What is the law of supply and demand in economics?
The law of supply and demand is the theory that prices are determined by the relationship between supply and demand. If the supply of a good or service outstrips the demand for it, prices will fall. If demand exceeds supply, prices will rise. The law of supply and demand is based on two other economic laws: the law of supply and the law of demand.
Who discovered the law of supply and demand?
The law of supply and demand, which dictates that a product's availability and appeal impacts its price, had several discoverers. But the principle, one of the best-known in economics, was noticed in the marketplace long before it was mentioned in a published work – or even given its name. John Locke.
Who developed the supply and demand curve in economics?
Alfred Marshall. After Smith's 1776 publication, the field of economics developed rapidly, and refinements were to the supply and demand law. In 1890, Alfred Marshall's Principles of Economics developed a supply-and-demand curve that is still used to demonstrate the point at which the market is in equilibrium.
What is Adam Smith's theory of supply and demand?
Adam Smith dealt extensively with the topic in his 1776 epic economic work, The Wealth of Nations. Often referred to as the Father of Economics, Smith explained the concept of supply and demand as an " invisible hand " that naturally guides the economy.

What Is the Law of Supply and Demand?
The law of supply and demand is a theory that explains the interaction between the sellers of a resource and the buyers for that resource. The theory defines the relationship between the price of a given good or product and the willingness of people to either buy or sell it. Generally, as price increases, people are willing to supply more and demand less and vice versa when the price falls.
Why Is the Law of Supply and Demand Important?
The Law of Supply and Demand is essential because it helps investors, entrepreneurs, and economists understand and predict market conditions. For example, a company launching a new product might deliberately try to raise the price of its product by increasing consumer demand through advertising.
How does the supply curve change over time?
Over longer intervals of time, however, suppliers can increase or decrease the quantity they supply to the market based on the price they expect to charge . So over time, the supply curve slopes upward; the more suppliers expect to charge , the more they will be willing to produce and bring to market.
Why is time important in supply and demand?
It is important for both supply and demand to understand that time is always a dimension on these charts. The quantity demanded or supplied, found along the horizontal axis, is always measured in units of the good over a given time interval. Longer or shorter time intervals can influence the shapes of both the supply and demand curves.
How does willingness affect supply and demand?
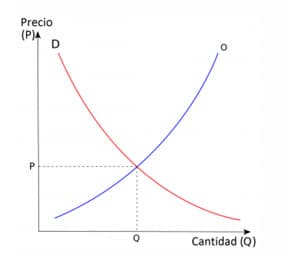
In practice, people's willingness to supply and demand a good determines the market equilibrium price, or the price where the quantity of the good that people are willing to supply just equals the quantity that people demand. However, multiple factors can affect both supply and demand, causing them to increase or decrease in various ways.
What is a shift in demand and supply?
A movement refers to a change along a curve. On the demand curve, a movement denotes a change in both price and quantity demanded from one point to another on the curve.
What is the relationship between price and demand?
The theory defines the relationship between the price of a given good or product and the willingness of people to either buy or sell it. Generally, as price increases, people are willing to supply more and demand less and vice versa when the price falls. The theory is based on two separate "laws," the law of demand and the law of supply.
John Locke
Locke addressed the concept of supply and demand as part of a discussion about interest rates in 17th-century England. Many merchants wanted the government to lower the cap on interest rates charged by private lenders so that people could borrow more money and thus purchase more goods.
Sir James Steuart
When Steuart wrote his treatise on political economy, one of his main concerns was the impact of supply and demand on laborers. Steuart noted that when supply levels were higher than demand, prices were significantly reduced, lowering the profits realized by merchants.
Adam Smith
Smith, often referred to as the father of economics, explained the concept of supply and demand as an "invisible hand" that naturally guides the economy. Smith described a society where bakers and butchers provide products that individuals need and want, providing a supply that meets demand and developing an economy that benefits everyone.
Alfred Marshall
After Smith's 1776 publication, the field of economics developed rapidly. In 1890, Alfred Marshall wrote "Principles of Economics," where he explained how supply and demand, costs of production and price elasticity work together.
Explanation
The law of supply and demand gives insight into the process of price and quantity determination in a competitive market through buyer and seller interaction. For example, the consumer often chooses products and services which come in affordable price tags with desired utility.
Real World Example s
The laws of supply and demand example can find in the electric cars market. Barely a decade or so ago, very few cars or models in supply were purely electric. Those that were (or which were hybrids) commanded high prices. Hence, the demand was also less.
Why is it Important?
For businesses, it is vital to consider the supply and demand scenario when planning to enter a particular market.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Law of Supply and Demand and its Definition. Here we explain the four basic laws of supply and demand and why it is vital with examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
Who developed the law of supply and demand?
The law of supply and demand is actually an economic theory that was popularized by Adam Smith in 1776. The principles of supply and demand have been shown to be very effective in predicting market behavior. However, there are multiple other factors that affect markets on both a microeconomic and a macroeconomic level.
What is supply and demand?
The theory of supply and demand relates not only to physical products such as television sets and jackets but also to wages and the movement of labor. More advanced theories of micro and macroeconomics often adjust the assumptions and appearance of the supply and demand curve to properly illustrate concepts like economic surplus, monetary policy, externalities, aggregate supply, fiscal stimulation, elasticity, and shortfalls. Before studying those more complex issues, the basics of supply and demand must be properly understood.
What is the difference between supply and demand graphs?
Whereas supply graphs are drawn from the perspective of the producer, demand is portrayed from the perspective of the consumer. As the price of a good increases, the demand for the product will—except for a few obscure situations—decrease.
What happens to the demand for a good as the price of a good increases?
As the price of a good increases, the demand for the product will—except for a few obscure situations—decrease. For purposes of our discussion, let's assume the product in question is a television set. If TVs are sold for the cheap price of $5 each, then a large number of consumers will purchase them at a high frequency. Most people would even buy more TVs than they need, putting one in every room and perhaps even some in storage.
What is supply curve?
The supply curve functions in a similar fashion, but it considers the relationship between the price and available supply of an item from the perspective of the producer rather than the consumer.
What is the ideal price a consumer would pay for a good?
Naturally, the ideal price a consumer would pay for a good would be "zero dollars.". However, such a phenomenon is unfeasible as producers would not be able to stay in business.
Why is the demand for a TV so high?
Essentially, because everyone can easily afford a TV, the demand for these products will remain high. On the other hand, if the price of a television set is $50,000, this gadget will be a rare consumer product as only the wealthy will be able to afford the purchase. While most people would still like to buy TVs, at that price, demand for them would be extremely low.
What is supply and demand in finance?
Supply and Demand are the core concepts of economics and finance. Most of the finance and economics models are primarily based on the supply and demand forces. A thorough understanding of these two forces will increase your analytical skills and help you solve an economy’s core problem. It will provide you a new vivid perspective to look at ...
What is supply in business?
Supply refers to the amount of goods and services producers desire to sell at different price levels.
What is shift in demand?
On the other hand, a shift refers to change in quantity demanded even when the price is constant. It is imperative to appreciate that your demand for a particular good and service may alter even when the price remains the same. For example, consider that you found a substitute for the hoodie as varsity jackets, which are way cheaper and better than hoodies.
Why does supply increase with price increase?
We have various theories, but the most prominent one is that each seller would want to chunk out higher profits for his or her goods and services. Higher profit means a higher price. That’s why quantity supply increases with a price increase.
What causes a shift in supply?
Because of this, the production is now becoming more efficient and effective. Now the producer would able to produce more as the new technology is saving his or her costs. Consequently, he or she will sell more at the same price level as it was before. Factors that cause shifts in supply are new technological advancement, taxes, cost of production, etc.
Is shift the same as demand?
Shifts and Movements here also are the same as the one in demand.
Is demand a function of price?
From the above graph, you would have noticed that demand is a function of price and quantity demanded. Price is always plotted on the y-axis, and the quantity demanded on the x-axis.

What Is the Law of Supply and Demand?
Understanding the Law of Supply and Demand
- It may seem obvious that in any sale transaction the price satisfies both the buyer and the seller…
Many medieval thinkers, like modern day critics of market pricing for select commodities, distinguished between a "just" price based on costs and equitable returns and one at which the sale was in fact transacted. 2 Our understanding of price as a signaling mechanism matching su…
The Law of Demand
- The law of demand holds that demand for a product changes inversely to its price, all else being …
Because buyers have finite resources, their spending on a given product or commodity is limited as well, so higher prices reduce the quantity demanded. Conversely, demand rises as the product becomes more affordable. - As a result, demand curves slope downward from left to right, as in the chart below. Changes in …
Naturally, there are exceptions. One is Giffen goods, typically low-priced staples also known as inferior goods. Inferior goods are those that see a drop in demand when incomes rise because consumers trade up to higher-quality products. But when the price of an inferior good rises and …
The Law of Supply
- The law of supply relates price changes for a product with the quantity supplied. In contrast wit…
Higher prices give suppliers an incentive to supply more of the product or commodity, assuming their costs aren't increasing as much. Lower prices result in a cost squeeze that curbs supply. As a result, supply slopes are upwardly sloping from left to right.
Equilibrium Price
- Also called a market-clearing price, the equilibrium price is the price at which demand matches s…
At the point where an upward-sloping supply curve and a downward-sloping demand curve intersect, supply and demand in terms of the quantity of the goods are balanced, leaving no surplus supply or unmet demand. The level of the market-clearing price depends on the shape a…
Factors Affecting Supply
- In industries where suppliers are not willing to lose money, supply will tend to decline toward zer…
Price elasticity will also depend on the number of sellers, their aggregate productive capacity, how easily it can be lowered or increased, and the industry's competitive dynamics. Taxes and regulations may matter as well.
Factors Affecting Demand
- Consumer income, preferences, and willingness to substitute one product for another are amon…
Consumer preferences will depend, in part, on a product's market penetration, since the marginal utility of goods diminishes as the quantity owned increases. The first car is more life-altering than the fifth addition to the fleet; the living-room TV more useful than the fourth one for the garage.
What Is a Simple Explanation of the Law of Supply and Demand?
- If you've ever wondered how the supply of a product matches demand, or how market prices are set, the law of supply and demand holds the answers. Higher prices cause supply to increase while demand drops. Lower prices boost demand while limiting supply. The market-clearing price is one at which supply and demand are balanced.
Why Is the Law of Supply and Demand Important?
- The Law of Supply and Demand is essential because it helps investors, entrepreneurs, and economists understand and predict market conditions. For example, a company considering a price hike on a product will typically expect demand for it to decline as a result, and will attempt to estimate the price elasticity and substitution effect to determine whether to proceed regardless.
What Is an Example of the Law of Supply and Demand?
- When gasoline consumption plunged with the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, prices quickly followed suit because the industry ran out of storage space. The price decline, in turn, served as a powerful signal to suppliers to curb gasoline production. Conversely, crude oil prices in 2022 provided producers with additional incentive to boost output.
Explanation
Real World Examples
Why Is It Important?
- Smith, often referred to as the father of economics, explained the concept of supply and demand as an "invisible hand" that naturally guides the economy. Smith described a society where bakers and butchers provide products that individuals need and want, providing a supply that meets demand and developing an economy that benefits everyone.
Recommended Articles