The significance of Guttation is as follows:
- It helps the plants to dispose of the unwanted solutes.
- It helps the plants to improve the acquisition of nutrients.
- It helps in maintaining water balance for the proper growth and development of the plant body.
- It helps in the progressive development of hydrostatic pressure that helps to pump water up to the leaves.
What is guttation?
· Why is Guttation important? Moreover these cells are very active in transporting water and other cellular components. Thus the epithem cells play a significant role in Guttation process. Guttation can also cause injuries to plants-depletion of vital nutrients, burns at the tips of leaves and hydathodes can allow microorganisms that infect plants.
What is the importance of guttation in plants?
Significance of Guttation The significance of Guttation is as follows: It helps the plants to dispose of the unwanted solutes. It helps the plants to improve the acquisition of nutrients. It helps in maintaining water balance for the proper growth and development of the plant body.
What is the purpose of guttation test?
· The importance of guttation for plants can be understood by the fact that it serves as a pressure-release valve in precipitation and continuous absorption of water, with resultant progressive development of hydrostatic pressure that pumps water up in the leaves.
What is Guttation fluid and why should you care?
Guttation is the expelling of excess water or nutrients through tiny openings on leaves and stems. This biological process enables plants to restore balance between their nutrient and water …

What is guttation responsibility?
Root pressure is the most important force responsible for guttation in plants. Guttation is the loss of water in the form of liquid through hydathodes.
Is guttation good for plants?
It isn't a common reaction, but guttation is one way of helping the plant evacuate excess water around roots. It's a coping the plant uses to protect roots from rotting.
What is guttation How is transpiration beneficial for the plant?
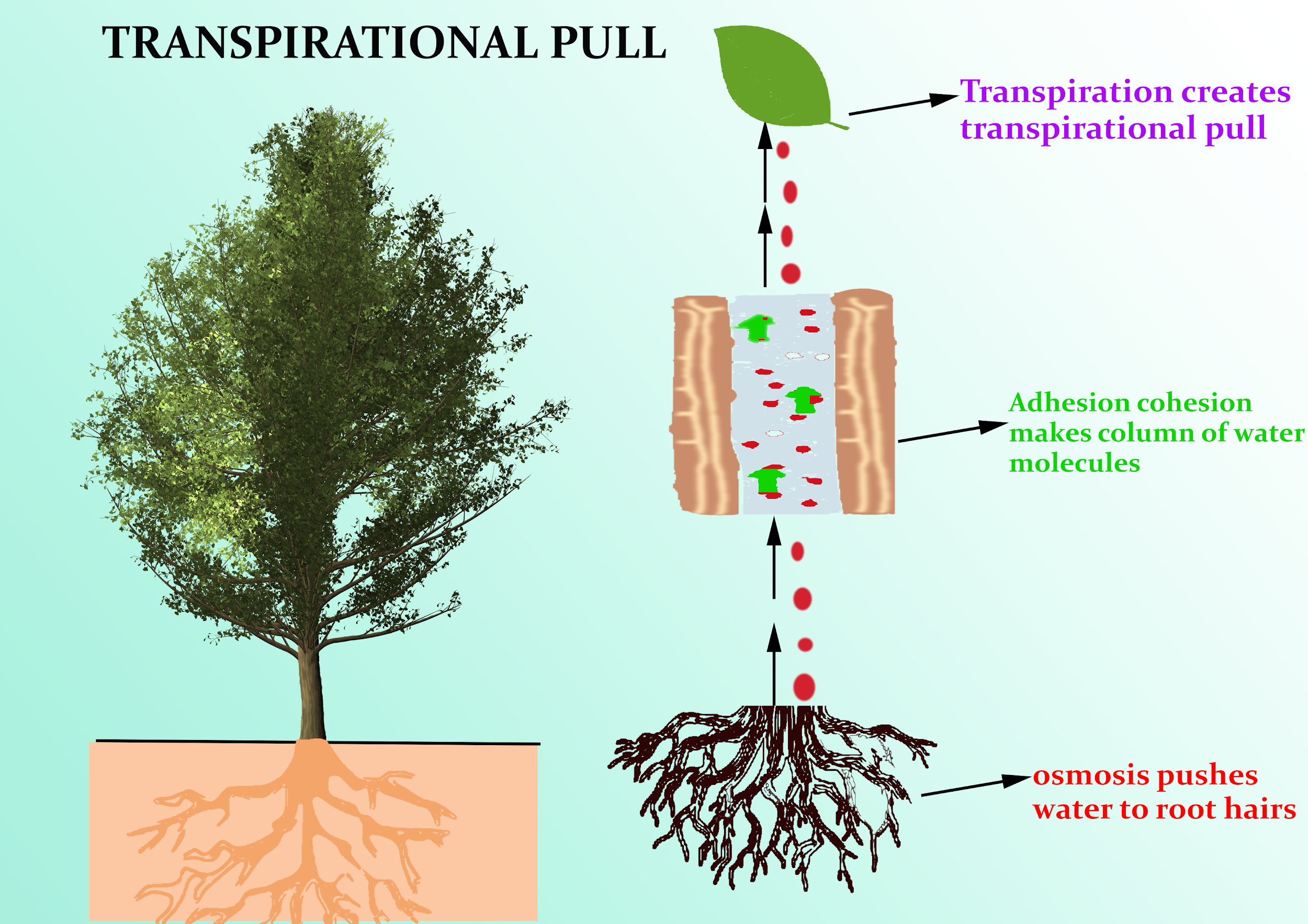
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. Water is necessary for plants but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. The remaining 97–99.5% is lost by transpiration and guttation.
Is too much guttation bad?
This is actually a very natural phenomenon in many plants, including monsteras. This common occurrence is called guttation, and it's nothing to worry about!
Why is my plant crying?
When leaves lose water as a liquid phase through special cells called hydathodes it is referred to as guttation. These guttation “tears” appear at the leaf margins or tips and contain various salts, sugars and other organic substances.
What is guttation for kids?
The process by which plants balance the amount of water they take in is called guttation. Plants like grass, wheat, tomatoes etc: have a vascular system. In these plants, the water accumulates at the tip of the leaves. This is called guttation.
What is guttation in plants?
Guttation is the exudation of drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves of some vascular plants, such as grasses, and a number of fungi. Guttation (from Latin gutta drop) is not to be confused with dew, which condenses from the atmosphere onto the plant surface.
What is the difference between transpiration and guttation?
Transpiration is the removal of water from the stomata present on the leaves. On the contrary, guttation is the process of removal of water from the hydathodes.
Q.1. What is Guttation?
Ans: Guttation is defined as the process of loss or excretion of water in the form of liquid droplets from the tips and margins of the leaves.
Q.2. What is the difference between transpiration and guttation?
Ans: Transpiration usually occurs during the day, whereas Guttation usually occurs at night or early in the morning. Transpiration occurs through s...
Q.3. Why is Guttation in plants important?
Ans: a. It helps in the disposal of unwanted solutes by the plants. b. It helps to improve the acquisition of nutrients by the plants. c. It helps...
Q.4. Is guttation good or bad?
Ans: Guttation is completely a natural phenomenon that is not at all harmful to plants. However, suppose more amount of fertilisers is used for the...
Q.5. What causes Guttation?
Ans: Guttation is caused when the transpiration is suppressed and relative humidity is maximum, as seen during the night. Primarily, root pressure...
When is the guttation process observed?
In general, the guttation process is observed the most when the transpiration is suppressed and relative humidity is maximum, as seen during the night.
What is guttation fluid?
Guttation fluid helps for non-invasive measurements and organic and inorganic chemical quantification.
What is the process of loss or excretion of water in the form of liquid droplets from the tips and margin
Q.1. What is Guttation ?#N#Ans: Guttation is defined as the process of loss or excretion of water in the form of liquid droplets from the tips and margins of the leaves.
What is water lost in guttation?
Water lost in Guttation is impure water, i.e., a dilute solution of different inorganic and organic salts.
What is the fluid that comes out of guttation?
The fluid coming out of Guttation often contains a variety of organic and inorganic compounds, mainly sugars and potassium.
Do all plants show guttation?
All plants do not show Gut tation. It is restricted to about 345 genera of herbaceous and some woody plants like garden nasturtium, oat, and other cereals, balsam, tomato, cucurbits.
Definition of Guttation
Guttation is the secretion of water in the form of water droplets of xylem sap on the tips or edges of small herbaceous plants such as grasses or such plants that don't have any kind of woody branches above the ground.
Brief Explanation on Guttation
Plants have small organs that connect their vasculature (veins) to the external world. These are called hydathodes. These organs are in the form of small pores, which also serves as a safe entry passage for the vascular pathogens (mainly disease-causing microbes). Guttation mainly occurs at night.
Process of Guttation
Transpiration does not usually arise at night since most plants' stomata are closed. Water will enter plant roots when the soil moisture level is high, because the water potential of the roots is lower than that of the soil solution. Water will gather within the plant, resulting in a minor root pressure.
Impact of Guttation
The status quo of guttation in fungus is crucial. Guttation fluid may contain a selection of natural and inorganic substances, the most common of which can be sugars and potassium. While the leaves start to dry, a white crust forms on the surface.
Uses of Guttation
The chemicals in guttation water provide opportunity for non-invasive tests to determine the nutritional status of soil and plants provided some interesting observations on the impact of guttation water on soil fertility.
Important Things To Remember
Guttation is the release of water in the form of water droplets of xylem sap at the ends or edges of small herbaceous plants such as grass or plants that do not have woody branches on the ground. At night, when root pressure is high, water droplets exit the vessels with the help of openings called "Hydathodes".
Sample Questions
Ans: Guttation is the secretion of water in the form of water droplets of xylem sap on the tips or edges of small herbaceous plants such as grasses or such plants that don't have any kind of woody branches above the ground.
Where does guttation come from?
It comes from latin “gutta” which means “drop”. An easy memory trick is to remember words in English like “gutter” and French “goutte” (also “drop”) and go from there. To understand why plants developed guttation as they evolved, it helps to brush up the following: how water is used in a plant.
Why does guttation occur in tropical forests?
In tropical regions, a lot of guttation occurs. This is because air moisture is often very high, which makes transpiration difficult. In a jungle, it’s quite common for it to be “raining” from the canopy even though not a cloud is in sight. In mangroves, guttation is how the trees return excess salt to the sea.
What plants are good for guttating?
Plants with sawtooth-like leaf edges ( serrated leaves) are usually good guttators. Grasses – almost all types of grasses, from the Pennisetum family to the banana tree, including fescue and bamboo. More often then not, when your lawn is wet in the morning, it’s not dew but guttation.
How high do plants gutt?
They all share their short height in common: guttation rarely occurs higher than 3 feet (1 meter) above ground . Only a few tree species that love wet soils are very prone to guttating.
Does guttation take over during daytime?
Even during daytime, guttation must take over to get sap circulating through the plant.
What does "gutta" mean?
“Guttant” is the fluid expelled. It comes from latin “gutta” which means “drop”.
Where are hydathodes placed?
Hydathodes are usually placed around the rim or tips of leaves, on the leaf surface, or at junctures between leaves and stems. Less than 5 % of all water that goes in a plant is released through guttation. Nine tenths is from transpiration, a more powerful phenomenon.
What is guttation dew?
Last but not least guttation should not be confused with dew. Dew is basically the condensation from the atmosphere onto the leaf surface. Share this with your friends.
When does guttation occur in plants?
So, guttation happens when the climate is cold and humid which is mostly during the night or very early in the morning. Transpiration occurs during the day when it is dry and hot.
What is the process of water gutting?
During the process when water undergoes guttation it will also pick up minerals and enzymes, such a process is called a xylem sap.
What is the difference between transpiration and guttation?
However, as mentioned earlier there is a difference between guttation and transpiration. Water is vital for plants. So, most of the key terms of plants always relate to water. The two words guttation and transpiration are also related to water in plants. Guttation in plants happens when the stomata are closed but transpiration in plants happen ...
Why is guttation important to plants?
Guttation is of negligible importance to plants. Occasionally, injury to leaf margins is caused by deposits of minerals left by evaporation of guttated water and it is claimed that the guttated liquid provides a pathway for the entrance of pathogenic organisms.
What is guttation in plants?
Guttation serves as a measure of injurious elements in plants and also carries the biological significance of elimination of unwanted products with it Therefore, one way in which plants are able to dispose of such compounds is via the mechanism of guttation.
Why do conifers have no guttation?
No guttation has ever been reported in conifers, as would be expected because of the absence of root pressure, but artificial guttation can be caused by subjecting the root system to pressure ( Klepper and Kaufmann, 1966 ). Guttation is of negligible importance to plants.
Why do trees gutt at night?
In tropical rain forests, guttation is common at night, but it is uncommon in woody plants of the Temperate Zone because the necessary combination of warm, moist soil and very humid air is less common than in the tropics. A few instances of guttation from the twigs of trees have been reported (Büsgen and Münch, 1931).
Does amiben inhibit guttation?
Thus, amiben seems to inhibit guttation in wheat. A current subject of discussion is whether the active secretions of water by plants (guttation) might be of significance for bees on account of residues of neonicotinoid pesticides possibly contained in them.
What is the radioactive component in guttation fluid?
Identification of the radioactive component in the guttation fluid should indicate the form of amiben transported from roots to shoots. Amiben (3-amino-2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid) is widely used as a herbicide for weed control in soybeans.
Is insect diversity greater in urban areas than rural areas?
If you recall from the earlier chapters, insect and plant diversity are greater in suburban areas compared to rural and inner-city areas. There is a growing conservation movement among landscape designers and managers, and urban gardeners to maintain urban green spaces as refuges for state and regional insect biodiversity. The dependence on urban spaces as a haven for insect biodiversity is commonly discussed in academic circles (87,88). These same urban areas, however, overlap in the United States with an extensive presence of insecticides. Recently, two species, the western honey bee and the Monarch butterfly, have dominated much of the published literature on insect conservation in urban landscapes, particularly relative to insecticide use ( Box 9.2 ). The concern and research efforts are related to significant population declines in overwintering Monarch butterflies in Mexico (89) and extensive annual overwintering losses in commercial western honey bee populations. In 2015, the United States EPA (90) released a preliminary report documenting 17 reported bee kill incidents associated with the use of neonicotinoid insecticides. Of those, nine were applications made to either landscape ornamental or turfgrass or in residential/urban areas. As discussed earlier, systemic insecticides move through (translocate) plant tissues. Certain neonicotinoid insecticides readily translocated into nectar and pollen in flowers, or guttation water of treated grasses and ornamental plants (29,30,91–93). Bees can also have seasonal effects on colony health from limited exposures to plant treated with certain neonicotinoid insecticides (94). In turfgrass, the primary concern is the treatment of flowering weeds like clover and dandelions ( Fig. 9.2) that are common plant associates and pollinator resources in urban lawns (95). The applications of many different types of insecticides, and not just neonicotinoids, can negatively impact beneficial insects by visiting flowers treated with insecticides or flowers on treated plants (94,96). For this reason, flower removal, via mowing, has been a recommended practice as a way to reduce hazards to beneficial insects visiting flowering weeds in lawns (91,96,97). In flowering ornamental plants, most insecticides now restrict applications of insecticides while plants are in flower. This has prompted research to investigate the timing of systemic insecticide applications relative to concentrations detected in the flowers. Ornamental plants have relatively high labeled rates for systemic insecticides per plant, especially when applied as a soil drench to trees and shrubs (29,30,93). There are few studies gauging insecticide translocation into pollen and nectar for ornamental plants. From those few studies, it is clear that treatment of plants weeks or months before bloom can translocate into pollen and nectar. Levels of insecticides detected in pollen or nectar, however, may not always exceed the current thresholds for acute or chronic toxicity to beneficial insects that visit ornamental plants ( Fig. 9.3 ). Furthermore, the active ingredients within the neonicotinoid chemical class have different ecotoxicological profiles. Finally, many insecticide labels have a range of rates that can be legally applied. For example, applications of thiamethoxam (a neonicotinoid insecticide) at the low range of the labeled rate as a foliar spray or drench never exceed threshold levels in pollen of annual sunflower. But, drench applications of the same active ingredient to annual sunflower at any time 10 weeks or less before bloom will produce above threshold levels in pollen (93).
Why is guttation visible?
Guttation is most noticeable when transpiration is suppressed and the relative humidity is high, such as during the night. Guttation formation in fungi is important for visual identification, but the process causing it is unknown.
What is the nutrient in Guttation fluid?
Guttation fluid may contain a variety of organic and inorganic compounds, mainly sugars, and potassium. On drying, a white crust remains on the leaf surface.
What is Guttation in Plants?
Water is essential in order for a plant to grow, germinate, and carry out its ultimate goal of reproduction. However, too much water could endanger the plant's survival by limiting the supply of oxygen, which is required for the plant to be able to breathe. Many small plants have a sort of built-in safety mechanism to alleviate this concern.
Guttation vs. Transpiration
Transpiration is another process used by plants to carry water throughout their vascular systems, and it can be easily confused with guttation. However, the two mechanisms are distinctly different because they occur under different conditions, take place at different times of day, and produce different types of liquids. More specifically:
Role of Hydathodes in Guttation
Transpiration may only take place during the day because of a reliance on the plant's stomata, or small pores located on the surface of a leaf.
