What are the different types of materialist theory?
Types of materialist theory Types distinguished by departures from the paradigm Type distinguished by its view of history Types distinguished by their account of mind History of materialism Greek and Roman materialism Modern materialism Twentieth-century materialism Translation central-state theories Disappearance central-state theories
What do you mean by materialism?
The word materialism has been used in modern times to refer to mechanical materialism, the theory that the world consists entirely of material objects. materialism | Definition, Theories, History, & Facts | Britannica BrowseSearch QuizzesGamesOn This Day
Is dialectical materialism an extreme materialism?
Dialectical materialists contrast their view with what they call “vulgar” materialism; and it does, indeed, appear that their theory is not an extreme materialism, whether mechanical or physicalist. They seem to hold merely that mental processes are dependent on or have evolved from material ones.
What is the main attraction of materialism in physics?
Reductionism, consciousness, and the brain. The main attraction of materialism is the way in which it fits in with a unified picture of science—a picture that has become very plausible. Thus, chemistry is reducible to physics inasmuch as there is a quantum-mechanical theory of the chemical bond.
What is materialism in science?
What is mechanical materialism?
How do materialists and analytical behaviorists differ?
What is the theory that all facts are causally dependent upon physical processes?
What is the theory of introspective reports?
What is a central state materialist?
What is analytical behaviorist?
See 4 more
About this website

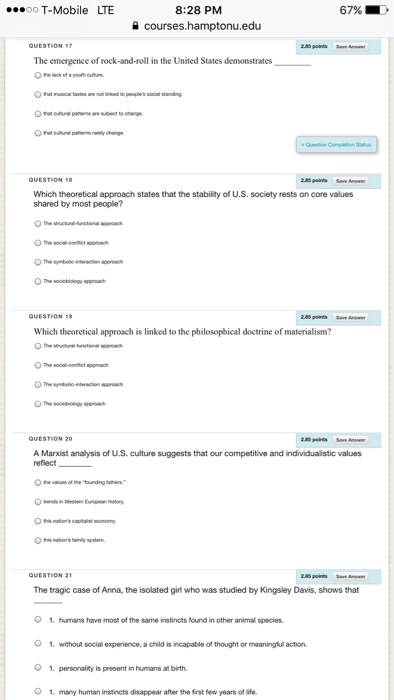
What theoretical approach is linked to materialism?
Materialism belongs to the class of monist ontology, and is thus different from ontological theories based on dualism or pluralism.
Which theoretical approach gives an evolutionary explanation?
Sociology FinalQuestionAnswerWhich theoretical approach gives an evolutionary explanation of why the sexual "double standard" is found around the world?the sociobiology approachThe term Homo sapiens, the name of our species, comes from Latin meaning"intelligent person."59 more rows
Which theoretical approach emphasizes the meaning that people attach to their behavior?
Symbolic interactionism as a social theoretical framework starts from the presupposition that our social world is constructed through the mundane acts of everyday social interaction. Through the repetitive act of interaction, individuals as actors in relation to social groups constitute symbolic and shared meanings.
Which theoretical approach states that the stability of US society?
Structural functionalism, or simply functionalism, is "a framework for building theory that sees society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability".
What are theoretical approaches?
1. A set of statements or principles devised to explain a group of facts or phenomena, especially one that has been repeatedly tested or is widely accepted and can be used to make predictions about natural phenomena.
What does the evolutionary approach focus on?
With the evolutionary perspective scientists look at the way a new trait will evolve in the average person. The evolutionary perspective says the only reason that the human race continues to survive and continues to function in the best way possible is through natural selection.
What are the 3 theoretical approaches?
These three theoretical orientations are: Structural Functionalism, Symbolic Interactionism, and Conflict Perspective. To understand a theoretical orientation in any profession it is critical to understand what is meant by the term theory.
What are the four theoretical approaches?
The four main theoretical perspectives are symbolic interactionism theory, social conflict theory, structural-functional theory, and feminist theory.
What does the functionalist perspective emphasizes?
The functionalist perspective emphasizes the interconnectedness of society by focusing on how each part influences and is influenced by other parts.
What is structural functionalism theory in sociology?
structural functionalism, in sociology and other social sciences, a school of thought according to which each of the institutions, relationships, roles, and norms that together constitute a society serves a purpose, and each is indispensable for the continued existence of the others and of society as a whole.
What theoretical approach focuses on the link between culture and social inequality?
The theoretical approach that highlights the link between culture and social inequality is the ________ Answers: structural-functional approach.
Which theoretical approach would best explain that the stability of US society rests on core values shared by most people as representative of their institutions?
some cultural elements change more quickly than others. judging another culture by the standards of one's own culture. Which theoretical approach asserts that the stability of U.S. society rests on core values shared by most people? structural-functional approach.
What methods are used in evolutionary psychology?
Because evolutionary psychology is an approach rather than a content area, researchers in the discipline use a variety of techniques. These include laboratory experiments, field experiments, mathematical and agent-based simulations, surveys, neuroimaging, and so on.
What is evolutionary theories in psychology?
Evolutionary psychology aims the lens of modern evolutionary theory on the workings of the human mind. It focuses primarily on psychological adaptations: mechanisms of the mind that have evolved to solve specific problems of survival or reproduction.
Is evolutionary perspective a theoretical framework?
Evolutionary psychology studies the human brain and its behavioral products from an evolutionary perspective; it uses evolutionary theory (and insights from evolutionary biology) as a meta-theoretical framework to generate hypotheses about human psychology and behavior.
What does evolutionary approach mean in psychology?
Evolutionary psychology is a theoretical approach to psychology that attempts to explain useful mental and psychological traits—such as memory, perception, or language—as adaptations, i.e., as the functional products of natural selection.
8 Examples of Materialism - Simplicable
Wealth Materialism is traditionally associated with the pursuit of wealth as this was considered a physical thing. This takes on interesting dimensions due to the process of dematerialization whereby wealth is increasingly non-physical. For example, knowledge, talent, intellectual property, digital money, digital property, digital environments, digital media and software are all non-physical ...
What does materialism mean? - definitions
Definition of materialism in the Definitions.net dictionary. Meaning of materialism. What does materialism mean? Information and translations of materialism in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web.
Materialism Overview & Examples | What is Materialism?
Learn about what materialism is. Understand different approaches towards materialism. Discover how to define materialistic and various examples of...
Why Materialism Is False, and Why It Has Nothing To Do with the Mind
31 Another argument to this effect appeals to intertheoretic identities: If theory T A is reducible to theory T B, then T B can take over all the descriptive and explanatory jobs of T A, but this kind of takeover requires that entities postulated by T A be identical to entities postulated by T B (Sklar, Lawrence, ‘ Types of Inter-Theoretic Reduction ’, British Journal for the Philosophy of ...
What is materialism in science?
The word materialism has been used in modern times to refer to a family of metaphysical theories (i.e. , theories of the nature of reality) that can best be defined by saying that a theory tends to be called materialist if it is felt sufficiently to resemble a paradigmatic theory that will here be called mechanical materialism.
What is mechanical materialism?
Mechanical materialism is the theory that the world consists entirely of hard, massy material objects, which, though perhaps imperceptibly small, are otherwise like such things as stones. (A slight modification is to allow the void—or empty space—to exist also in its own right.) These objects interact in the sort of way that stones do: by impact and possibly also by gravitational attraction. The theory denies that immaterial or apparently immaterial things (such as minds) exist or else explains them away as being material things or motions of material things.
How do materialists and analytical behaviorists differ?
An analyticalbehaviourist, on the other hand, argues that, in talking about the mind, one is not talking about an actual entity, whether material (e.g., the brain) or immaterial (e.g., the soul); rather, one is somehow talking about the way in which people would behave in various circumstances. According to the analytical behaviourist, there is no more of a problem for the materialist in having to identify mind with something material than there is in identifying such an abstraction as the average plumber with some concreteentity. Analytical behaviourism differs from psychological behaviourism, which is merely a methodological program to base theories on behavioral evidence and to eschewintrospectivereports. The analytical behaviourist usually has a theory of introspective reports according to which they are what are sometimes called “avowals”: roughly, he contends that to say “I have a pain” is to engage in a verbal surrogate for a wince. Epistemic materialism is a theory that can be developed either in the direction of central-state materialism or in that of analytical behaviourism and that rests on the contentionthat the only statements that are intersubjectively testable are either observation reports about macroscopic physical objects or statements that imply such observation reports (or are otherwise logically related to them).
What is the theory that all facts are causally dependent upon physical processes?
Materialism, in philosophy, the view that all facts are causally dependent upon physical processes, or even reducible to them. The word materialism has been used in modern times to refer to mechanical materialism, the theory that the world consists entirely of material objects.
What is the theory of introspective reports?
The analytical behaviourist usually has a theory of introspective reports according to which they are what are sometimes called “avowals”: roughly, he contends that to say “I have a pain” is to engage in a verbal surrogate for a wince.
What is a central state materialist?
A central-state materialist identifies mental processes with processes in the brain.
What is analytical behaviorist?
An analytical behaviourist, on the other hand, argues that, in talking about the mind, one is not talking about an actual entity, whether material ( e.g., the brain) or immaterial (e.g., the soul ); rather, one is somehow talking about the way in which people would behave in various circumstances.
Which model of the brain was not widely studied?
Pribram's holonomic model of brain function did not receive widespread attention at the time, but other quantum models have been developed since, including brain dynamics by Jibu & Yasue and Vitiello's dissipative quantum brain dynamics.
How does quantum consciousness work?
It describes human cognition by modeling the brain as a holographic storage network . Pribram suggests these processes involve electric oscillations in the brain's fine-fibered dendritic webs, which are different from the more commonly known action potentials involving axons and synapses. These oscillations are waves and create wave interference patterns in which memory is encoded naturally, and the wave function may be analyzed by a Fourier transform. Gabor, Pribram and others noted the similarities between these brain processes and the storage of information in a hologram, which can also be analyzed with a Fourier transform. In a hologram, any part of the hologram with sufficient size contains the whole of the stored information. In this theory, a piece of a long-term memory is similarly distributed over a dendritic arbor so that each part of the dendritic network contains all the information stored over the entire network. This model allows for important aspects of human consciousness, including the fast associative memory that allows for connections between different pieces of stored information and the non-locality of memory storage (a specific memory is not stored in a specific location, i.e. a certain cluster of neurons).
What is the same series of operations used in holographic memory models?
Several studies have shown that the same series of operations used in holographic memory models are performed in certain processes concerning temporal memory and optomotor responses. This indicates at least the possibility of the existence of neurological structures with certain holonomic properties.
How did Karl Pribram work with Karl Lashley?
Karl Pribram had worked with psychologist Karl Lashley on Lashley's engram experiments, which used lesions to determine the exact location of specific memories in primate brains. Lashley made small lesions in the brains and found that these had little effect on memory. On the other hand, Pribram removed large areas of cortex, leading to multiple serious deficits in memory and cognitive function. Memories were not stored in a single neuron or exact location, but were spread over the entirety of a neural network. Lashley suggested that brain interference patterns could play a role in perception, but was unsure how such patterns might be generated in the brain or how they would lead to brain function.
What is the Holonomic Brain?
Holonomic brain theory, also known as The Holographic Brain, is a branch of neuroscience investigating the idea that human consciousness is formed by quantum effects in or between brain cells. This is opposed by traditional neuroscience, which investigates the brain's behavior by looking at patterns of neurons and the surrounding chemistry, ...
What is materialism in science?
The word materialism has been used in modern times to refer to a family of metaphysical theories (i.e. , theories of the nature of reality) that can best be defined by saying that a theory tends to be called materialist if it is felt sufficiently to resemble a paradigmatic theory that will here be called mechanical materialism.
What is mechanical materialism?
Mechanical materialism is the theory that the world consists entirely of hard, massy material objects, which, though perhaps imperceptibly small, are otherwise like such things as stones. (A slight modification is to allow the void—or empty space—to exist also in its own right.) These objects interact in the sort of way that stones do: by impact and possibly also by gravitational attraction. The theory denies that immaterial or apparently immaterial things (such as minds) exist or else explains them away as being material things or motions of material things.
How do materialists and analytical behaviorists differ?
An analyticalbehaviourist, on the other hand, argues that, in talking about the mind, one is not talking about an actual entity, whether material (e.g., the brain) or immaterial (e.g., the soul); rather, one is somehow talking about the way in which people would behave in various circumstances. According to the analytical behaviourist, there is no more of a problem for the materialist in having to identify mind with something material than there is in identifying such an abstraction as the average plumber with some concreteentity. Analytical behaviourism differs from psychological behaviourism, which is merely a methodological program to base theories on behavioral evidence and to eschewintrospectivereports. The analytical behaviourist usually has a theory of introspective reports according to which they are what are sometimes called “avowals”: roughly, he contends that to say “I have a pain” is to engage in a verbal surrogate for a wince. Epistemic materialism is a theory that can be developed either in the direction of central-state materialism or in that of analytical behaviourism and that rests on the contentionthat the only statements that are intersubjectively testable are either observation reports about macroscopic physical objects or statements that imply such observation reports (or are otherwise logically related to them).
What is the theory that all facts are causally dependent upon physical processes?
Materialism, in philosophy, the view that all facts are causally dependent upon physical processes, or even reducible to them. The word materialism has been used in modern times to refer to mechanical materialism, the theory that the world consists entirely of material objects.
What is the theory of introspective reports?
The analytical behaviourist usually has a theory of introspective reports according to which they are what are sometimes called “avowals”: roughly, he contends that to say “I have a pain” is to engage in a verbal surrogate for a wince.
What is a central state materialist?
A central-state materialist identifies mental processes with processes in the brain.
What is analytical behaviorist?
An analytical behaviourist, on the other hand, argues that, in talking about the mind, one is not talking about an actual entity, whether material ( e.g., the brain) or immaterial (e.g., the soul ); rather, one is somehow talking about the way in which people would behave in various circumstances.
