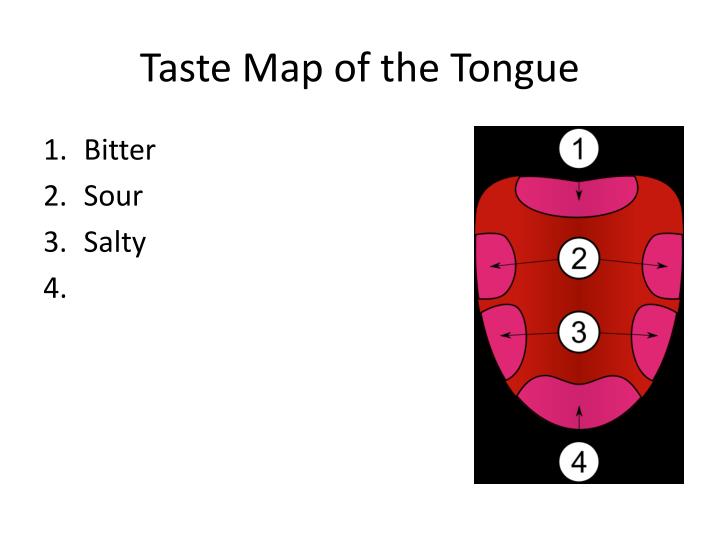
The tongue taste map is WRONG: Flavours are actually perceived by neurons in the brain, scientists reveal Scientists at Columbia University say brain not tongue decides taste They say our thousands of taste buds can all detect different flavours These are salty, bitter, sour, sweet and savoury
Is the Tongue Taste map wrong?
The tongue taste map is WRONG: Flavours are actually perceived by neurons in the brain, scientists reveal Scientists at Columbia University say brain not tongue decides taste They say our thousands of taste buds can all detect different flavours These are salty, bitter, sour, sweet and savoury
Where are the taste buds on the tongue?
You might know the map: The taste buds for "sweet" are on the tip of the tongue; the "salt" taste buds are on either side of the front of the tongue; "sour" taste buds are behind this; and "bitter" taste buds are way in the back.
What does the tongue map tell us?
Everybody has seen the tongue map – that little diagram of the tongue with different sections neatly cordoned off for different taste receptors. Sweet in the front, salty and sour on the sides and bitter at the back.
Is the ability to taste sweet and sour on the tongue real?
In fact, it was debunked by chemosensory scientists (the folks who study how organs, like the tongue, respond to chemical stimuli) long ago. The ability to taste sweet, salty, sour and bitter isn’t sectioned off to different parts of the tongue.

Is the tongue taste map accurate?
It's possibly the most recognizable symbol in the study of taste, but it's wrong. In fact, it was debunked by chemosensory scientists (the folks who study how organs, like the tongue, respond to chemical stimuli) long ago.
Why is it wrong to taste maps?
You may have even seen a drawing of a tongue with colored regions identifying the “taste zones.” This is inaccurate, though: Our taste receptors are actually well-distributed on our tongues—and scientists have known this for decades. The myth of the tongue map or taste map was the result of misinterpreted data.
Does the tongue really have different taste zones?
“The tongue does not have different regions specialized for different tastes,” says Brian Lewandowski, a neuroscientist and taste expert at the Monell Chemical Senses Center in Philadelphia. “All regions of the tongue that detect taste respond to all five taste qualities.
What is the tongue taste map?
The tongue map or taste map is a common misconception that different sections of the tongue are exclusively responsible for different basic tastes. It is illustrated with a schematic map of the tongue, with certain parts of the tongue labeled for each taste.
Why can only certain parts of the tongue taste sweet flavors?
They've demonstrated that each type of taste stimulates a specific receptor protein found in taste cells in the mouth, throat, and tongue. While sweet flavors activate the same receptor, bitter foods activate a completely different one.
Which part of the tongue is most sensitive to taste?
tip ofThe tip of the tongue is the region most sensitive to sweet, salt, and umami tastes. The sides are most sensitive to sour, and the back of the tongue to bitter tastes. Figure 24.2. Although all tastes can be perceived across the entire tongue, sensitivity levels vary for each taste.
Why do we taste things differently?
"Our food preferences are determined by multiple factors, including genes, experience, and age." Genes play a part by giving a person a predetermined taste preference, and our environment is a factor in learning new tastes.
What is umami tongue?
It can be described as a pleasant "brothy" or "meaty" taste with a long-lasting, mouthwatering and coating sensation over the tongue. The sensation of umami is due to the detection of the carboxylate anion of glutamate in specialized receptor cells present on the human and other animal tongues.
Which part of tongue tastes spicy?
But, there are more sensitive parts of your tongue. The tip and edges of your tongue generally have more taste sensitivity than the middle of your tongue, so there's a legitimate reason to pretentiously swish something around in your mouth when you're playing connoisseur.
Can you taste without a tongue?
Reba], a sensory neuroscientist at the National Institutes of Health. Ryba and his colleagues found that you can actually taste without a tongue at all, simply by stimulating the "taste" part of the brain—the insular cortex.
Which taste can be detected by the tip of the tongue?
According to the map, we detect sweetness on the tip of our tongue, bitterness at the back, and saltiness and sourness along the sides.
Are taste buds real?
Taste buds have very sensitive microscopic hairs called microvilli (say: mye-kro-VILL-eye). Those tiny hairs send messages to the brain about how something tastes, so you know if it's sweet, sour, bitter, or salty. The average person has about 10,000 taste buds and they're replaced every 2 weeks or so.
What are some environmental factors that can influence the PTC taster phenotypes?
With the PTC tasting example, scientists estimate that the gene controls about 85% of the ability to taste. Environmental factors that play a role include how dry your mouth is or how recently you have eaten. The degree to which your phenotype is determined by your genotype is referred to as 'phenotypic plasticity'.
What are the four taste zones on the human tongue?
Today we know that different regions of the tongue can detect sweet, sour, bitter and salty.
What is umami tongue?
It can be described as a pleasant "brothy" or "meaty" taste with a long-lasting, mouthwatering and coating sensation over the tongue. The sensation of umami is due to the detection of the carboxylate anion of glutamate in specialized receptor cells present on the human and other animal tongues.
Can you taste without a tongue?
Reba], a sensory neuroscientist at the National Institutes of Health. Ryba and his colleagues found that you can actually taste without a tongue at all, simply by stimulating the "taste" part of the brain—the insular cortex.
What does Linda Bartoshuk call the gourmet?
Linda Bartoshuk calls the gourmet’s taste for particular foods “eccentric” in that it has nothing to do with physiological needs. The gourmet’s preferences are strongly influenced by other epicurean opinion, but, she says, these acquired sensitivities, the skills used in making distinctions, are real, along with the pleasure taken. She makes the comparison to an appreciation for music: “subtlety for its own sake.” ●
What are the four tastes of the mouth?
O nly the four basic tastes — sweet, sour, bitter, and salty — are perceived in the mouth, though some would argue for the addition of other tastes, such as metallic or the meaty taste that the Japanese call umami, represented by MSG. The rest of flavor is aroma, perceived by smelling before tasting or through vapors rising from the back of the mouth into the nose. The complex interaction between the two senses is little understood, but certainly the mind creates the impression of an array of flavors in the mouth.
Where are the taste buds buried?
Three kinds of papillae make up the oval: parallel lines along the sides, large bumps at the back of the tongue, and quite small ones in front. (The papillae in the center without taste buds are a fourth kind.)
What is the holy grail of batteries?
The 'holy grail' of batteries: Scientists develop an 'iron-air' battery that stores electricity for days... 15 rare giant land snails that can grow to be the size of a person's FIST and cause a rare form of... Mercedes-Benz is investing $47 BILLION to go all-electric by 2030 - but warns the shift in technology will...
How long did the Ingenuity helicopter fly on Mars?
Ingenuity completes its 15th flight on Mars! NASA's helicopter flies for over two minutes as it begins to...
What robot can walk over leaves?
Engineers design 3D-printed robot 'ants' that can walk over leaves, link up like a centipede and call for...
How was the finding made?
The finding was made by feeding chemicals with specific tastes to mice.
What do neurons in the brain not cells in the tongue decide?
Scientists at Columbia University say neurons in the brain not cells in the tongue decide taste. They say our thousands of taste buds can all detect different flavours: bitter (top of diagram), sour (number two), salty (number three), sweet (bottom) and savoury
How many taste buds are there on our tongues?
They studied the 8,000 or so taste buds that are scattered over our tongues, reports the BBC.
What are the different tastes of our tongue?
In school we're taught that our tongues have specific areas that are susceptible to different tastes: salty, bitter, sour, sweet or savoury. But scientists say that is a myth, and they’ve found that each of the several thousand sensors on our tongue can recognise any of the tastes.
How many tastes are there on the tongue?
There are five basic tastes identified so far, and the entire tongue can sense all of these tastes more or less equally. As reported in the journal Nature this month, scientists have identified a protein that detects sour taste on the tongue.
What is the taste of umami?
This is the taste of glutamate.
How to prove the tongue map is wrong?
The tongue map is easy enough to prove wrong at home. Place salt on the tip of your tongue. You'll taste salt. For reasons unknown, scientists never bothered to dispute this inconvenient truth.
How many receptors are in a tastebud?
Later research has revealed that taste bud seems to contain 50 to 100 receptors for each taste. The degree of variation is still debated, but the kindest way to describe the tongue map is an oversimplification. Why textbooks continue to print the tongue map is the real mystery now.
Where are the salt and sweet taste buds on the tongue?
You might know the map: The taste buds for "sweet" are on the tip of the tongue; the "salt" taste buds are on either side of the front of the tongue; "sour" taste buds are behind this; and "bitter" taste buds are way in the back. Wineglasses are said to cater to this arrangement.
What is Christopher's book about?
For Live Science, Christopher covers public health, nutrition and biology, and he occasionally opines with a great deal of healthy skepticism. His "Food at Work" book and project, commissioned by the U.N.'s International Labor Organization, concerns workers health, safety and productivity.
Where are taste receptors located?
Collings found that all tastes can be detected anywhere there are taste receptors—around the tongue, on the soft palate at back roof of the mouth, and even in the epiglottis, the flap that blocks food from the windpipe. Later research has revealed that taste bud seems to contain 50 to 100 receptors for each taste.
What is the tongue map?
Everybody has seen the tongue map – that little diagram of the tongue with different sections neatly cordoned off for different taste receptors. Sweet in the front, salty and sour on the sides and bitter at the back.
Which nerve is responsible for taste perception?
There are two cranial nerves responsible for taste perception in different areas of the tongue: the glossopharyngeal nerve in the back and the chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve in the front. If tastes were exclusive to their respective areas, then damage to the chorda tympani, for instance, would take away one’s ability to taste sweet.
Which part of the tongue is sensitive to taste?
It is true that the tip and edges of the tongue are particularly sensitive to tastes, as these areas contain many tiny sensory organs called taste buds. Hänig found that there was some variation around the tongue in how much stimulus it took for a taste to register.
Where did the taste map originate?
Origins of the taste map. That familiar but not-quite-right map has its roots in a 1901 paper, Zur Psychophysik des Geschmackssinnes, by German scientist David P Hänig.
Does chorda tympani damage taste?
If tastes were exclusive to their respective areas, then damage to the chorda tympani, for instance, would take away one’s ability to taste sweet. In 1965, surgeon TR Bull found that subjects who had had their chorda tympani cut in medical procedures also reported no loss of taste.
Where are sweet and bitter receptors located?
You taste with your whole tongue. If the tongue map were correct, one would expect sweet receptors to be localized to the front of the tongue and bitter receptors restricted to the back. But this is not the case. Rather, each receptor type is found across all taste areas in the mouth.
Where is each receptor type found?
Rather, each receptor type is found across all taste areas in the mouth. Despite the scientific evidence, the tongue map has burrowed its way into common knowledge and is still taught in many classrooms and textbooks today. The true test doesn’t require a laboratory, though. Brew a cup of coffee. Crack open a soda.
How many taste receptors are there in the tongue?
At the front of your tongue you find a lot of taste buds. in bump-like structures, and each of those taste buds. has 50 to 100 specialized taste receptor cells. that will respond to different taste qualities. Some that respond to sweet, some to sour,
How long does it take for taste buds to regenerate?
In general, the taste system is pretty robust. and your taste cells can have kind of a lifetime. between one week, two weeks, maybe three weeks, and then they will regenerate. Rarely you can lose function to those taste buds. because of damage to a branch of the nerve. that is normally connecting to that taste bud.
Origins of the taste map
That familiar but not-quite-right map has its roots in a 1901 paper, Zur Psychophysik des Geschmackssinnes, by German scientist David P Hänig.
Long in dispute
In the decades since the tongue map was created, many researchers have refuted it.
Molecular biologists weigh in
Modern molecular biology also argues against the tongue map. Over the past 15 years, researchers have identified many of the receptor proteins found on taste cells in the mouth that are critical for detecting taste molecules.