
Endocytosis engulfs vacuums that engulf energy-producing materials. As enzymes digest the contents of the vacuole, lysosomes attach to these organelles and fuse. A eukaryotic cell’s digestive system is made up of lysosomes and vacuoles that work together.
Does an eukaryotic cell have a Golgi body?
What Cells Have A Golgi Bodies? Alternatively known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, the Golgi apparatus is an membrane-bound eukaryotic organelle discovered in cells (cells with clearly defined nuclei) that consists of cisternae, hollow stacked pouches.
What are the functions of eukaryotic organelles?
Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells Below is a list of organelles that are commonly found in eukaryotic cells. Organelle: Function: Nucleus: The “brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. ...
What do all eukaryotic cells have in common?
Eukaryotic cells are very diverse in shape, form and function. Some internal and external features, however, are common to all. These include a plasma (cell) membrane, a nucleus, mitochondria, internal membrane bound organelles and a cytoskeleton.
Do eukaryotic cells have restriction enzymes?
No, eukaryotic cells do not have restriction endonucleases. All the restriction endonucleases have been isolated from various strains of bacteria. Prokaryotes/ bacteria have this enzyme as a defence mechanism to destroy the foreign DNA or to restrict the growth of bacteriophages.
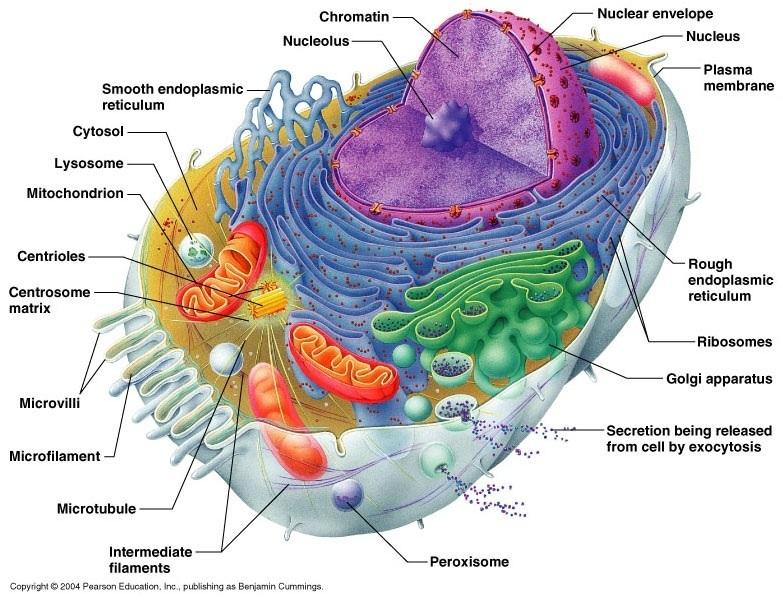
How do organelles function in eukaryotic cells?
This simple cartoon shows general similarities and differences between eukaryote and prokaryote cells....Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells.OrganelleFunctionMitochondriaMake energy out of foodRibosomesMake proteinGolgi ApparatusMake, process and package proteinsLysosomeContains digestive enzymes to help break food down6 more rows
Do eukaryotes work together?
These communities of cells evolved to become what are now known as plants, fungi and animals — including us. Eukaryotes can also work together to build enormous, complex organisms — such as this horse.
How do eukaryotic cells stick together?
Cells adhere to each other and to the extracellular matrix through cell-surface proteins called cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)—a category that includes the transmembrane adhesion proteins we have already discussed.
What are some organelles that work together?
Cell Functions Cells are membrane-bound groups of organelles that work together to allow it to function. Some of the major organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus. Plant cells also include chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis.
What are the structures of a typical eukaryotic cell and what are their functions?
A eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane. It has mitochondria, Golgi bodies, cell wall. It also contains locomotory organs such as cilia and flagella. The nucleus has a DNA that carries all the genetic information.
Which traits are shared by all eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells are very diverse in shape, form and function. Some internal and external features, however, are common to all. These include a plasma (cell) membrane, a nucleus, mitochondria, internal membrane bound organelles and a cytoskeleton.
How do organelles within a cell work together?
Different organelles make close contacts with each other via MCSs. These contact sites are generally thought to form via membrane proteins that act as tethers on the interacting organelles [2]. Often these tethers are part of large multiprotein complexes [2].
How do cells interact with each other?
The three main ways for cells to connect with each other are: gap junctions, tight junctions, and desmosomes. These types of junctions have different purposes, and are found in different places.
What organelles do all eukaryotes have?
All eukaryotic cells have within them a functionally interrelated membrane system, the endomembrane system which consists of the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, vesicles and other organelles derived from them (for example, lysosomes, peroxisomes), and the plasma membrane.
How do nucleus and all organelles work together?
The nucleus holds the DNA, the instruction manual for building proteins. Within the nucleus is another organelle called the nucleolus, which makes ribosome components. The ribosomes will leave the nucleus and go to the cytoplasm, where they will make proteins. Outside the nucleus is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
How do ribosomes and mitochondria work together?
Protein synthesis takes place on ribosomes. Mitochondrial ribosomes synthesize proteins in the mitochondria, which are controlled by mtDNA genes. They produce 13 mitochondrial proteins that are necessary for oxidative phosphorylation.
How do the mitochondria and Golgi apparatus work together?
The mitochondria segregate the Golgi from lateral regions of the plasma membrane, the nucleus, and the basal part of the cytoplasm. The Golgi is therefore placed between the principal Ca(2+) release sites in the apical region of the cell and the important Ca(2+) sink formed by the peri-granular mitochondria.
What is difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information.
What are 5 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes don't have membrane-bound organelles whereas eukaryotes have....What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells?Prokaryotic CellEukaryotic cellEndoplasmic reticulum absentEndoplasmic reticulum presentMitochondria absentMitochondria presentCytoskeleton absentCytoskeleton presentRibosomes smallerRibosomes larger19 more rows•May 20, 2022
Are all eukaryotes related?
The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea....Phylogeny.ArchaeplastidaGlaucophyta Rhodophyta ViridiplantaeHacrobiaHaptista Cryptista2 more rows
What can eukaryotes do that prokaryotes Cannot?
The ability to maintain different environments inside a single cell allows eukaryotic cells to carry out complex metabolic reactions that prokaryotes cannot. In fact, it's a big part of the reason why eukaryotic cells can grow to be many times larger than prokaryotic ones.