What is specific gravity of soil?
With an increase in organic matter of the soil, the particle density decreases. When particle density is divided by density of water, a relative weight number is obtained is called specific gravity. 2. Bulk Density: Bulk density is defined as the mass (weight) per unit volume of a dry soil (volume of solid and pore spaces).
What are the factors affecting the bulk density of soil?
If the soil containing more pore spaces than that of solid spaces per unit volume, then the value of bulk density will be very low. (ii) Compactness of the soil. In high compacted soil or waterlogged soils the bulk density will be more. (iii) Texture of the soil.
How do you find the dry density of soil?
The mass of compacted soil and the volume of the mold gives bulk density of the soil. From the bulk density the dry density can be determined for the water content used (w). The same procedure from (1-8) is repeated by increasing the water content in the soil by 2 to 3%.
How do you find the mass of compacted soil?
Hence the mass of the compacted soil (W s) is determined as: Ws = Wm -Wms The mass of compacted soil and the volume of the mold gives bulk density of the soil. From the bulk density the dry density can be determined for the water content used (w). The same procedure from (1-8) is repeated by increasing the water content in the soil by 2 to 3%.

What are the types of soil density?
In three-phase (solid, liquid and gas) soil system, soil density can be categorized as soil particle density, bulk or dry density, and wet density.
How dense is clay soil?
1,3 gram/cm3A fine and well-structured clay soil has a typical gross density of 1,3 gram/cm3 or 1 300 kg/m3. Compacted sub-soils can have a bulk density of more than 2,0 g/cm3.
Which soil has highest porosity?
ClayClay is the most porous sediment but is the least permeable.
Is sand more dense than soil?
The grain density is the actual density of the particles, which might be a mineral. The bulk density is less than the grain density of the constituent mineral (or mineral assemblage), depending on the porosity....Density of Rocks and Soils.Soil TypeDensity/g/cm3sand1.52sandy loam1.44loam1.36silt loam1.2813 more rows•Jul 12, 2021
What is the density of sandy soil?
1.3–1.7 g/cm3Sandy soils usually have higher bulk densities (1.3–1.7 g/cm3) than fine silts and clays (1.1 – 1.6 g/cm3) because they have larger, but fewer, pore spaces.
Is loam soil dense?
Soil bulk density must be below the critical value in order for roots to grow....Critical bulk density values.Critical bulk density values for difference soil texturesclay, silt loam1.4-1.55silty clay, silty clay loam, silt1.4-1.45clay loam1.45-1.55loam1.45-1.66 more rows
Which soil is very fertile?
Alluvial soilAlluvial soil is formed by deposition of alluvium and sediments carried by rivers and sea waves over many years, which make this soil very fertile. It consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay. It is also rich in organic nutrients.
Which soil has the highest permeability?
Sandy soils are known to have high permeability, which results in high infiltration rates and good drainage. Clay textured soils have small pore spaces that cause water to drain slowly through the soil. Clay soils are known to have low permeability, which results in low infiltration rates and poor drainage.
What is bigger sand silt or clay?
Starting with the finest, clay particles are smaller than 0.002 mm in diameter. Some clay particles are so small that ordinary microscopes do not show them. Silt particles are from 0.002 to 0.05 mm in diameter. Sand ranges from 0.05 to 2.0 mm.
What is more dense sand or clay?
Sandy soils have relatively high bulk density since total pore space in sands is less than that of silt or clay soils. Finer-textured soils, such as silt and clay loams, that have good structure have higher pore space and lower bulk density compared to sandy soils.
What is density of clay?
Densities of clay minerals range from 2 to 3, but many are near 2.65 g cm –3. The density of humus is usually less than 1.5 g cm –3.
What is the density of silt soil?
As a rule of thumb, most rocks have a density of 2.65 g/cm3 so ideally, a silt loam soil has 50% pore space and a bulk density of 1.33 g/cm3.
Why is clay soil heavy?
Clay soils are considered to be one of the heavier soils. The soil can hold a ton of nutrients and a lot of water due to the capillary action between the clay particles, and it takes a little bit longer to drain. Out of all the soils, clay soil has the smallest particles. Identifying clay soil is relatively easy to do.
How can you tell if soil is clay?
The best way to tell what type of soil you have is by touching it and rolling it in your hands.Sandy soil has a gritty element – you can feel sand grains within it, and it falls through your fingers. ... Clay soil has a smearing quality, and is sticky when wet. ... Pure silt soils are rare, especially in gardens.
Is clay soil hard or soft?
1. Clay soil: This rough, thick, and heavy soil makes it hard for many different types of perennial and annual plants to grow. Its mineral particles attract plenty of nutrients, but they also compact densely. Some plant types—like aster and hosta flowers, for example—are tough enough to make their way through the soil.
What clay soil feels like?
Clay feels sticky when wet. It easily forms into a ball and a ribbon at least 5 cm long. Water drains very slowly through clay soil. Therefore, clay soil remains saturated after a heavy rain.
What is the particle density of soil?
Generally in the normal soils the particle density is 2.65 grams per cubic centimetre or mega grams per cubic metre. The particle density is higher if large amounts of heavy minerals such as magnetite, limonite, hematite and zircon are present. With an increase in organic matter of the soil, the particle density decreases.
How to find bulk density of soil?
2. The bulk density of a soil can be calculated on the basis of dry weight of that soil divided by its volume.
What is bulk density?
Bulk density is defined as the mass (weight) per unit volume of a dry soil (volume of solid and pore spaces). It is also expressed in gm./c.c. (G.G.S. system) or lb/cft (F.P.S. system) or mega gram per cubic metre. The bulk density of a soil is always smaller than its particle density. Loose and porous soils have low weights per unit volume and compact soils have high values.
What is the weight per unit volume of soil called?
The weight per unit volume of the solid portion of soil is called particle density . It is also termed as true density. It is expressed in gm./c.c. (C.G.S. system) or lb/cft (F.P.S. system). It depends upon the accumulative densities of the individual inorganic and organic constituents of the soil. Generally in the normal soils the particle density is 2.65 grams per cubic centimetre or mega grams per cubic metre.
How does soil structure affect bulk density?
Soil structure affects bulk density by influencing the porosity of the soil. More for example, crumb soil structure shows low bulk density than that of platy soil structure. A metal cylinder pushed into a loam soil is removed from the field and the soil it contains is dried in an oven.
Why is bulk density important?
Bulk density is of greater importance than particle density in understanding the physical behaviour of soils. Generally, soils having low and high bulk densities exhibit favourable and poor physical conditions respectively.
What is density in chemistry?
Density is the weight per unit volume of a substance. It is expressed in gram per cubic centimeter or pound per cubic foot or mega gram per cubic metre (Mg m -3 ). Two density measurements—particle density and bulk density are common for soils.
What is the soil needed for a construction site?
The soil at the construction site must be stable enough to carry the loads from the structures through footings without undergoing undesirable settlements during the construction process and during the service period.
What is the water content of a soil sample?
The water content of the sample after addition must be less than the optimum water content.
What is the measure of moisture content in soil?
The determination of maximum dry density and optimum moisture content of the soil is a measure of compaction level of soils. This can be measured by mainly two methods Standard Proctor Compaction Test and Modified Proctor Compaction Test. Both the tests help to determine the optimum moisture content that is required for soil to attain maximum compaction i.e maximum dry density for performing construction.
What is the OMC of soil?
The Optimum moisture content (OMC) or Optimum Water Content (OWC) is the moisture content at which the soil attains maximum dry density. This OMC value is with respect to the specific amount of compaction energy applied to the soil.
What is the peak point of soil compaction?
The maximum peak point of the soil compaction curve obtained is called the Maximum dry density value. The water content corresponds to this point is called the Optimum water content (O.W.C) or optimum moisture content (O.M.C).
How tall is a standard mold?
The apparatus consists of a standard mold of 4 inches in internal diameter. The effective height of this standard mold is 4.6 inches. The maximum capacity of the mold is 1/30 cubic foot. The apparatus is shown in the figure-1 below.
What happens when soil particles are lubricated?
When the soil particles are lubricated with the increase in the water content, the soil particles will be densely packed resulting in increased density. Now beyond a limit (OMC) the addition of water will not bring a change in dry density or will decrease the dry density.
What does "soil health" mean?
Eight and Roman Numerals. The concept of soil health also means that healthy soils have the ability to sustain. Plant and animal life and productivity, soil biodiversity, maintain and enhance water and air quality, support human health and wildlife habitat. The ideal soil matrix composition for most plants.
What is the mineral that is rich in calcium carbonate?
Sedimentary rock rich in calcium carbonate derived from shells of sea organisms and mineral calcite, including dolomite, which is rich in calcium an magnesium carbonate
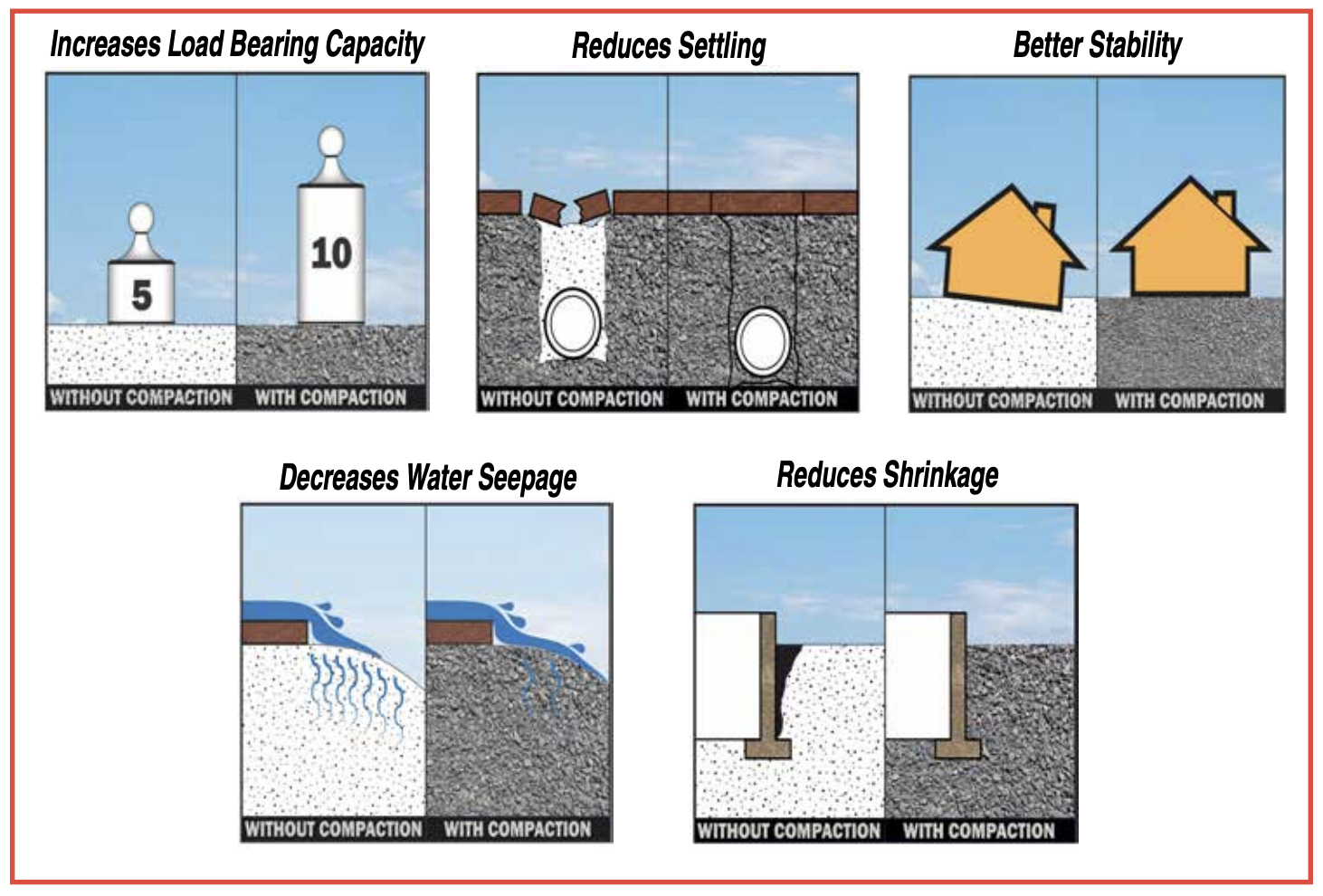
What causes compaction in soil?
Pressure applied to the soil surface causes compaction.