
When does ketogenesis occur in diabetes?
Ketogenesis takes place in the setting of low glucose levels in the blood, after exhaustion of other cellular carbohydrate stores, such as glycogen. It can also take place when there is insufficient insulin (e.g. in type 1 (and less commonly type 2) diabetes ), particularly during periods of "ketogenic stress" such as intercurrent illness.
What causes ketone bodies in diabetes mellitus?
Individuals with diabetes mellitus can experience overproduction of ketone bodies due to a lack of insulin. Without insulin to help extract glucose from the blood, tissues the levels of malonyl-CoA are reduced, and it becomes easier for fatty acids to be transported into mitochondria, causing the accumulation of excess acetyl-CoA.
What is ketosis and what causes it?
Ketosis will take place when the body needs energy and there is not sufficient glucose available for the body. This can typically happen when the body is lacking insulin and blood glucose levels become high. Other causes can be the result of being on a low carb diet.
What causes diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Other causes of DKA include: 1 Heart attack or stroke. 2 Physical injury, such as from a car accident. 3 Alcohol or drug use. 4 Certain medicines, such as some diuretics (water pills) and corticosteroids (used to treat inflammation in the body).
What is the relationship between ketosis and diabetes?
Does Keto Work if You Have Diabetes? Research suggests that people with type 2 diabetes can slim down and lower their blood sugar levels with the keto diet. In one study, people with type 2 lost weight, needed less medication, and lowered their A1c when they followed the keto diet for a year.
Why does diabetes cause Ketonuria?
If you are fasting or have health conditions like diabetes, your body makes more ketones than it can use. This increases the levels of ketone bodies in your liver. Your body tries to get rid of them when you pee, resulting in high ketone levels in urine, or ketonuria.
How does insulin affect ketogenesis?
Ketogenesis is considered to be controlled by the islet hormones, insulin and glucagon (20). Insulin strongly inhibits ketosis, predominantly by reducing lipolysis in adipocytes and reducing the supply of free fatty acids, the substrate for ketone body production.
Why does DKA cause ketosis?
Ketosis can occur as a result of an extremely low carbohydrate diet, known as a ketogenic diet, or from fasting. DKA only happens when you don't have enough insulin in your body to process blood sugar into energy. If this happens, your liver starts to process fat into energy, which releases ketones into the blood.
What are the causes of ketosis?
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which your blood has a high concentration of ketones, namely beta-Hydroxybutyrate ( 1 ). It occurs when your body starts using fat as its main fuel source due to limited access to glucose, or blood sugar, typically caused by starvation, fasting, or following a very low carb diet ( 1 ).
Why does glucagon increase ketogenesis?
Insulin has a major antilipolytic action and prevents free fatty acids from leaving the adipose tissue. Glucagon stimulates ketogenesis by enhancing fatty acid oxidation in the liver.
What is the purpose of ketogenesis?
At the same time, ketogenesis, i.e. the production by the liver of the ketone bodies β-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate (AcAc), is a physiologically important process to produce an alternative metabolic source of energy during the neonatal period, starvation or prolonged physical effort [30].
Does insulin regulate ketones?
Insulin influences the activity of three key processes: FFA availability (lipolysis), ketone body production (ketogenesis), and disposal in peripheral tissues. All of these processes can be altered in pathophysiologic conditions such as type 1 and type 2 diabetes, obesity, starvation, and hyperthyroidism.
How is ketosis different from ketoacidosis?
Ketosis is a metabolic state the body goes into when it doesn't have enough glycogen from carbohydrates to burn for energy. Ketoacidosis is a complication of diabetes (typically Type 1) that causes the body to produce excess blood acids.
How does DKA cause metabolic acidosis?
Acidosis in DKA is due to the overproduction of β-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid. At physiological pH, these 2 ketoacids dissociate completely, and the excess hydrogen ions bind the bicarbonate, resulting in decreased serum bicarbonate levels.
What is ketoacidosis and why does it happen?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening problem that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body starts breaking down fat at a rate that is much too fast. The liver processes the fat into a fuel called ketones, which causes the blood to become acidic.
What causes glycosuria in diabetes?
Diabetes causes glycosuria because there either isn't enough insulin, or your body can't use what's available. WIthout insulin, blood glucose levels become too high, and your kidneys can't filter and reabsorb it. Your body gets rid of the excess through your urine.
What is the causes of diabetes insipidus?
Diabetes insipidus is caused by problems with a chemical called vasopressin (AVP), which is also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH). AVP is produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary gland until needed. The hypothalamus is an area of the brain that controls mood and appetite.
What hormones are involved in the ketogenic pathway?
Regulation of Ketogenesis. Ketogenesis can be upregulated by hormones such as glucagon, cortisol, thyroid hormones, and catecholamines by causing a more significant breakdown of free fatty acids, thus increasing the amount available to be used in the ketogenic pathway.
Why does the liver not use ketone bodies?
Although it is the primary site that produces ketone bodies, the liver does not use ketone bodies because it lacks the necessary enzyme beta ketoacyl-CoA transferase. Mechanism. Ketogenesis occurs primarily in the mitochondria of liver cells.
What is the name of the pathway that produces ketone bodies?
Biochemistry, Ketogenesis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf. Ketogenesis is a metabolic pathway that produces ketone bodies, which provide an alternative form of energy for the body. The body is constantly producing small amounts of ketone bodies that can make 22 ATP each in normal circumstances, and it is regulated mainly by insulin.
What happens when carbohydrate stores are significantly decreased?
When carbohydrate stores are significantly decreased or fatty acid concentration increases, there is an upregulation of the ketogenic pathway and an increased production of ketone bodies. This can be seen in conditions such as type 1 diabetes, alcoholism, and starvation.
What is the threshold for DKA?
The threshold for DKA is a glucose level of 250. However, it is typically greater than this amount. Once carbohydrate stores become depleted and gluconeogenesis cannot occur anymore, ketogenesis is substantially increased, and greater amounts of ketone bodies are produced.
How is acetoacetate converted to acetone?
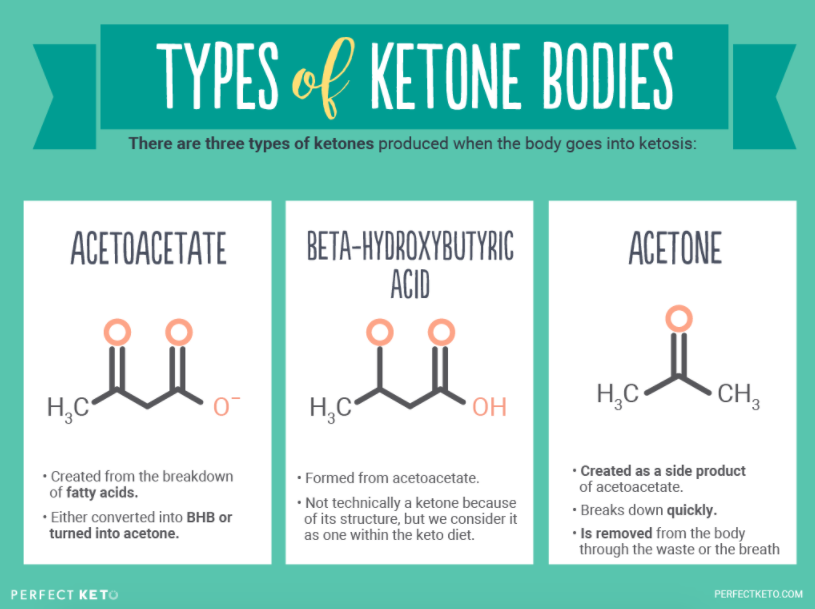
Acetoacetate can be converted to either acetone through non-enzymatic decarboxylation or to beta-hydroxybutyrate via beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. Acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are the two ketone bodies used by the body for energy.
What is the process of producing acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate?
Ketogenesis produces acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate molecules by breaking down fatty acids. These ketones are water-soluble lipid molecules made up of two R-groups attached to a carbonyl group (C = O). Because they are water-soluble, they do not require lipoproteins for transport.
What happens when you have diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus particularly type 1 is a state where alongwith deficiency of insulin there is an increase in counter regulatory hormones like cortisol, adrenaline, growth hormone. These hormones cause lipolysis which means breakdown of lipids. When lipolysis occurs free fatty acids are released. These acids are metabolised to form ketone bodies namely acetone ,acetoacetate , beta hydroxy butyrate. Since there is deficiency of insulin carbohydrate is not utilised for energy production. When these ketones accumulate the body provides a buffer system to neutralise. When the amount of ketones re
How does insulin deficiency affect lipolysis?
In diabetes due to the insulin deficiency there is increased hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipolysis And this lipolysis inturn increases free fatty acids. Now you know that as insulin is deficient in diabetes glucose cant be utilised as a energy source. So to get the energy an alternative source of these free fatty acids are used. End ketones being the end product of this fatty acid metabolism it gets accumulated. Initially it causes ketonemia (increased ketone bodies in blood) but this cycle keeps on going at ketoacidosis occurs.
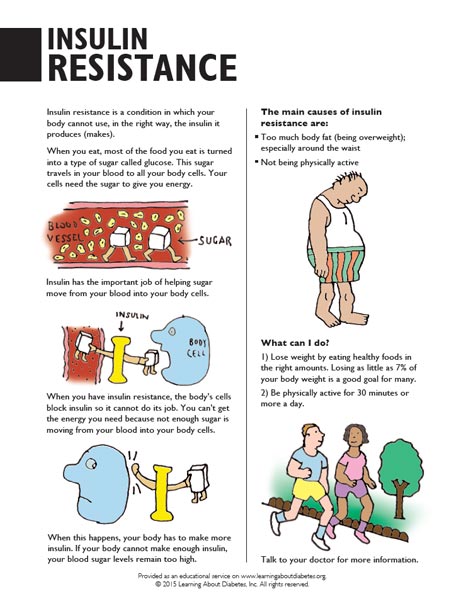
How does insulin help with diabetes?
Normally, insulin helps sugar enter your cells. Without enough insulin, your body can't use sugar properly for energy. This prompts the release of hormones that break down fat as fuel, which produces acids known as ketones. Excess ketones build up in the blood and eventually "spill over" into the urine. The ketogenic (keto) diet, high in fat and low in carbs, can potentially change the way your body stores and uses energy, easing diabetes symptoms. ... The ketogenic diet may improve blood glucose (sugar) levels while also reducing the need for insulin. However, the diet does come with risks. G
Does drinking water help with ketoacidosis?
The condition develops when your body can't produce enough insulin. Many people suggest that drinking more water may help reduce a person's keto breath. This is because the body expels more ketones in urine rather than as a breath. By drinking water, people will produce more urine, which will help expel many of the ketones from the body. Go to my Profile and you can find all about Keto Diet material there...
What causes ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is usually triggered by: An illness. An infection or other illness can cause your body to produce higher levels of certain hormones, such as adrenaline or cortisol. Unfortunately, these hormones counter the effect of insulin — sometimes triggering an episode of diabetic ketoacidosis.
What is the treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is treated with fluids, electrolytes — such as sodium, potassium and chloride — and insulin. Perhaps surprisingly, the most common complications of diabetic ketoacidosis are related to this lifesaving treatment.
Why is there so little insulin in my system?
Missed insulin treatments or inadequate insulin therapy or a malfunctioning insulin pump can leave you with too little insulin in your system, triggering diabetic ketoacidosis.
How long does it take for ketoacidosis to develop?
Diabetic ketoacidosis signs and symptoms often develop quickly, sometimes within 24 hours. For some, these signs and symptoms may be the first indication of having diabetes. You may notice: Excessive thirst. Frequent urination. Nausea and vomiting. Stomach pain. Weakness or fatigue.
How to check blood sugar levels?
Monitor your blood sugar level. You might need to check and record your blood sugar level at least three to four times a day, or more often if you're ill or stressed.
Can ketones cause shortness of breath?
You have ketones in your urine and can't reach your doctor for advice. You have many signs and symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis — excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, stomach pain, weakness or fatigue, shortness of breath, fruity-scented breath, and confusion.
Is ketoacidosis a risk factor?
Risk factors. The risk of diabetic ketoacidosis is highest if you: Have type 1 diabetes. Frequently miss insulin doses. Uncommonly, diabetic ketoacidosis can occur if you have type 2 diabetes. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis may be the first sign that you have diabetes.
How does ketogenesis occur?
Ketogenesis may or may not occur, depending on levels of available carbohydrates in the cell or body. This is closely related to the paths of acetyl-CoA: 1 When the body has ample carbohydrates available as energy source, glucose is completely oxidized to CO 2; acetyl-CoA is formed as an intermediate in this process, first entering the citric acid cycle followed by complete conversion of its chemical energy to ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. 2 When the body has excess carbohydrates available, some glucose is fully metabolized, and some of it is stored in the form of glycogen or, upon citrate excess, as fatty acids (see lipogenesis ). Coenzyme A is recycled at this step. 3 When the body has no free carbohydrates available, fat must be broken down into acetyl-CoA in order to get energy. Under these conditions, acetyl-CoA cannot be metabolized through the citric acid cycle because the citric acid cycle intermediates (mainly oxaloacetate) have been depleted to feed the gluconeogenesis pathway. The resulting accumulation of acetyl-CoA activates ketogenesis.
Which hormones regulate ketogenesis?
Insulin and glucagon are key regulating hormones of ketogenesis, with insulin being the primary regulator. Both hormones regulate hormone-sensitive lipase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Hormone-sensitive lipase produces diglycerides from triglycerides, freeing a fatty acid molecule for oxidation. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes the production ...
What is the role of AMPK in ketogenesis?
Ketogenesis in healthy individuals is ultimately under the control of the master regulatory protein AMPK, which is activated during times of metabolic stress, such as carbohydrate insufficiency. Activation in the liver inhibits lipogenesis, promotes fatty acid oxidation, switches off acetyl-CoA carboxylase, turns on malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, ...
Which amino acids are ketogenic?
Deaminated amino acids that are ketogenic, such as leucine, also feed TCA cycle, forming acetoacetate & ACoA and thereby produce ketones. Besides its role in the synthesis of ketone bodies, HMG-CoA is also an intermediate in the synthesis of cholesterol, but the steps are compartmentalised. Ketogenesis occurs in the mitochondria, whereas ...
How is acetone metabolized?
Acetone, which is generated through the decarboxylation of acetoacetate, either spontaneously or through the enzyme acetoacetate decarboxylase. It can then be further metabolized either by CYP2E1 into hydroxyacetone (acetol) and then via propylene glycol to pyruvate, lactate and acetate (usable for energy) and propionaldehyde, ...
Where are ketones produced?
Ketone bodies are produced mainly in the mitochondria of liver cells , and synthesis can occur in response to an unavailability of blood glucose, such as during fasting. Other cells, e.g. human astrocytes, are capable of carrying out ketogenesis, but they are not as effective at doing so. Ketogenesis occurs constantly in a healthy individual.
Does acetyl-CoA cause ketone bodies to increase?
The accumulation of acetyl-CoA in turn produces excess ketone bodies through ketogenesis. The result is a rate of ketone production higher than the rate of ketone disposal, and a decrease in blood pH. There are some health benefits to ketone bodies and ketogenesis as well.
What causes DKA in diabetics?
Missing insulin shots, a clogged insulin pump, or the wrong insulin dose. Other causes of DKA include: Heart attack or stroke. Physical injury, such as from a car accident. Alcohol or drug use. Certain medicines, such as some diuretics (water pills) and corticosteroids (used to treat inflammation in the body).
What happens when you have too many ketones?
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up to dangerous levels in your body. Read on to learn more about DKA, how you can prevent DKA, and how to treat it if needed.
What is DKA in diabetes?
DKA is most common among people with type 1 diabetes. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA. DKA develops when your body doesn’t have enough insulin to allow blood sugar into your cells for use as energy. Instead, your liver breaks down fat for fuel, a process that produces acids called ketones. When too many ketones are produced too ...
What does DKA mean in Spanish?
Español (Spanish) minus. Related Pages. Elevated ketones are a sign of DKA, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated right away. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening. DKA is most common among people with type 1 diabetes.
How to prevent DKA?
Prevent DKA. DKA is a serious condition, but you can take steps to help prevent it: Check your blood sugar often, especially if you’re sick. Keep your blood sugar levels in your target range as much as possible. Take medicines as prescribed, even if you feel fine.
Can you test for ketones if you have DKA?
You should also test for ketones if you have any of the symptoms of DKA. Call your doctor if your ketones are moderate or high. Elevated ketones are a sign of DKA, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Is keto diet good for diabetes?
The ketogenic, or keto, diet is popular as a way to help people lose weight. But is it a safe, effective method to keep diabetes under control? Scientists are still studying how the diet affects people with the condition, but here’s what we know.
Is ketoacidosis a type 1 diabetes?
But ketoacidosis is a dangerous condition that happens when your body doesn’t have enough insulin and ketones build up too much. Symptoms include excessive thirst, urinating often, confusion, and weakness or fatigue. It’s more common for people with type 1 than type 2.
Does keto help with diabetes?
There are fewer studies looking at the keto diet for people with type 1 diabetes. One small study found that it helped people with type 1 lower their A1c levels, but we need a lot more research to get the full picture of the diet’s effects.
Does ketosis lower A1C?
Ketosis happens with much lower, safer levels of ketones than ketoacidosis. In fact, this process happens in the course of everyday life, depending on the amount of carbs and proteinyou eat. It’s the state that can lead to weight loss, especially belly fat, and lower A1c for many people with diabetes.
Can you get keto if you have type 1 diabetes?
That depends on the type of diabetes you have. In general, people with type 2 who are overweightseem to get good results safely. If you have type 1 and want to try the keto diet, it’s essential that you talk to your doctor first. You’ll need to carefully monitor your health and watch for signs of ketoacidosis.
Does keto make diabetes worse?
But for others, the keto diet could make diabetes worse.
What causes DKA in diabetics?
There is often a particular underlying problem that has led to the DKA episode; this may be intercurrent illness ( pneumonia, influenza, gastroenteritis, a urinary tract infection ), pregnancy, inadequate insulin administration (e.g. defective insulin pen device), myocardial infarction (heart attack), stroke or the use of cocaine. Young people with recurrent episodes of DKA may have an underlying eating disorder, or may be using insufficient insulin for fear that it will cause weight gain.
Why does ketoacidosis occur?
Diabetic ketoacidosis arises because of a lack of insulin in the body. The lack of insulin and corresponding elevation of glucagon leads to increased release of glucose by the liver (a process that is normally suppressed by insulin) from glycogen via glycogenolysis and also through gluconeogenesis.
How is diabetic ketoacidosis diagnosed?
Diabetic ketoacidosis may be diagnosed when the combination of hyperglycemia (high blood sugars), ketones in the blood or on urinalysis and acidosis are demonstrated. In about 10% of cases the blood sugar is not significantly elevated ("euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis").
What causes DKA in the body?
Triggers may include infection, not taking insulin correctly, stroke and certain medications such as steroids. DKA results from a shortage of insulin; in response, the body switches to burning fatty acids, which produces acidic ketone bodies.
How long does it take for ketoacidosis to show symptoms?
Signs and symptoms. The symptoms of an episode of diabetic ketoacidosis usually evolve over a period of about 24 hours. Predominant symptoms are nausea and vomiting, pronounced thirst, excessive urine production and abdominal pain that may be severe. In severe DKA, breathing becomes rapid and of a deep, gasping character, ...
What is the risk of death for diabetic mellitus type 1?
Previously considered universally fatal, the risk of death with adequate and timely treatment is around 1–4% .
What is the treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis?
The main aims in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis are replacing the lost fluids and electrolytes while suppressing the high blood sugars and ketone production with insulin. Admission to an intensive care unit (ICU) or similar high-dependency area or ward for close observation may be necessary.
Overview
- Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when your body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. The condition develops when your body can't produce enough insulin. Insulin normally plays a key role in helping sugar (glucose) — a major source of energy for your muscles and other tissues — enter your cells. ...
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
Prevention