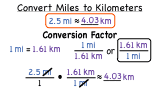
When doing dimensional analysis problems, follow this list of steps:
- Identify the given (see previous concept for additional information).
- Identify conversion factors that will help you get from your original units to your desired unit.
- Set up your equation so that your undesired units cancel out to give you your desired units. ...
- Multiply through to get your final answer. Don’t forget the units and sig figs!
How to solve problems using dimensional analysis?
Some major limitations of dimensional analysis are:
- The dimensional analysis doesn't provide information about the dimensional constant.
- Dimensional analysis cannot derive trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions.
- Dimensional analysis doesn't give information about the scalar or vector identity of a physical quantity. ...
- M = Mass of the object
- L = Length of the object
- T = Time taken
How do you calculate dimensional analysis?
When doing dimensional analysis problems, follow this list of steps:
- Identify the given (see previous concept for additional information).
- Identify conversion factors that will help you get from your original units to your desired unit.
- Set up your equation so that your undesired units cancel out to give you your desired units. ...
- Multiply through to get your final answer. Don’t forget the units and sig figs!
Does dimensional analysis use conversion factors?
Dimensional analysis is used in converting different units of measure through the multiplication of a given proportion or conversion factor. Learn how to solve single-step and multi-step problems using dimensional analysis and understand the cancellation of units in a numerator and denominator. Updated: 08/22/2021
How to perform dimensional analysis?
method to analyse scientific equations called dimensional analysis. One should note that while units are arbitrarily chosen (an alien civilisation will not use seconds or weeks), dimensions represent fundamental quantities such as time. Basic dimensions are written as follows: Dimension Symbol Length L Time T Mass M Temperature K Electrical current I
How is dimensional analysis used in chemistry?
Dimensional analysis is used in chemistry in a variety of ways. It can be used to convert between weights or temperatures. But the most common way it is used is to calculate molecules from grams (or vice versa) and with balanced chemical equations.
What is dimensional analysis?
Dimensional analysis is the process by which we convert between units and whether we should divide or multiply. You may do simple problems like this frequently throughout the day. For example, when watching the clock and waiting for a boring lecture to be over, you may think to yourself, 'We have only 5 minutes left, which is equal to only 300 seconds, which is really not that long!' You just converted from minutes to seconds.
Why is dimensional analysis important?
Sometimes in conversions it is easy to forget if we need to divide or if we need to multiply two things together. Dimensional analysis fixes this problem because we are also multiplying and dividing units, and if we don't end up with the correct units, then we did it wrong:
How to find the number of seconds in minutes?
In the example of changing between minutes to seconds, we know that there are 60 seconds per minute, so we can multiply the number of minutes by 60 and we get the number of seconds. Dimensional analysis would indicate this as such:
Can you cancel out units in dimensional analysis?
The nice thing about dimensional analysis is that we can cancel out units like in math, which you can see in the places where the minutes variable is cancelled out. If we were dividing 9/9, we know this equals 1, so it can cancel out in the equation. The same works with the units. If we are dividing minutes by minutes, then it cancels out into '1'.