, as well as an acquisition: A firm may deliberately lower prices to force rivals out of the market. Also, firms might take over a potential rival by purchasing sufficient shares to gain a controlling interest.
Why are barriers to entry important?
The existence of barriers to entry make the market less contestable and less competitive. The greater the barrier s to entry which exist, the less competitive the market will be . Barriers to entry are an essential aspect of monopoly markets.
What would happen if a new firm entered the market and produced Q2?
A firm producing at Q1 has lower average costs. If a new firm enters and produces Q2, its average costs will make it uncompetitive. 2. Natural / Geographical Barriers, e.g. Zimbabwe has 85% of the world supply of Chromium.
What is limit pricing?
Limit Pricing. This occurs when a firm sets price sufficiently low to deter entry. A monopoly may engage in limit pricing – even though it means fewer profits, it prefers to keep prices lower to prevent competition. It is related to economies of scale. 5.
How to build consumer loyalty?
3. Brand loyalty through advertising. Developing consumer loyalty through establishing a strong brand image can deter entry. With a very strong brand image, a new firm would have to spend a lot of money on advertising, which is a sunk cost and a deterrent to entry.
What is predatory pricing?
This occurs when an incumbent firm responds to a new firm entering the market by starting a price war and trying to push the rival firm out of business. It is illegal so it may be difficult to implement in practice.
Why is it so hard to enter a new company?
It can be difficult for a new firm to enter because people are reluctant to use a service that not many others do use.
Why is it difficult to compete with low output?
Economies of scale occur when increased output leads to lower average costs. Therefore new firms, with relatively low output, will find it difficult to compete because theirs average costs will be higher than the incumbent firms benefiting from economies of scale. The prospect of higher average costs may deter entry.
What are natural monopolies?
Natural monopolies result from economies of scale, while network effects come from diseconomies of scale.
Why do companies invest in monopoly profits?
Monopoly profits give firms more reason to invest in the creation of new products through research and development.
How do natural monopolies and network effects differ?
Natural monopolies result from economies of scale, while network effects come from the benefits to consumers from having many people use a service. Natural monopolies result from the benefits to consumers from having many people use a service, while network effects come from economies of scale.
How do monopolies find profits?
Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, a monopoly finds profits and losses by comparing total revenue to total cost.
Is a player's best response always a dominant strategy?
Yes, if a player has a dominant strategy, then it is his best response, and every best response is always a dominant strategy. B. Yes, if a player's best responses depend on the strategy choices of other players, then a player's best response will be the same as his dominant strategy. C.
Do regulators get involved in pricing decisions?
It is difficult to set a fair price, so regulators do not get involved in the pricing decisions of any monopolists.
Is there a high entry barrier in perfect competition?
In perfect competition, there are high entry barriers, but with monopoly, barriers to entry are low.
