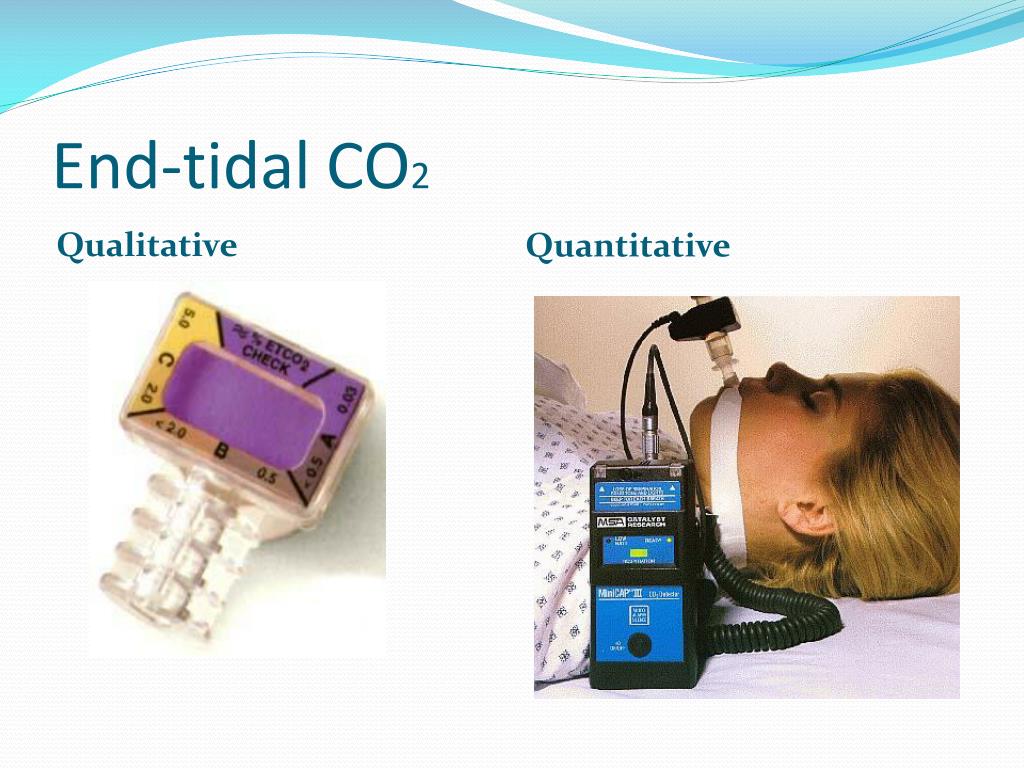
Why is end tidal CO2 important? End-tidal carbon dioxide (ETco 2) monitoring provides valuable information about CO2 production and clearance (ventilation). Also called capnometry or capnography, this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
What is the abbreviation for end tidal carbon dioxide?
End-tidal carbon dioxide (ETco 2) monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance (ventilation). Also called capnometry or capnography, this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. In fact, it’s commonly called the “ventilation vital sign.”.
What are the symptoms of CO2 retention?
- Acute paranoia, depression, or confusion
- Coma
- Dilation (widening) of blood vessels in the skin
- Fainting
- Hyperventilating
- Panic attack
- Respiratory failure
- Seizure
- Swelling of the optic nerve ( papilledema)
What can we do with CO2?
These uses of CO2 could cut emissions — and make trillions of dollars
- Concrete building materials. There are several technologies here, all related to concrete, which is a mix of cement, water, and aggregates.
- Liquid fuels. Today, liquid fuels — gasoline, diesel, and more rare variants like jet fuel — are made by refining hydrocarbons drilled from underground.
- Chemicals and plastics. ...
- Algae. ...
- Novel materials. ...
What is the difference between CO2 and 2CO2?
What is the difference between CO2 and 2co2? The substance with the chemical formula is called as carbon dioxide, whereas ( )is called as dicarbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is composed of 1 atom of carbon and 1 atom of Oxygen, whereas dicarbon dioxide is composed of 2 carbon atoms and 2 oxygen atoms.

What is the significance of end tidal CO2?
In critical care, End Tidal CO2 monitoring is used to assess adequacy of circulation to the lungs, which provides clues about circulation to the rest of the body. Low EtCO2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion, which can be caused by hypovolemia, sepsis or dysrhythmias.
What do you want end tidal CO2 to be?
Teams should aim for EtCO2 at least >10 mm Hg and ideally >20 mm Hg. Where do these numbers come from? These values are approximately 1/4 the normal EtCO2 (35-45 mm Hg), and ideal CPR will provide at least 1/4 of cardiac output. This is an example of capnography during CPR.
What is a good end tidal?
Remember, a normal end-tidal is between 35 and 45.
How does ETCO2 reflect cardiac output?
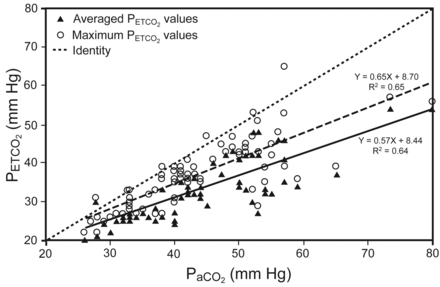
We conclude that the increase in Pvco2 and the concurrent decrease in ETco2 reflect a critical reduction in cardiac output, which reduces alveolar blood flow to the extent that carbon dioxide clearance by the lung fails to keep pace with systemic CO2 production.
What should CO2 be during CPR?
On average during CPR, if adequate chest compressions are being delivered a cardiac index of 1.6-1.9 L/min/m2 can be generated, which correlates with ETCO2 pressures of 20mmHg. (1) ACLS guidelines define high quality chest compressions as achieving ETCO2 pressures of at least 10-20 mmHg.
What does an ETCO2 of greater than 40 indicate?
If the values rise to normal (35-45) or above, the patient probably has had a return of pulse so check the rhythm and pulse carefully at the next rhythm check. Keep in mind this monitoring can be accomplished even if no advanced airway is inserted. Here is a great example of ETCO2 monitoring during an arrest.
What is the normal range of ETCO2 in MM?
End-tidal CO2 - EtCO2 is a noninvasive technique which represents the partial pressure or maximal concentration of CO2 at the end of exhalation. Normal value is 35-45 mmHg.
What is the target range for ETCO2 in a trauma patient?
Standardized ventilation protocols were used by most paramedics; however, one agency instituted ETCO2 monitoring during the second trial year, with paramedics instructed to target ETCO2 values of 30 to 35 mmHg.
What is ETCO 2 monitoring?
A standard of care in the operating room for more than 25 years, ETco 2 monitoring is becoming a common adjunct in the intensive-care and procedural-care settings.
What gases diffuse from the alveolus?
As a result, oxygen from the alveolus (where Po 2 is about 100 mm Hg) diffuses into the blood, and CO 2 diffuses from the blood into the alveolus (where Pco 2 measures about 40 mm Hg). Because inspired air has negligible CO 2 amounts (less than 0.04%), exhaled CO 2 can be monitored and used as a correlate to assess CO 2 gas exchange and effective ventilation.
What is ETCO 2?
ETco 2 monitoring yields significant information about a patient’s ventilation status when combined with thorough physical assessment. It can be used in a wide range of settings, from prehospital settings to emergency departments and procedural areas.
Where is ETCO 2 used?
It’s commonly used in procedural areas, such as gastroenterology labs, where moderate sedation is administered. Its main limitations are cost and the need for a monitor separate from the bedside monitor or ventilator. Interpreting ETco 2 monitoring data.
Does ETCO 2 indicate acid-base balance?
While ETco 2 monitoring doesn’t directly indicate acid-base balance, it can shed light on ventilation efficacy. CO 2 combines with water to create H 2 CO 3, which can degrade to bicarbonate, water, and CO 2.
Can ETCO 2 be used in non-intubated patients?
Although ETco 2 is used in non-intubated patients, here we focus on its use in patients with endotracheal intubation. Keep in mind that ETco 2 findings are interpreted within the context of physical and other traditional assessment methods.
What is end tidal capnography?
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) at the end of an exhaled breath.
When is end-tidal capnography recommended?
Usually, end-tidal capnography is used by emergency physicians and paramedics to determine the respiration of the patient. End-tidal capnography can also be used in the following settings:
What is phase 2 of CO2?
Phase II: In this phase, CO2 from the lungs reaches the upper airway and mixes with dead space air, which causes a rapid increase in CO2. Carbon is detected using capnogram in exhaled air. It is also called an ascending phase or early exhalation.
Where is CO2 recorded in phase 3?
Phase III: In this phase, there is CO2 recorded uniformly in the nose/mouth and lungs.
What is etco2 monitoring?
End-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) monitoring is a measure of metabolism, perfusion, and ventilation. In the ED, we typically think of a EtCO2 as a marker of perfusion and ventilation. However, EtCO2 is an extremely powerful surrogate for endotracheal tube (ETT) P osition, CPR Q uality, R eturn of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), S trategies for treatment, and T ermination (of CPR). Do these letters look familiar? They should! In this post we take a deep dive into each of these potential uses of EtCO2 in the ED.
How specific is an increase in etCO2?
An increase of EtCO2 to normal values (35-45 mm Hg) or an increase by 10 mm Hg is about 97% specific. One caveat is that sodium bicarbonate may transiently raise the EtCO2, but this does not reflect ROSC. 2.
What is the normal etCO2 for CPR?
Where do these numbers come from? These values are approximately 1/4 the normal EtCO2 (35-45 mm Hg), and ideal CPR will provide at least 1/4 of cardiac output.
How long does it take for EtCO2 to be able to terminate CPR?
EtCO2 may provide an additional data point when deciding whether it is appropriate to terminate CPR. Approximately 20 minutes into a resuscitation, the likelihood of ROSC is significantly higher if EtCO2 >20 mm Hg and much less if EtCO2 <10 mm Hg. 4
Is etCO2 used in CPR?
There is incredible utility in using EtCO2 in CPR. Examples include:
Background
Position of The Ett
- ACEP’s policy on verification of ETT placement reminds us that physical examination and fogging in the tube are not reliable to confirm placement. Providers should use EtCO2 detectors (e.g. waveform capnography or colorimetry) to confirm ETT position. Ultrasound in the hands of an experienced provider is also recommended. 3 Waveform EtCO2 (versus colorimetric) can be par…
Quality of CPR
- EtCO2 is essentially to ensuring quality CPR. We typically assess quality of CPR by palpable pulses, but this can be challenging and even unreliable. Arterial diastolic pressure >25 mm Hg may be useful, but not all patient scenarios will be amenable to placement of an arterial line. However, EtCO2 provides the same information and is more reliable....
Return of Spontaneous Circulation
- With the use of EtCO2, teams may recognize ROSC before a scheduled pulse check. An increase of EtCO2 to normal values (35-45 mm Hg) or an increase by 10 mm Hg is about 97% specific. One caveat is that sodium bicarbonate may transiently raise the EtCO2, but this does not reflect ROSC.2
Strategies For Treatment
- The waveform morphology during CPR can help us decide what our next intervention should be. Examples include ETT dislodgment, cuff leak, and bronchospasm.
Termination
- EtCO2 may provide an additional data point when deciding whether it is appropriate to terminate CPR. Approximately 20 minutes into a resuscitation, the likelihood of ROSC is significantly higher if EtCO2 >20 mm Hg and much less if EtCO2 <10 mm Hg.4
Caveats
- The PQRST mnemonic should be applied to patients with an ETT. The utility of EtCO2 in patients who are receiving bag mask ventilation (BVM) or have a laryngeal mask airway (LMA) is less understood and researched. The correlation between serum pCO2 and EtCO2 is also less understood; animal studies do not show much correlation, and as you would expect with CPR, th…
Take-Home Points
- There is incredible utility in using EtCO2 in CPR. Examples include: 1. Evaluating the position of the ETT 2. Evaluating the quality of CPR 3. Timely recognition of ROSC 4. Identifying best treatment strategies 5. Contributing to the decision to terminate resuscitation Keep these points in mind the next time you receive an alert that a patient is en route with CPR in progress! Check …