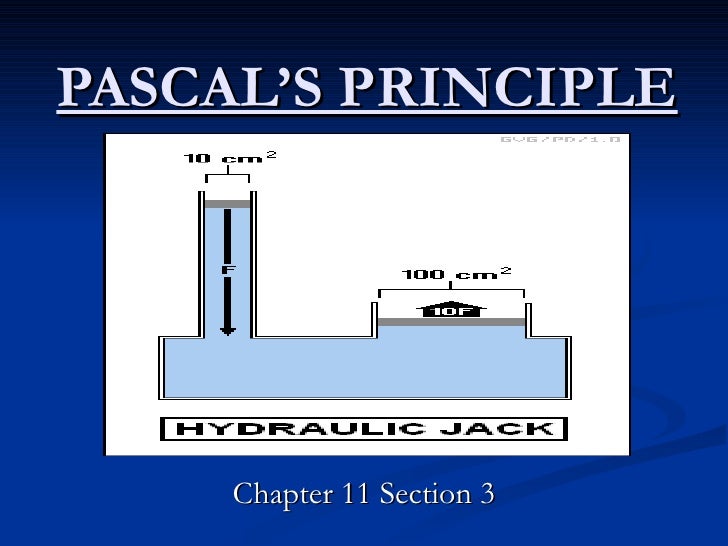
Pascal’s principle is what makes pressure so important in fluids. Since a change in pressure is transmitted undiminished in an enclosed fluid, we often know more about pressure than other physical quantities in fluids.
What does pascals principle help to explain?
Pascal's Law
- Pascal Law Formula. Where F is the force applied, P is the pressure transmitted, and A is the cross-sectional area.
- Example of Pascal’s Law. Let us understand the working principle of Pascal’s law with an example. ...
- Applications of Pascal’s Law. ...
- Pascal’s Law Derivation. ...
How do you use pascals principle in daily lives?
Section Summary
- Pressure is force per unit area.
- A change in pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to all portions of the fluid and to the walls of its container.
- A hydraulic system is an enclosed fluid system used to exert forces.
What is the formula for pascals principle?
Where:
- p is the total pressure at depth
- h is the measure in Pascals
- p_0 is the pressure on the free surface of the fluid
- rho is the density of the fluid
- g is the acceleration of gravity.
What are some examples of Pascal's principle?
Pascal's law finds numerous examples in our daily life such as :
- automobiles
- hydraulic brake system
- hydraulic jack
- hydraulic press
- hydraulic machines.

What is Pascal’s Law?
According to Pascal’s Law, “The external static pressure applied on a confined liquid is distributed or transmitted evenly throughout the liquid in...
What is the application of Pascal’s Law?
Hydraulic lift work on the principle of Pascal’s Law.
Does Pascal’s Law apply to gases?
Pascal’s Law applies to gases. Pascal’s principle is also known as the principle of transmission of fluid (which is water or gas) pressure.
Who stated Pascal’s Law?
French mathematician Blaise Pascal stated the Pascal law in 1653.
What is the principle of Pascal’s Law?
Pascal’s law says that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid will be transmitted without a change in magnitude to every point of the fluid and the...
What is Pascal's principle?
Pascal's principle says that a change in pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to all portions of the fluid and to the walls of its container. Mathematically, pressure is force, F, measured in Newtons, divided by area, A, measured in meters squared (F / A). So Pascal's principle says that the pressure, F divided by A, ...
What is the application of Pascal's principle?
Applications of Pascal's Principle. Hydraulics is defined as the branch of science and technology concerned with the conveyance of liquids through pipes and channels, especially as a source of mechanical force or control. And this is by far the most common application of Pascal's principle. There are many, many uses of the principle, ...
What is Pascal's law?
What is Pascal’s Law? According to Pascal’s Law, “The external static pressure applied on a confined liquid is distributed or transmitted evenly throughout the liquid in all directions”. The static pressure acts at right angles to any surface in contact with the fluid.
What does Pascal's law say about pressure?
Pascal’s law says that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid will be transmitted without a change in magnitude to every point of the fluid and the walls of the container. The pressure at any point in the fluid is equal in all directions.
Who discovered that the pressure at a point for a static fluid would be the same across all planes passing through
In 1653, Pascal law was stated by French mathematician Blaise Pascal.
What is Pascal's law?
It states that the pressure change occurring at any point in a confined fluid will be transmitted equally in all direction.
What is the basic working principle of hydraulic systems?
Hydraulic System: The basic working principle of every hydraulic system is Pascal’s law. Hydraulic systems are used for lifting, holding or moving loads with a small applied force. It uses incompressible hydraulic fluids and works with the concept of force multiplication (discussed above).
What is Pascal's principle?
Pascal's Principle and Hydraulics. DESCRIPTION: A set of mathematics problems dealing with hydraulics. Hydraulic systems use a incompressible fluid, such as oil or water, to transmit forces from one location to another within the fluid. Most aircraft use hydraulics in the braking systems and landing gear. Pneumatic systems use compressible fluid, ...
What is Pascal's law?
Applied to a more complex system below, such as a hydraulic car lift, Pascal's law allows forces to be multiplied. The cylinder on the left shows a cross-section area of 1 square inch, while the cylinder on the right shows a cross-section area of 10 square inches.
What is the law of pneumatics?
Pascal's law states that when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase at every other point in the container. A container, as shown below, contains a fluid.
What does a 1 pound piston do?
The 1 pound load on the 1 square inch area causes an increase in pressure on the fluid in the system. This pressure is distributed equally throughout and acts on every square inch of the 10 square inch area of the large piston. As a result, the larger piston lifts up a 10 pound weight.
What are some examples of Pascal's law?
The most common examples of Pascal's Law is the hydraulic braking system present in the automobiles. A liquid, brake or hydraulic fluid, enclosed in the container, is used to transmit the pressure from the brake pedal to the wheels of the vehicle against the brake discs or brake drums. 190 views. ·.
Who first stated the principle of pressure?
The principle was first stated clearly in 1652 by Blaise Pascal (for who the unit of pressure is named) A change in the pressure applied to an enclosed in-compressible fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid to the walls of its container. Pascal's principle put more simply, basically means that an in-compressible fluid ...
What is the basis of hydraulic lever?
Pascal's principle put more simply, basically means that an in-compressible fluid transmits pressure. This is the basis to hydraulic lever.
How does hydraulic lever work?
In a hydraulic lever, for example, you apply a force to the left-hand piston over a given area, this force is then transformed in to a pressure which is transmitted through the hydraulic fluid or oil. This pressure then transforms back in to an output force over another given area for the right-hand piston.
What is Bernoulli's principle?
Bernoulli's principle. This is an application of conservation of energy. This is normally used to find conditions at a particular point when we know the conditions at some other point. But be careful. This is applicable only for non-viscous, incompressible and steady flows.
What is the difference between hydraulic and pneumatic systems?
The difference is that hydraulic systems use liquids and pneumatic systems use gases, usually air. Liquids are only slightly compressible and in hydraulic systems, this property can often be neglected. Gases, however, are very compressible.
What is Pascal's principle?
Pascal's principle is based on the idea that fluids at rest are incompressible, allowing very large forces to be transmitted with the application of a smaller force.
What are Pascal's laws?
News You Can Use 1 Pascal's law was discovered during an experiment that was allegedly performed in the 1600's. A 10 m long pole was vertically inserted into a barrel that was filed with water. As the water was poured into the vertical tube, Pascal discovered that the pressure from the water caused the barrel to burst. 2 As water is poured into the top of the vertical tube, the barrel begins to burst 3 The modern equivalent of this can be seen in any hydraulic automobile jacks present in some household garages. Two pistons are connected together by a fluid; one piston is much smaller than the other. A small force is applied to the small piston that produces a change in pressure which is transmitted to the fluid. This pressure is given as begin {align*}frac {F_1} {A_1}end {align*}, where begin {align*}F_1end {align*} is the applied force and begin {align*}A_1end {align*} is the area of the small piston. Since the pressure at the small end must equal the pressure at the large end, it is easily seen that the force on the larger piston is:
Why did Pascal's hydraulic jack burst?
As the water was poured into the vertical tube, Pascal discovered that the pressure from the water caused the barrel to burst. As water is poured into the top of the vertical tube, the barrel begins to burst. The modern equivalent of this can be seen in any hydraulic automobile jacks present in some household garages.