One approach to pollution control is incentive-based regulation. In this tactic: pollution control laws establish emission targets and industries are provided enticements to reduce emissions Pollution is considered an external cost because; its cost to the environment is not reflected in the price of the product that produces it. Click to visit
Why are pollution controls so expensive?
This is because more aggressive pollution controls tend to cost more money. Economists and company analysts work to find the sweet spot where there is a balance between the cost of pollution and costs of cleanup.
Is pollution a positive or negative externality?
Pollution as a negative externality Pollution is a negative externality. Economists illustrate the social costs of production with a demand and supply diagram. The social costs include the private costs of production incurred by the company and the external costs of pollution that are passed on to society.
What are the costs of air pollution?
Let’s say that, if these pollutants were emitted into the air and water, they would create costs of $100 per refrigerator produced. These costs might occur because of injuries to human health, impact on property values, destruction of wildlife habitat, reduction of recreation possibilities, or because of other negative impacts.
What is the economics of pollution?
Therefore, in the economics of pollution we see that there is a point where both society and the environment have some satisfaction. This is the optimum amount of pollution, or the point where the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost of pollution.

Is air pollution an external cost?
Pollution is a negative externality. Economists illustrate the social costs of production with a demand and supply diagram. The social costs include the private costs of production incurred by the company and the external costs of pollution that are passed on to society.
Why is air pollution considered an externality?
Air pollution is essentially a negative externality: it imposes external costs to people who are external to the transaction of a polluting product. Further, economists typically define air pollution as a negative externality in production.
What type of cost is pollution?
The difference between private costs and total costs to society of a product, service, or activity is called an external cost; pollution is an external cost of many products.
Is pollution an opportunity cost?
Pollution has long been seen as a health problem, but increasingly its being redefined as an opportunity cost to both individuals and society - and as a burden on future generations.
How does pollution affect economy?
It can have an impact on the economy in many forms such as higher rates of asthma, diabetes or chronic respiratory diseases leading to reduced ability to work and lower participation rates in the labor force.
Why is pollution an example of market failure?
In markets, industry, business, etc, the goal is to be as efficient as possible because that means you're saving money, and that means you're maximizing profits. Thus, if we are putting out a lot of pollution, we're actually operating very inefficiently, and that means we're wasting massive amounts of money.
What are external costs?
An external cost is a cost not included in the market price of the goods and services being produced, i.e. a cost not borne by those who create it.
Which of the following is an example of an external cost?
External costs (also known as externalities) refer to the economic concept of uncompensated social or environmental effects. For example, when people buy fuel for a car, they pay for the production of that fuel (an internal cost), but not for the costs of burning that fuel, such as air pollution.
What is pollution damage cost?
Damage cost is the cost incurred by repercussions (effects) of direct environmental impacts (for example, from the emission of pollutants) such as the degradation of land or human—made structures and health effects.
What are externalities examples?
Externalities by nature are generally environmental, such as natural resources or public health. For example, a negative externality is a business that causes pollution that diminishes the property values or health of people in the surrounding area.
What are the effects of pollution?
Exposure to high levels of air pollution can cause a variety of adverse health outcomes. It increases the risk of respiratory infections, heart disease and lung cancer. Both short and long term exposure to air pollutants have been associated with health impacts. More severe impacts affect people who are already ill.
How does pollution affect business?
When it comes down to it, how does air pollution impact businesses? Well, there are four main impact areas: productivity, absentee rates and sick leave, recruiting, and opportunity losses.
What are environmental externalities?
Environmental externalities refer to the economic concept of uncompensated environmental effects of production and consumption that affect consumer utility and enterprise cost outside the market mechanism.
What are some negative externalities?
Some examples of negative production externalities include:Air pollution. Air pollution may be caused by factories, which release harmful gases to the atmosphere. ... Water pollution. ... Farm animal production.
Which of the following would be considered a negative externality?
Air and noise pollution are commonly cited examples of negative externalities.
What is a positive externality example?
A positive externality is a benefit of producing or consuming a product. For example, education is a positive externality of school because people learn and develop skills for careers and their lives. In comparison, negative externalities are a cost of production or consumption.
What are some examples of government policy interventions to address the problem of plastic pollution?
Examples of government policy interventions to address the problem of plastic pollution. Banning microbeads from consumer products. Bans on plastic cotton buds and other products. Plastic bag charge/ tax to reduce single use bags. Encourage businesses to develop recyclable polymers.
How much plastic is dumped into the ocean every year?
Plastic marine litter disintegrates into tiny pieces and ends up in food. Around 8 million tonnes of plastic is dumped into the sea every year, affecting the lives of so many creatures. 😢 #BluePlanet2 pic.twitter.com/gG1fqIDVnw.
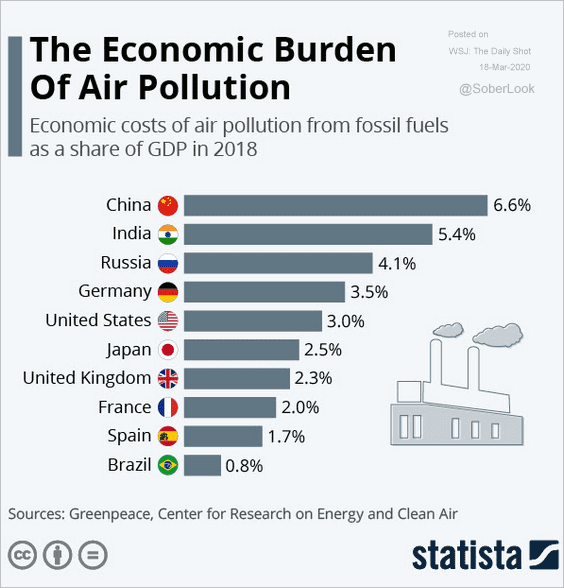
How does air pollution affect the economy?
Air pollution negatively impacts the U.S. economy, costing the U.S. roughly 5 percent of its yearly gross domestic product (GDP) in damages ($790 billion in 2014). The highest costs come from early deaths, attributable to exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
What is the main cause of utilities damage?
Utilities-related damages, for example, are largely driven by sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ), a by-product of coal combustion, which forms secondary PM2.5 downwind of the smokestacks it comes from. Decreases in SO 2 have driven down damages from utilities in recent years. Ammonia, the largest contributor of damages from agriculture, is emitted through both livestock-raising and fertilizer application, forming secondary PM2.5 downwind of farms.
What are the top four sectors responsible for the highest external damages?
Air pollution damages are largely concentrated within a small number of economic sectors: the top four sectors responsible for the highest external damages (agriculture, utilities, manufacturing, and transportation ) contribute just under 20 percent of GDP, but are responsible for more than 75 percent of all air pollution-related damages.
What causes PM2.5 to be released into the atmosphere?
While some PM2.5 in the atmosphere is the result of natural processes, such as forest fires or windblown dust, the majority of the damages from PM2.5 are related to human activities, most of which can be attributed to different sectors of the economy, such as manufacturing and agriculture.
Do all emissions are equal?
Such recommendations will be further refined in the team’s follow-up work, which will focus on how damages from each sector are distributed across the country, as not all emissions are equal. Pollutants emitted in close proximity to urban areas do far more harm than those emitted where few people are around to breathe the dirty air.
Is air pollution falling?
However, damages from air pollution in the U.S. are sharply falling, as levels of outdoor air pollutants have decreased in recent years, according to recent research from the Center for Air Quality, Climate, and Energy Solutions ( CACES) at Carnegie Mellon University.
How much would a refrigerator cost if it was polluted?
Let’s say that, if these pollutants were emitted into the air and water, they would create costs of $100 per refrigerator produced.
Why do companies have to dispose of waste at no cost?
In a market with no anti-pollution restrictions, firms can dispose of certain wastes at no cost.
Why are externalities considered an example of market failure?
Because externalities represent a case where markets no longer consider all social costs but only some of them, economists commonly refer to externalities as an example of market failure. When there is market failure, the private market fails to achieve efficient output because either firms do not account for all costs incurred in the production of output and/or consumers do not account for all benefits obtained, in the case of a positive externality. In the case of pollution, at the market output, social costs of production exceed social benefits to consumers, and the market produces too much of the product.
How do economists illustrate the social costs of production?
Economists illustrate the social costs of production with a demand and supply diagram. The social costs include the private costs of production incurred by the company and the external costs of pollution that are passed on to society. The diagram below shows the demand and supply for manufacturing refrigerators.
How to show the market for cigarettes in equilibrium?
Show the market for cigarettes in equilibrium, assuming that there are no laws banning smoking in public. Label the equilibrium private market price and quantity as and . Add whatever is needed to the model to show the impact of the negative externality from secondhand smoking. Label the social optimal output and price as and . On the graph, shade in the deadweight loss at the market output. Hint: In this case it is the consumers, not the sellers, who are creating the negative externality.
What is externality in business?
An externality, sometimes called a spillover, occurs when an exchange between a buyer and seller has an impact on a third party who is not part of the exchange. Externalities can be positive or negative.
What are the environmental issues that are affecting the environment?
Along with the still-high levels of air and water pollution, other issues include hazardous waste disposal, destruction of wetlands and other wildlife habitats, and the impact of pollution on human health.
Why does the marginal cost of pollution go up?
As the amount of pollution released goes down, the marginal abatement cost tends to go up. This is because more aggressive pollution controls tend to cost more money. Economists and company analysts work to find the sweet spot where there is a balance between the cost of pollution and costs of cleanup. Using our example of the scrubbers, if the marginal cost of pollution is greater than the marginal cost of abatement or cleanup, then it is in the best interest of society for the power plant to install and use the scrubbers. If the marginal cost of pollution is less than the marginal cost of abatement, then the company may not need to install the scrubbers.
Why is pollution a marginal benefit?
Marginal benefit is the increase in satisfaction received from a unit increase.
What is the optimum amount of pollution?
Therefore, in the economics of pollution, we see that there is a point where both society and the environment have some satisfaction, or in other words, there is an optimum amount of pollution. The optimum amount of pollution can be defined as the point where the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost of pollution.
Why would society suffer from pollution?
In other words, just as the body can suffer from too much bacteria being removed, society could start to suffer if a company tries to clean up too much pollution. For instance, one way society could suffer is if exorbitant or over-the-top costs of pollution cleanup are passed on to them. This would make the cost of producing energy from the power plant too much for society to afford.
What is marginal cost?
Marginal cost is a term that comes from the study of economics that is defined as the change in total cost that arises due to producing one more unit of a good. For example, if a widget factory decides to produce a new line of widgets, the marginal cost of the new widget line would include all of the additional costs that come with extra materials, added production and more worker hours.
What happens if the cost of a product goes too high?
If the cost of a product goes too high, this could lead to decreased benefits for society. Therefore, in the economics of pollution we see that there is a point where both society and the environment have some satisfaction. This is the optimum amount of pollution, or the point where the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost of pollution.
What is an abatement cost?
In general, an abatement cost is the expense a company incurs in order to address or clean up a detrimental effect it created. For example, a coal-burning power plant will produce emissions of sulfur dioxide, which are gases that are harmful to the environment.