
Methyl groups are also vital for phase II liver detoxification, protein methylation, homocysteine metabolism (increasing the methyl groups decreases inflammation), neurotransmitter synthesis, and nucleic acid
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, or large biomolecules, essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three compone…
What is the function of the methyl group?
- Aldehydes are named by replacing the terminal -e of the parent alkane with the suffix -al; the suffix for ketones is -one.
- Number the substituents and write the name, listing substituents alphabetically.
- When an aldehyde is a substituent on a ring, it is referred to as a -carbaldehyde group.
What does the addition of methyl groups to DNA cause?
What is the Role of DNA Methylation in Cell Functioning
- Tissue-Specific Gene Expression. The cells of the tissues are differentiated to perform a specific function in the body. ...
- Inactivation of X Chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes while males have an X chromosome and Y chromosome in their genome. ...
- Genomic Imprinting. ...
- Conclusion. ...
Is a methyl group a functional group?
A methyl group is a functional group derived from methane containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, -CH3. In chemical formulas, it may be abbreviated as Me. However, methyl on its own is extremely reactive. The methyl group in a compound is typically the most stable functional group in the molecule.
What is an example of a methyl group?
What is an example of a methyl group? Examples of Methyl Groups Examples of compounds containing the methyl group are methyl chloride, CH3Cl, and methyl alchohol or methanol, CH3OH. Is demethylation an oxidation?
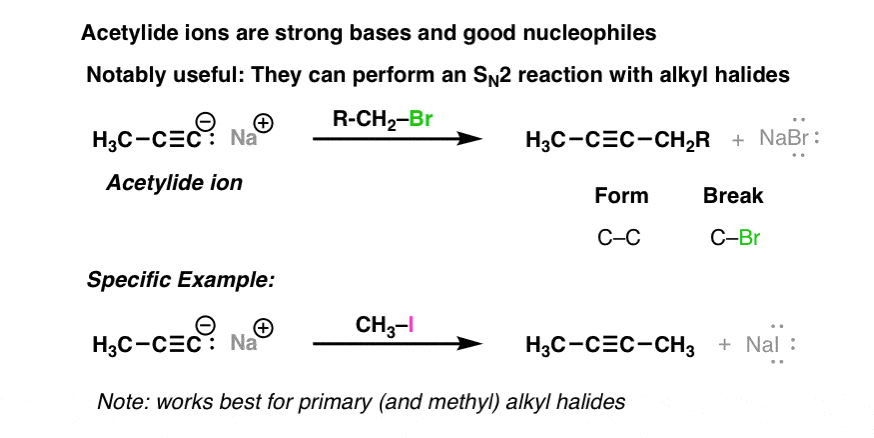
Why is methylation so important?
When methylation is going well, the process helps repair your DNA, regulates hormones, produces energy, protects against cancer, supports detoxification, keeps your immune system healthy, supports the protective coating along your nerves, strengthens the nervous system and on and on and on.
What is the role of methyl groups on DNA?
DNA methylation is essential for silencing retroviral elements, regulating tissue-specific gene expression, genomic imprinting, and X chromosome inactivation. Importantly, DNA methylation in different genomic regions may exert different influences on gene activities based on the underlying genetic sequence.
How do methyl groups affect genes?
The methyl groups turn genes on or off by affecting interactions between the DNA and other proteins. In this way, cells can remember which genes are on or off. The second kind of mark, called histone modification, affects DNA indirectly.
What is a methyl group in DNA methylation?
DNA methylation refers to the addition of a methyl (CH3) group to the DNA strand itself, often to the fifth carbon atom of a cytosine ring. This conversion of cytosine bases to 5-methylcytosine is catalysed by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs).
What are the functions of methyl groups?
Although methyl groups have low reactivity, they still impart a sizable influence on their surroundings, thereby affecting cellular functions.
What is a methyl group?
Methyl groups are highly stable, consisting of a central carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms. The functional group itself is typically unreactive, even in the presence of very strong acids or bases. Despite this stable configuration, methyl groups can be involved in reactions that translocate the entire functional group to another compound, in a process called “methylation.” This enzyme-mediated reaction is crucial to processes such as epigenetics, gene expression, liver detoxification, and neurotransmitter synthesis.
What is manganese dioxide used for?
Manganese dioxide can also be used for oxidations of activated alkyl groups , as demonstrated by the oxidation of the clinical dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibitor trimethoprim 586, to give the aryl ketone 587, without any need for protection of the two amino groups <2006BML4366>.
Diving Deeper Into Methylation- By Dr. Kendal Stewart
Methyl groups are “CH3" groups that are utilized extensively in the body for transport of nutrients in fat-soluble states and in epigenetic processes, turning genes on or off. In patients with decreased activity in the methylation pathway, there is a shortage of methyl groups in the body needed to execute a variety of important functions.
The Importance Of The Methylation Pathway
New cell synthesis and repair Mutations in the methylation pathway can cripple the ability of the body to make the building blocks (purines and pyrimidines) needed for new DNA and RNA synthesis. A reduced capacity for new DNA and RNA synthesis means that any new cell synthesis is impaired.
What is the role of methylation in detoxification?
When optimal methylation occurs, it has a significant positive impact on many biochemical reactions in the body that regulate the activity of the cardiovascular, neurological, reproductive, and detoxification systems , including those relating to: DNA production. Neurotransmitter production. Detoxification.
What is methylation in biology?
WHAT IS METHYLATION? The topic of methylation is getting its fair share of attention lately, and rightly so. Methylation is a simple biochemical process – it is the transfer of four atoms - one carbon atom and three hydrogen atoms (CH3) – from one substance to another.
How does methylation of CH3 happen?
HOW DOES METHYLATION HAPPEN? CH3 is provided to the body through a universal methyl donor known as SAMe (S-adenosylmethionine). SAMe readily gives away its methyl group to other substances in the body, which enables the cardiovascular, neurological, reproductive, and detoxification systems to perform their functions.
How to find out if you have a problem with your methylation cycle?
First, you can have a simple and easy genetic test to find out if you have a problem with your methylation cycle. This test looks at specific enzymes that are affected by your genetic makeup, including the enzyme MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase), which is the most important enzyme involved in creating 5-MTHF.
What happens when the methylation switch is turned off?
When the methylation switch is turned off and isn’t creating enough SAMe, then a number of important molecules cannot be efficiently produced, including: Glutathione. Coenzyme Q10. Melatonin. Serotonin.
Does 5-MTHF work in the methylation cycle?
Simply put, if enough 5-MTHF is present, the methylation cycle will work efficiently. Folic acid from the diet or supplements must be converted to this active form, 5-MTHF, before it can be used in the body in the methylation cycle.