Gene duplications are an essential source of genetic novelty that can lead to evolutionary innovation. Duplication creates genetic redundancy, where the second copy of the gene is often free from selective pressure —that is, mutations of it have no deleterious effects to its host organism.
Full Answer
What is multiplication of host cell and cloning of genes?
Introduction to Multiplication of Host Cell and Cloning of Genes: The host cell containing foreign DNA in addition to its own DNA is allowed to multiply forming a clone having millions of identical cells. Each member of the clone contains in addition to its normal DNA segment of foreign DNA joined to a DNA of cloning vehicle.
How are genes like instructions for the cell?
So genes are instructions for the cell. Like instructions, genes have a “start.” Their string of base pairs must follow in a specific order until they reach some defined “end.” If genes are like a basic recipe, alleles (Ah-LEE-uhls) are versions of that recipe.
What are genes and why are they important?
Every human being has cells that consist of genes, nuclei and other parts. Genes are essentially the building blocks that determine what color eyes or hair you might have. They can also help you grow and tell the cells in your body to do different things. Genes are an important part of the biological function of your body.
How many genes do you have?
Before looking at our AncestryDNA to 23andMe comparison, you probably want to know how many genes you have. Scientists in the past thought that humans had around 50,000 genes, and some actually believed this number was closer to 100,000 or even more. Recent research found that we actually have a much smaller number of just 20,500 genes.
How do genes multiply?
The cell replicates itself in an organized, step-by-step fashion known as the cell cycle. Tight regulation of this process ensures that a dividing cell's DNA is copied properly, any errors in the DNA are repaired, and each daughter cell receives a full set of chromosomes.
Does every gene have 2 copies?
Every person has two copies of each gene, one inherited from each parent. Most genes are the same in all people, but a small number of genes (less than 1 percent of the total) are slightly different between people. Alleles are forms of the same gene with small differences in their sequence of DNA bases.
Does DNA only replicate once?
Abstract. The preparation for DNA replication initiation is tightly linked to cell-cycle progression, ensuring that replication occurs only once per cycle. The time is ripe for a molecular dissection of the links between the two processes.
Do humans have two copies of most genes?
People have two copies of most genes, one copy inherited from each parent. In some cases, however, the number of copies varies—meaning that a person can have one, three, or more copies of particular genes. Less commonly, both copies of a gene may be missing.
Can two humans have the same DNA?
Theoretically, same-sex siblings could be created with the same selection of chromosomes, but the odds of this happening would be one in 246 or about 70 trillion. In fact, it's even less likely than that.
Do genes duplicate themselves?
Rate of gene duplication Comparisons of genomes demonstrate that gene duplications are common in most species investigated. This is indicated by variable copy numbers (copy number variation) in the genome of humans or fruit flies. However, it has been difficult to measure the rate at which such duplications occur.
What Cannot replicate itself?
A virus cannot replicate alone; instead, it must infect cells and use components of the host cell to make copies of itself. Often, a virus ends up killing the host cell in the process, causing damage to the host organism.
Can a cell replicate without DNA?
In mammalian cells, there is no example of cell division without DNA replication, except during meiosis. Examples are limited to the division of Saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid cells that results in the generation of cells with less than 1 C value10,11,12.
What does DNA not replicate?
The cell cycle will not proceed to the next stage. Due to which the subsequent division will not happen. This will lead to cell death.
Is changing DNA harmful?
It is well established that changes in genes can alter a protein's function in the body, potentially causing health problems. Scientists have determined that changes in regions of DNA that do not contain genes (noncoding DNA) can also lead to disease.
Why do siblings not look exactly the same?
But brothers and sisters don't look exactly alike because everyone (including parents) actually has two copies of most of their genes. And these copies can be different. Parents pass one of their two copies of each of their genes to their kids. Which copy a child gets is totally random.
Can you have a missing gene?
Genes and chromosomes sometimes change or have missing or extra parts. This can cause serious health conditions and birth defects in your baby.
Why do we have 2 copies of every gene?
A copy comes from one each of the sperm and egg cell (animals). During meiosis, the genetic material is halved so that the gamete (sex cell) has half the genetic information in. During fertilisation, both these halves fuse to give 100% DNA, half from each parent.
Which organisms have 2 copies of each gene?
Since diploid organisms have two copies of each chromosome, they have two of each gene.
What is the introduction to the multiplication of host cells and cloning of genes?
Introduction to Multiplication of Host Cell and Cloning of Genes: The host cell containing foreign DNA in addition to its own DNA is allowed to multiply forming a clone having millions of identical cells. Each member of the clone contains in addition to its normal DNA segment of foreign DNA joined to a DNA of cloning vehicle. ADVERTISEMENTS:
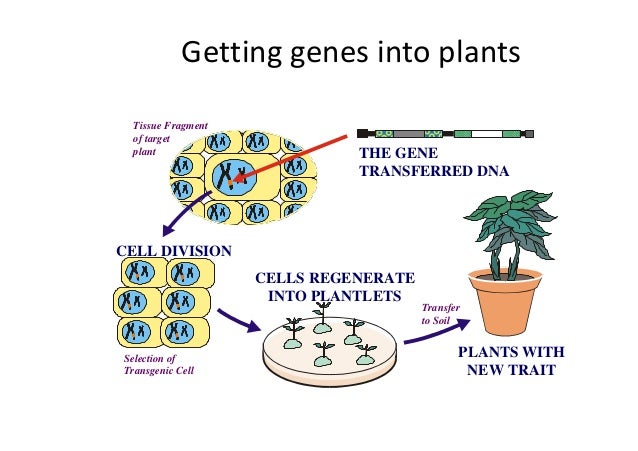
How is DNA converted into a useful product?
The information in DNA must be converted into a useful product. To make a product useful the information in DNA is usually transferred from the gene to the site where a new protein molecule is synthesized through gene expression. A number of problems may be associated with the expression of cloned genes in the recipient cell.
How many mRNA sequences are in an eukaryotic cell?
An eukaryotic cell may contain thirty thousand different mRNA sequences. The cDNA clone bank is defined as a population of bacterial transformants, each containing a plasmid with single cDNA insert and with sufficiently large number of individual transformants so that every mRNA molecule is represented at least once in the bacterial population.
How is cloned DNA produced?
The cloned DNA are produced by the following method: 1. Isolation of DNA fragments to be cloned. 2. Isoining the fragments to a suitable vector (usually phage). 3. Introduction of recombinant DNA into the host cell at high efficiency to get a large number of independent clones. ADVERTISEMENTS: 4.
Why is fractionation of DNA important?
For fractionation of DNA (about 10 kb or more in length) to be cloned is important in approaching the maximum cloning capacity of the vector used. DNA fragments of size not suitable for cloning, if ligated to vector, will lower the efficiency of introduction of recombinant DNA into cells.
What happens when a gene contains introns?
Problems are encountered if the gene contains introns or it contains signals which act as terminators in bacterial host. This results in premature termination and the recombinant protein may not be synthesized properly and folded correctly, or it may even be degraded.
How does recombinant DNA work?
Recombinant DNA works when the host cell expresses protein from recombinant gene. A significant amount of recombinant protein will not be produced by the host unless expression factor are available in the cell. Protein expression depends upon the gene surrounded by a collection of signals which provide instructions for the transcription ...
How many people are the same in terms of genes?
One thing you may not know is that humans are more than 99% the same in terms of their genes. You share the same genes with the people in your family and some genes with the people who live down the street or across the country. Each gene essentially determines what you look like, though some environmental factors can also determine your appearance.
How many genes are there in the human body?
Scientists in the past thought that humans had around 50,000 genes, and some actually believed this number was closer to 100,000 or even more. Recent research found that we actually have a much smaller number of just 20,500 genes. Evolutionary scientists found proof that humans evolved over time and the way we look and function today is because ...
Why do X-Men have mutations?
The superheroes from comic books and films called the X-Men suffer from genetic mutations. Those mutations let them heal quickly and bend metal with their minds. While you probably can’t read minds or control the abilities of others, you may suffer from one or more genetic mutations. During your body’s development, your genes will divide and multiply several times. Any number of things can affect that division and cause mutations to form. Those mutations can occur because your mother drank or smoked while pregnant or because she worked around toxic chemicals or radiation. Some of these mutations can also cause severe genetic disorders.
Why are dominant and recessive genes stronger?
This is because the genes that you have allow you to inherit traits from your parents as well as any ancestors that came before them. There are both dominant and recessive genes. A dominant gene is much stronger than a recessive gene and can present itself in a physical way. One way to look at how dominant genes work is with a look ...
How do genes affect your appearance?
The genes that you have will essentially determine your appearance, but they can also determine how you act the way you do and relate to some aspects of your personality. As we already explained, you get half of your genetic code from each parent. If both of your parents have dark hair and dark eyes, you’ll probably have dark hair and eyes too. There is a chance that the recessive genes in your family line can come through though. Let’s say that you have ancestors with red hair several generations back in your family line. That recessive gene can result in you having red hair that darkens over time.
Why do mutations occur in the body?
Those mutations can occur because your mother drank or smoked while pregnant or because she worked around toxic chemicals or radiation.
What is a gene?
Gene is one of the more common words that you might hear when looking at home DNA testing kits. Even if you read over our AncestryDNA review, you’ll see that we mention this term a few times. If you graduated from high school or college more than a few years ago, you probably have no idea of what a gene is or what it does. Every human being has cells that consist of genes, nuclei and other parts. Genes are essentially the building blocks that determine what color eyes or hair you might have. They can also help you grow and tell the cells in your body to do different things.
What is the sum rule in genetics?
According to the sum rule, the probability that any of several mutually exclusive events will occur is equal to the sum of the events’ individual probabilities.
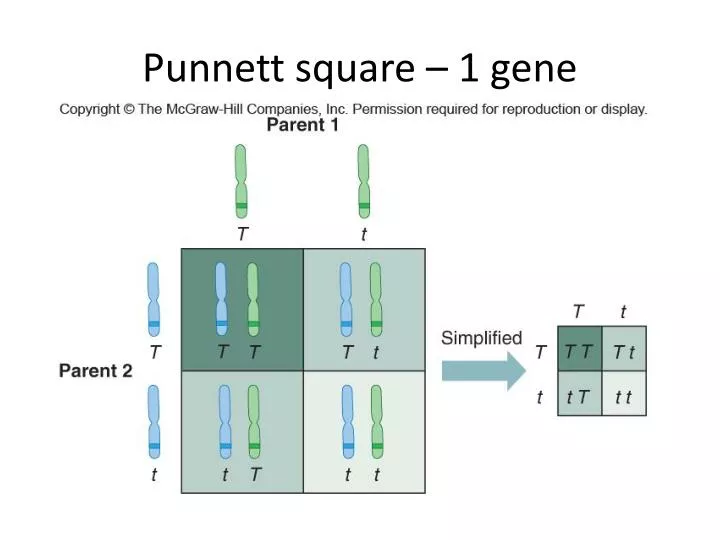
How many chances do you get an a allele from a male parent?
There's a 1/2 chance of getting an a allele from the male parent, corresponding to the rightmost column of the Punnett square. Similarly, there's a 1/2 chance of getting an a allele from the maternal parent, corresponding to the bottommost row of the Punnett square. The intersect of these the row and column, corresponding to the bottom right box of the table, represents the probability of getting an a allele from the maternal parent and the paternal parent (1 out of 4 boxes in the Punnett square, or a 1/4 chance ).
How to find the probability of getting a Bb genotype?
To calculate the probability of getting a Bb genotype, we can draw a -square Punnett square using the parents' alleles for the coat color gene only, as shown above. Using the Punnett square, you can see that the probability of the Bb genotype is . (Alternatively, we could have calculated the probability of Bb using the product rule for gamete contributions from the two parents and the sum rule for the two gamete combinations that give Bb .) Using a similar Punnett square for the parents' fur texture alleles, the probability of getting an Cc genotype is also . To get the overall probability of the BbCc genotype, we can simply multiply the two probabilities, giving an overall probability of .
What is the dominant homozygote in a Punnett square?
Once again, this is the same result we’d get with a Punnett square. One out of the four boxes of the Punnett square holds the dominant homozygote, AA. Two more boxes represent heterozygotes, one with a maternal A and a paternal a, the other with the opposite combination. Each box is out of the boxes in the whole Punnett square, and since the boxes don't overlap (they’re mutually exclusive), we can add them up () to get the probability of offspring with the dominant phenotype.
How to find probability of offspring with a dominant phenotype?
So, the probability of offspring with a dominant phenotype is: (probability of A from Mom and A from Dad) + (probability of A from Mom and a from Dad) + (probability of a from Mom and A from Dad) = .
How to use the product rule?
In general, you can think of the product rule as the “and” rule: if both event X and event Y must happen in order for a certain outcome to occur, and if X and Y are independent of each other (don’t affect each other’s likelihood), then you can use the product rule to calculate the probability of the outcome by multiplying the probabilities of X and Y.
How to calculate probability of two events occurring together?
One probability rule that's very useful in genetics is the product rule, which states that the probability of two (or more) independent events occurring together can be calculated by multiplying the individual probabilities of the events. For example, if you roll a six-sided die once, you have a chance of getting a six. If you roll two dice at once, your chance of getting two sixes is: (probability of a six on die 1) x (probability of a six on die 2) = .
Why is the bacterial genome duplicating?
The reason for this duplication seems to be purely evolutionary. A bacterial genome is always in balance needing compromise between its length and its efficiency.
How many copies of rRNA are there in bacteria?
We found that the number of rRNA genes correlates with the rate at which phylogenetically diverse bacteria respond to resource availability. Soil bacteria that formed colonies rapidly upon exposure to a nutritionally complex medium contained an average of 5.5 copies of the small subunit rRNA gene, whereas bacteria that responded slowly contained an average of 1.4 copies. In soil microcosms pulsed with the herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), indigenous populations of 2,4-D-degrading bacteria with multiple rRNA genes ( = 5.4) became dominant, whereas populations with fewer rRNA genes ( = 2.7) were favored in unamended controls. These findings demonstrate phenotypic effects associated with rRNA gene copy number that are indicative of ecological strategies influencing the structure of natural microbial communities."
Do bacteria have multiple copies of rRNA?
Usually, bacteria have multiple copies of 16S rRNA genes and also for some other functional genes. But most of the genes seem to exist in single copy in the chromosome. What is the reason for those differences?
How many chromosomes are in each generation of a human?
The other type of cell division, meiosis, ensures that humans have the same number of chromosomes in each generation. It is a two-step process that reduces the chromosome number by half—from 46 to 23—to form sperm and egg cells. When the sperm and egg cells unite at conception, each contributes 23 chromosomes so the resulting embryo will have ...
What is the process of genetic variation in meiosis?
Meiosis also allows genetic variation through a process of gene shuffling while the cells are dividing. Mitosis and meiosis, the two types of cell division. Credit: U.S. National Library of Medicine.
What is the process of mitosis?
During mitosis, a cell duplicates all of its contents, including its chromosomes, and splits to form two identical daughter cells. Because this process is so critical, the steps of mitosis are carefully controlled by certain genes.
What are the two types of cell division?
Learn more. There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis . Most of the time when people refer to “cell division,” they mean mitosis, the process of making new body cells. Meiosis is the type of cell division that creates egg and sperm cells. Mitosis is a fundamental process for life.
How many mutations do mothers transmit to their offspring?
As reviewed by Cochran and Harpending (2013), mothers transmit on average a number x of new mutations to their offspring. This number x is independent of the age of the Mother. Fathers, however, transmit a number of new mutations to their offsprings that is very much dependent on the age of the father for developmental reasons.
What factors increase or decrease the mutation rate?
Of course, as it has been pointed out there are various environmental factors that may increase or diminish the mutation rate (such as the mutagens (Tobacco, X -ray, ..))
What is the term for all the modifications that occur around or on the DNA but which are not the modification of the sequence?
We have to talk about epigenetics also. Epigenetics refers to all the modification that occur "around" or "on" the DNA but which are not the modification of the sequence of nucleotides. It is possible that the transmission of epigenetic modification is dependent on the age of the parents. But I have never heard of any case where this happens.
Do pre-sperm cells have more mutations in 12 years?
Pre-sperm cells divide constantly, and will have more mutations in 12 years. Unfortunately, neither the genes (nor the father) are likely to be smarter. There is some evidence that children from older fathers are more prone to diseases like autism and schizophrenia.
Can behavioral changes cause gene mutations?
Recent studies have yielded results which state that some behavioral actions may cause gene mutations.
Can mutations be transmitted through mitosis?
Every time a cell replicates some mutations may occur (even through mitosis ). Of course, any mutation that occurs in cells are located in your hand or in your brain, for example, will not be transmitted to the offsprings. Only mutations occurring in the germline (cells in the testis and in the ovaries whose descendent or themselves go through meiosis) are possibly passed to the offsprings. Interestingly, because of the developmental pathways of sperm cells and ovules, sperm cells go through a lot more mitosis than ovules do, resulting in more mutations in the sperms than in the ovules. Therefore, if you look at a mutation in an individual and assuming you know that the mutation occurred during the lifetime of the parents, then you are more likely that the mutation comes from the father than from the mother.

Overview
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. Gene duplications can arise as products of several types of errors in DNA replication and repair machinery as well as through fortuitous capture by selfish genetic elements. Common sources of gene duplications include ectopic recombination,
Mechanisms of duplication
Duplications arise from an event termed unequal crossing-over that occurs during meiosis between misaligned homologous chromosomes. The chance of it happening is a function of the degree of sharing of repetitive elements between two chromosomes. The products of this recombination are a duplication at the site of the exchange and a reciprocal deletion. Ectopic recombination is typical…
As an evolutionary event
Comparisons of genomes demonstrate that gene duplications are common in most species investigated. This is indicated by variable copy numbers (copy number variation) in the genome of humans or fruit flies. However, it has been difficult to measure the rate at which such duplications occur. Recent studies yielded a first direct estimate of the genome-wide rate of gene duplication in C. …
Identifying duplications in sequenced genomes
The two genes that exist after a gene duplication event are called paralogs and usually code for proteins with a similar function and/or structure. By contrast, orthologous genes present in different species which are each originally derived from the same ancestral sequence. (See Homology of sequences in genetics).
It is important (but often difficult) to differentiate between paralogs and orthologs in biological res…
As amplification
Gene duplication does not necessarily constitute a lasting change in a species' genome. In fact, such changes often don't last past the initial host organism. From the perspective of molecular genetics, gene amplification is one of many ways in which a gene can be overexpressed. Genetic amplification can occur artificially, as with the use of the polymerase chain reaction technique to amplify short strands of DNA in vitro using enzymes, or it can occur naturally, as described above…
See also
• Comparative genomics
• DbDNV (2010)
• De novo gene birth
• Exon shuffling
• Gene fusion
External links
• A bibliography on gene and genome duplication
• A brief overview of mutation, gene duplication and translocation