Why do arteries and veins have different fibres?
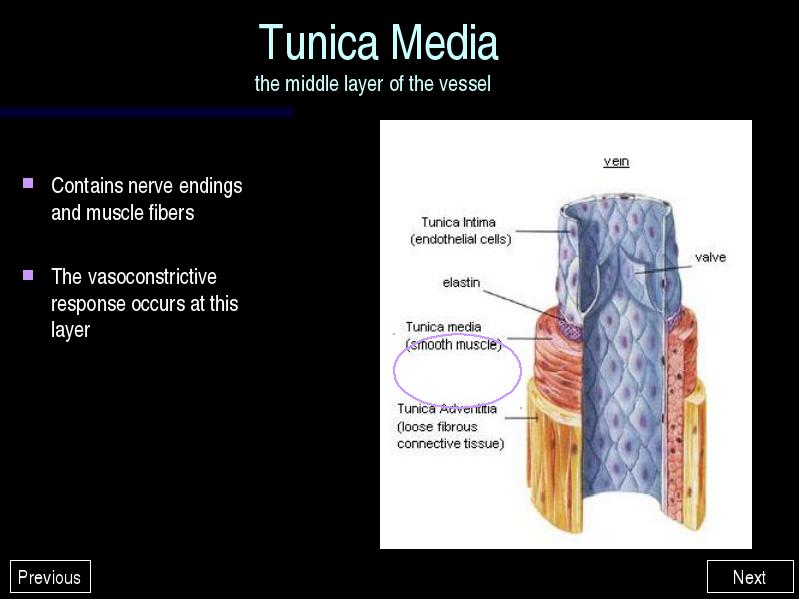
These fibers allow the arteries and veins to stretch to prevent over expansion due to the pressure that is exerted on the walls by blood flow. Tunica Media - the middle layer of the walls of arteries and veins. It is composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibers. This layer is thicker in arteries than in veins.
Which layer is thicker in arteries than in veins?
This layer is thicker in arteries than in veins. Tunica Intima - the inner layer of arteries and veins. In arteries, this layer is composed of an elastic membrane lining and smooth endothelium (a special type of epithelial tissue) that is covered by elastic tissues. Veins do not contain the elastic membrane lining that is found in arteries.
What type of tissue is found in arteries and veins?
It is composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibers. This layer is thicker in arteries than in veins. Tunica Intima - the inner layer of arteries and veins. In arteries, this layer is composed of an elastic membrane lining and smooth endothelium (a special type of epithelial tissue) that is covered by elastic tissues.
What is the structure of the vein wall?
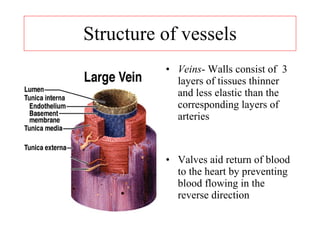
The vein wall consists of three layers: Tunica Adventitia - the strong outer covering of arteries and veins. It is composed of connective tissue as well as collagen and elastic fibers. These fibers allow the arteries and veins to stretch to prevent over expansion due to the pressure that is exerted on the walls by blood flow.

Do veins have elastic fibers?
But unlike the arteries, the venous pressure is low. Veins are thin-walled and are less elastic. This feature permits the veins to hold a very high percentage of the blood in circulation.
Why do veins not have elastic walls?
Veins: Unlike arteries, veins don't have to carry highly pressurized blood, but they do have to carry large volumes of deoxygenated blood back to your heart. Thin, less elastic walls help them handle high volumes and low pressure.
Do capillaries have elastic membranes?
There is no external elastic lamina, and the adventitia consists of a thin layer of collagen and isolated elastic fibers. By the contraction of their muscle fibers, the arterioles generate the "peripheral resistance" that reduces the blood pressure at the periphery, and thereby protects the capillaries and venules.
Why do veins have elastic walls?
The elastic wall of arteries helps to maintain a pressure gradient that drives the blood through the arterial system.
What are the 4 differences between arteries and veins?
Arteries carry blood away from the heart, and veins carry blood towards the heart. With the exception of pulmonary blood vessels, arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood. Arteries have thick walls with muscle tissue. Veins have thinner walls and use valves to keep your blood flowing.
Do veins have thick elastic walls?
Arteries are under more pressure, while veins are under less pressure. Arteries are big, while veins are small. No worries!
What are veins made of?
Each vein is made up of three layers: A layer of membranous tissue on the inside. A layer of thin bands of smooth muscle in the middle. A layer of connective tissue on the outside.
Which vessel lacks elastic tissue?
Capillaries are simply connectors and lack elastic tissues. Capillaries are vessels with small walls made up of a single endothelial layer. Due to the small capillary walls, the exchange of nutrients and metabolites occurs mainly by circulation. The arteriolar lumen regulates blood flow through the capillaries.
What type of tissue are veins?
The largest blood vessels are arteries and veins, which have a thick, tough wall of connective tissue and and many layers of smooth muscle cells (Figure 22-22). The wall is lined by an exceedingly thin single sheet of endothelial cells, the endothelium, separated from the surrounding outer layers by a basal lamina.
Are walls in artery elastic?
The wall of an artery consists of three layers. The innermost layer, the tunica intima (also called tunica interna), is simple squamous epithelium surrounded by a connective tissue basement membrane with elastic fibers. The middle layer, the tunica media, is primarily smooth muscle and is usually the thickest layer.
Which of the blood vessels have elastic walls?
Arteries are the blood vessels that have elastic walls and are the blood vessels with non - elastic thin walls.
Why are arteries so elastic?
These need to be elastic because: They are relatively thin compared to their diameter. When the heart contracts, and ejects blood into these arteries, the walls need to stretch to accommodate the blood surge, storing energy.
Why do arteries have more elastic walls than veins?
As heart pumps out blood through arteries to different parts of the body, thereby blood flows in high pressure in arteries and can withstand ,so its more elastic than veins. Arteries have more smooth muscle in their walls than veins to accommodate the pulses of blood generated by each contraction of the heart.
Why do arteries have more elastic and muscular tissue than veins quizlet?
Elastic arteries: Closer to heart=more stretch/recoil= more elastic tissue (than muscular arteries). Muscular arteries: Farther from heart=less stretch/recoil, but more need to constrict=more muscle tissue. Low pressure in veins makes it difficult for them to return blood uphill to the heart.
Why arteries have thick wall and veins have thin wall?
The heart pumps blood at high pressure. If arteries have thin walls they would burst because of high blood pressure. That is why arteries have thick walls.
Why do arteries need to have elastic walls?
These need to be elastic because: They are relatively thin compared to their diameter. When the heart contracts, and ejects blood into these arteries, the walls need to stretch to accommodate the blood surge, storing energy.
What are the layers of the vein wall?
Veins are composed of layers of thin tissue. The vein wall consists of three layers: Tunica Adventitia - the strong outer covering of arteries and veins. It is composed of connective tissue as well as collagen and elastic fibers.
Why do veins have problems?
Vein problems are typically the result of a blockage or defect. Blockages occur due to blood clots that develop in either superficial veins or deep veins, most often in the legs or arms. Blood clots develop when blood cells known as platelets or thrombocytes become activated due to a vein injury or disorder.
How big is a vein?
Vein Size. A vein can range in size from 1 millimeter to 1-1.5 centimeters in diameter. The smallest veins in the body are called venules. They receive blood from the arteries via the arterioles and capillaries. The venules branch into larger veins which eventually carry the blood to the largest veins in the body, the vena cava.
What is a clot in the veins called?
A clot that occurs in deep veins is called deep vein thrombosis . Vein problems can also arise from a defect. Varicose veins are the result of damaged vein valves that allow blood to pool in the veins. The accumulation of blood causes inflammation and bulging in the veins located near the skin's surface.
What is a vein?
our editorial process. Regina Bailey. Updated October 20, 2018. A vein is an elastic blood vessel that transports blood from various regions of the body to the heart. Veins are components of the cardiovascular system, which circulates blood to provide nutrients to the cells of the body. Unlike the high pressure arterial system, ...
What is the layer of arteries?
In arteries, this layer is composed of an elastic membrane lining and smooth endothelium (a special type of epithelial tissue) that is covered by elastic tissues. Veins do not contain the elastic membrane lining that is found in arteries.
What are the four main types of veins?
Veins can be categorized into four main types: pulmonary, systemic, superficial, and deep veins . Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. Systemic veins return oxygen-depleted blood from the rest of the body to the right atrium of the heart. Superficial veins are located close to the surface ...
What is the outermost layer of a vein?
Veins are composed of three main layers: The tunica adventitia: The outermost layer of a vein is the tunica adventitia, or adventitia for short. This layer is the thickest layer of a vein’s lining and is made of loose connective tissues and an external elastic membrane. The adventitia fuses with surrounding tissue in the body.
What is the middle layer of a vein?
The tunica media: The tunica media, or media, is the middle layer of a vein’s wall. This layer is built of collagen, elastic fibers, and smooth muscle fibers. The tunica intima: The tunica intima, or intima, is the innermost layer of a vein’s lining. This is the thinnest layer of the vein’s wall and is composed of an internal elastic membrane ...
What is the anatomy of a vein?
The Anatomy of a Vein. Varicose and spider veins are the consequences of deteriorating and clogged veins. These side effects of improper vein care are often discussed, but how they relate to your venous health is typically overlooked. Understanding the makeup of our circulatory system and the anatomy of a vein is an essential part ...
Why are my veins weak?
As a result, swelling of the thin walls in veins causes the valves to become farther away from each other and rendered ineffective.
How to prevent varicose veins?
When problems occur within a vein, blood may begin pooling and can lead to varicose veins or other serious conditions. Exercise, a healthy diet, avoiding tobacco products, and limiting intake of sugars, sodium, and saturated fats are all great ways to maintain healthy veins.
What is a vein center in New Jersey?
The New Jersey Vein and Vascular Center is a state-of-the-art vein center committed to personalized patient care and exceptional vein health. Visit us today to discuss your venous and vascular health!
Which layer of the vein is the thinnest?
This is the thinnest layer of the vein’s wall and is composed of an internal elastic membrane and connective tissue. The intima also includes endothelium, a layer that is directly exposed to blood flow within the vein. This layer of the vein is first to experience consequences of venous insufficiency.
Why do veins have thin walls?
Pulmonary arteries and veins: These arteries have thin walls as a result of a significant reduction in both muscular and elastic elements, while the veins have a well-developed media of smooth muscle cells.
What are the layers of the vascular wall?
The tissue components (endothelium, smooth muscle, elastic elements and connective tissue) that form the vascular walls are arranged in concentric layers.
What are sequential vascular segments?
The sequential vascular segments can be classified as follows: elastic arteries (conducting arteries), muscular arteries (distributing arteries), arterioles, capillaries, venules (pericytic and muscular), and veins (small, medium, and large).
What are the two types of blood vessels?
Blood vessels are divided into two broad categories: macrovasculature and microvasculature. The macrovasculature is composed of those blood vessels that can be seen with the naked eye. The microvasculature is composed of blood vessels that are smaller than 100 microns may only be seen through the microscope.
Which arteries are composed of many concentric layers of smooth muscle cells arranged in a low angle helix?
Muscular arteries follow the elastic arteries. Through the controlled contraction of their walls, these arteries distribute the blood to different parts of the body according to regional needs. The media of muscular arteries is composed of many concentric layers of smooth muscle cells arranged in a low angle helix, interspersed with less frequent and sometimes discontinuous elastic lamellae. The internal elastica marks the conventional boundary between intima and media. The external elastica separates the media from the adventitia. The media and adventitia of muscular arteries are approximately equal in thickness.
Which arteries have a thin wall?
Cerebral arteries and veins: These arteries are rather thin-walled for their caliber, with a well-developed internal elastica and virtually no elastic fibers in the rest of the vascular wall. The veins have a thin wall devoid of smooth muscle cells.
Which tissue is less permeable?
Capillaries with a continuous endothelium are less permeable and are present in muscles, lung, connective tissue, and skin.
Which arteries have elastic laminae?
In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present.
Where is the elastic lamina found?
It is very thin in veins and venules. In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present.
Why is my elastic lamina reduplicated?
Reduplication of internal elastic lamina can be seen in elderly individuals due to intimal fibroplasia, which is part of the aging process.