As the exchange rate increases, the demand for the currencies decreases. Similarly, if the supply of a country's currency increases, and more money is needed in order to purchase foreign currencies. The ratio drives up the price. In contrast, if the supply goes up but the will fall.
How does the exchange rate affect the value of currency?
In market economy currency price fluctuates under the influence of supply and demand. If the exchange rate is too high, the currency supply exceeds demand, and price of the currency will decline. If the price is too low, demand will exceed supply, and the rate will increase.
What happens to exchange rate when supply and demand increase?
As the exchange rate increases, the demand for the currencies decreases. Similarly, if the supply of a country's currency increases, and more money is needed in order to purchase foreign currencies. The ratio drives up the price. In contrast, if the supply goes up but the will fall.
What determines the supply and demand for foreign currency?
The demand for currency of the seller of goods will depend on the price of foreign currency (the exchange rate). The supply of currency by the selling country appears, in its turn, due the necessity to buy the goods (i.e. the demand for the product) in the purchasing country of its products.
What is the relationship between foreign exchange rate and demand schedule?
It is understood from the demand schedule that the relationship, between the quantities of the foreign exchange demanded that the rate of foreign exchange is inverse in such a way that a fall in the rates of exchange is followed and inverse in the quantity of the foreign exchange demanded.

What is the relationship between foreign exchange rate and demand for foreign exchange?
Ans. Exchange rate of foreign currency is inversely related to the demand. When price of a foreign currency rises, it results into costlier imports for the country. As imports become costlier, the demand for foreign products also reduce.
How does exchange rate affect money supply?
Exchange Rates in the Long Run (cont.) A permanent increase in a country's money supply causes a proportional long run depreciation of its currency. depreciation first and a smaller subsequent appreciation. A permanent decrease in a country's money supply causes a proportional long run appreciation of its currency.
What affects the supply and demand of foreign currency?
The supply of a currency is determined by the domestic demand for imports from abroad. For example, when the UK imports cars from Japan it must pay in yen (¥), and to buy yen it must sell (supply) pounds. The more it imports the greater the supply of pounds onto the foreign exchange market.
What is the relationship between foreign exchange rate and supply of foreign currency?
Similarly, when foreign exchange rate falls, domestic goods become costlier for foreign buyers, decreasing demand for the exports, causing fall in supply of foreign exchange. Thus, foreign exchange rate and supply of foreign exchange are directly related.
How exchange rates affect imports and exports?
A rising level of imports and a growing trade deficit can have a negative effect on a country's exchange rate. A weaker domestic currency stimulates exports and makes imports more expensive; conversely, a strong domestic currency hampers exports and makes imports cheaper.
What factors affect foreign exchange rates?
9 Factors That Influence Currency Exchange RatesInflation. Inflation is the relative purchasing power of a currency compared to other currencies. ... Interest Rates. ... Public Debt. ... Political Stability. ... Economic Health. ... Balance of Trade. ... Current Account Deficit. ... Confidence/ Speculation.More items...•
What increases demand for foreign currency?
1. When price of a foreign currency falls, imports from that foreign country become cheaper. So, imports increase and hence, the demand for foreign currency rises. For example, if price of 1 US dollar falls from Rs 50 to Rs 45, then imports from USA will increase as American goods will become relatively cheaper.
What will cause an increase in demand for foreign currency?
A country's terms of trade improves if its exports prices rise at a greater rate than its imports prices. This results in higher revenue, which causes a higher demand for the country's currency and an increase in its currency's value. This results in an appreciation of exchange rate.
How exchange rates are determined a supply and demand analysis?
Currency prices can be determined in two main ways: a floating rate or a fixed rate. A floating rate is determined by the open market through supply and demand on global currency markets. Therefore, if the demand for the currency is high, the value will increase.
Why supply of foreign exchange is positively related to the rate of foreign exchange?
The foreign exchange rate and supply of foreign exchange is positively related and it is upward sloping curve as because the components of supply of foreign exchange rise as foreign exchange rate rises. For example, exports rise as the foreign exchange rate rises.
What affects the money supply?
The Fed can influence the money supply by modifying reserve requirements, which generally refers to the amount of funds banks must hold against deposits in bank accounts. By lowering the reserve requirements, banks are able to loan more money, which increases the overall supply of money in the economy.
What increases the supply of a currency?
As the price of a foreign currency increases, the quantity supplied of that currency increases. Exchange rates are determined just like other prices: by the interaction of supply and demand. At the equilibrium exchange rate, the supply and demand for a currency are equal.
What decreases the supply of a currency?
Lower interest rates. Higher money supply puts downward pressure on interest rates. Lower interest rates will also tend to reduce the value of the currency.
Does a higher rate of growth of the money supply lower interest rates?
A larger money supply lowers market interest rates, making it less expensive for consumers to borrow. Conversely, smaller money supplies tend to raise market interest rates, making it pricier for consumers to take out a loan.
Why do exchange rates vary?
Generally, exchange rates vary as demand for goods from nations vary. More demand for British goods, for example, would change the demand for the British pound. Just as supply and demand dictate the value of a good, supply and demand will dictate the value of the British pound as well.
How are foreign exchange rates determined?
Foreign currency exchange rates are determined in open markets by both supply and demand. Learn about the effect of supply and demand, how changes happen, and the impact of exchange rates between currencies. Updated: 09/07/2021
How does the supply curve of the British pound work?
The only way for someone from England to convert their pounds into dollars is to come to you and trade, so you end up with more British pounds than you had before. Effectively, the decrease in the value of the dollar has created a higher supply of pounds. From the perspective of the British, the supply curve of the British pound is really the demand curve of the U.S. dollar.
Why does demand fall for pounds?
Conversely, a fall in demand would shift the demand curve left and lead to a falling pound and rising dollar.
What is the demand curve for British pounds?
The demand curve for British pounds in terms of the U.S. dollar is a normal downward sloping demand curve. This is because if the value of the British pound went down relative to the U.S. dollar, the quantity of pounds demanded by Americans would increase; when pounds go on sale, more pounds are sold! Pretty much the same idea behind the demand of a good.
Why does the dollar appreciate against the pound?
A new intersection for supply and demand occurs at a lower exchange rate, and the dollar appreciates against the pound because of the increased supply of pounds.
How is the value of a currency determined?
Just like the value of a good is determined by the supply and demand for that good, the value of a nation's currency is determined by the supply and demand for that currency. For example, during the 2012 Summer Olympics in London, tourism to England increased. That could have caused an increase in demand for the British pound and the value of the pound to rise. Generally, exchange rates vary as demand for goods from nations vary. More demand for British goods, for example, would change the demand for the British pound. Just as supply and demand dictate the value of a good, supply and demand will dictate the value of the British pound as well.
What are the factors that affect the supply and demand of foreign exchange?
The supply and demand of foreign. exchange depends on lots of factors. They are: Economic Factors have. a direct impact on the foreign exchange market, for example economic. policies formulated by central Banks and government agencies, economic. reports, conditions and other economic indicators all of which can cause.
What are the factors that affect foreign exchange rates?
One of the key factors that effects. the foreign exchange rates is the supply and demand for each particular. currency. As the exchange rate increases, the demand for the currencies. decreases. Similarly, if the supply of a country's currency increases, the value of that currency will decrease in relation to other currencies.
What happens to the rate of exchange when the demand for a foreign currency increases?
Thus, we conclude that if the demand for a foreign currency increases, its rate of exchange must go up , and if its supply exceeds its demand, the rate must decline.
What is the demand for foreign exchange?
The Demand for Foreign Exchange. Generally, the demand for foreign currency arises from the traders who have to make payments for imported goods. If a person wants to invest his capital in foreign countries, he requires the currency of that country.
How to find equilibrium rate of foreign exchange?
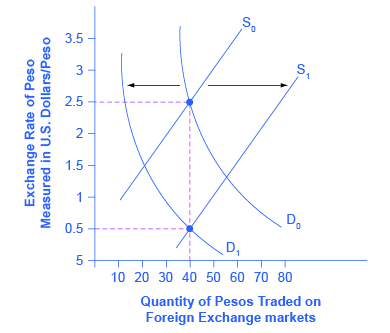
After deriving the demand and supply curves relating to foreign exchange, the equilibrium rate of foreign exchange in the foreign exchange market is determined through the point of intersection between the supply and demand curves of foreign exchange. The rate of exchange refers to the rate at which the currency of one country can be converted into the currency of another country. Thus, it indicates the exchange ratio between the currencies of two countries.
What is rate of exchange?
The rate of exchange refers to the rate at which the currency of one country can be converted into the currency of another country. Thus, it indicates the exchange ratio between the currencies of two countries. In this figure the demand for and supply of foreign exchange have been measured along the axis OX, and the rate of exchange along that ...
How is the rate of exchange determined?
To make the demand and supply functions to foreign exchange, like the conventional market demand and supply functions, we define the rate of exchange as the price of one unit of the foreign currency expressed in terms of the units of the home currency.
What is the need for and supply of foreign currency?
The need for and supply of foreign currency arises from the exporters who have exported goods and services to foreign countries. The supply schedule or curve of foreign exchange shows the different quantities of foreign exchange, which would be available at different rate of foreign exchange, in the foreign exchange market.
Why is foreign exchange higher than imports?
The main reason for this relationship is that, a higher rate of foreign exchange by rendering imports more expensive reduces the demand for them and consequently, also reduces the amount demande d of foreign exchange which is required to pay for imports. On the other hand, a lower rate of exchange by making the imports cheaper causes ...
Why is there a demand for foreign currency?
The demand for the foreign currency appears from the need to buy goods and services abroad. The demand for the currency of any country in the foreign exchange market indicates that there is a demand of foreigners for goods and services of this country. The level of demand for the currency depends on the price of the offered good. With the decline in prices of goods more buyers are willing and able to buy it.
How does the reduction of national currency affect the growth of exports?
The reduction in prices of the national currency reduces prices of national products, which are denominated in foreign currency (the goods become cheaper for foreigners). This contributes to the growth of exports, which is becoming more competitive. At the same time, the price of foreign goods, which are denominated in local currency, rises and their imports decline. The rise in the exchange rate of national currency makes domestic goods more expensive, the prices of which are expressed in foreign currency (the goods become more expensive for foreigners). Their exports decline and become less competitive. At the same time, the price of foreign goods, which are expressed in national currency, reduces and imports rise.
What is the purchasing power parity?
Currency on world markets compared to international value of certain amount of goods and services, presented by one or another currency unit. There is a relationship of two currencies, in which a certain amount of money can be exchanged for the "market basket" of goods and services with same composition and volume in both countries in the process of the international and global economic relations. This will be the purchasing power parity, that is, a level of the exchange rate of two currencies that equalizes the purchasing power of each of them all other things being equal.
What is the relative increase in labor productivity?
The relatively faster productivity growth in one country (the relative increase in labor productivity) in the long run leads to higher relative purchasing power of national currencies in relation to the goods and therefore to the increase of the exchange rate of the country.
What factors determine the long term trend of exchange rate?
In the field of management of the factors determining the long-term trend of movement of the exchange rate, there are: the inflation, its rate compared with the rate of depreciation of major currencies. The higher rates of national inflation, other things being equal, lead to a decrease of the exchange rate of the country in relation to countries with relatively low rates of depreciation of money. In the case of inflation, the exchange rate change is purely nominal, and is opposed to the real exchange rate in the case of the relative change in labor productivity. If in the first case it is possible to influence the exchange rate towards its improvement by using monetary policy (the reduction of emission of money, the increase of lending rates, etc.), then in the second case - by means, directed on the increase of labor productivity to a level that ensures competitiveness in the world market.
What are the long term factors that determine the exchange rate?
The long-term fundamental factors, determining the exchange rate movements, are the processes in the area of national production and circulation. This, above all, the relative (relative to the world level) labor productivity and, respectively, production costs, the long-term growth rates of the GNP, the place and role in world trade and the export of capital. The relatively faster productivity growth in one country (the relative increase in labor productivity) in the long run leads to higher relative purchasing power of national currencies in relation to the goods and therefore to the increase of the exchange rate of the country. This makes it possible to predict the long-term development of the exchange rates.
How does currency dumping affect the economy?
The decline in the national currency promotes the dumping of goods. However, currency dumping brings additional revenue only when the external depreciation of currency, i.e. reduction of its exchange rate, is ahead of internal depreciation, i.e. decline in the purchasing power of money in the country. Only in this case, the product selling for the same (or lower) price in a foreign currency, the exporter swaps this currency to more of his own national currency as a result of the drop of the latest one. This allows him to buy more domestic equipment, raw materials and labor for the production expansion.
What will happen to the currency market if domestic inflation increases?
This domestic inflation will make your goods relatively less competitive and export demand will fall. Therefore, there will be less demand for the currency and its value will tend to fall on the exchange rate markets.
How does higher money supply affect interest rates?
Also, if you increased the money supply, (through a Central Bank creating more money), then this reduces interest rates. Higher money supply puts downward pressure on interest rates. Lower interest rates will also tend to reduce the value of the currency.
What was the UK's monetary policy during the Great Recession?
The great recession is fairly unique in that the UK pursued expansionary monetary policy (zero interest rates, quantitative easing and even forward guidance to try an increase inflation expectations). But, UK inflation fell from mid-2011, even though monetary policy remained expansionary.
What will happen if the monetary policy of expansion cuts interest rates?
Alternatively, if expansionary monetary policy involves cutting interest rates – lower interest rates will tend to increase aggregate demand leading to possible inflationary pressure. ( Effect of lower interest rates) This domestic inflation will make your goods relatively less competitive and export demand will fall.
Why is lower interest rate better?
Lower interest rates – to make it cheaper to borrow and encourage both consumption and investment. Increasing the money supply, e.g. through quantitative easing – creating money electronically. In many circumstances, an increase in the money supply could lead to a depreciation in the exchange rate. This is for two main reasons: 1.
Why does inflation happen?
Everything else being equal, an increase in the money supply is likely to cause inflation. This is because with more currency chasing the same quantity of goods, firms will respond by putting up prices. (See why an increase in the money supply causes inflation)
Does an increase in the money supply lower interest rates?
An increase in the money supply doesn’t always cause lower interest rates. In a liquidity trap, monetary policy can’t reduce interest rates because they are already at the ‘Lower zero bound rate’
Why is the central bank concerned about exchange rates?
A central bank will be concerned about the exchange rate for three reasons: (1) Movements in the exchange rate will affect the quantity of aggregate demand in an economy; (2) frequent substantial fluctuations in the exchange rate can disrupt international trade and cause problems in ...
How does foreign trade affect the economy?
Foreign trade in goods and services typically involves incurring the costs of production in one currency while receiving revenues from sales in another currency. As a result, movements in exchange rates can have a powerful effect on incentives to export and import, and thus on aggregate demand in the economy as a whole.
What currency do banks use to lend money?
Most international loans are measured in a few large currencies, like U.S. dollars, European euros, and Japanese yen. In countries that do not use these currencies, banks often borrow funds in the currencies of other countries, like U.S. dollars, but then lend in their own domestic currency.
What countries have depreciated their currency?
In 1997–1998, countries across eastern Asia, like Thailand, Korea, Malaysia, and Indonesia, experienced a sharp depreciation of their currencies, in some cases 50% or more. These countries had been experiencing substantial inflows of foreign investment capital, with bank lending increasing by 20% to 30% per year through the mid-1990s. When their exchange rates depreciated, the banking systems in these countries became bankrupt. Argentina experienced a similar chain of events in 2002. When the Argentine peso depreciated, Argentina’s banks found themselves unable to pay back what they had borrowed in U.S. dollars.
How much did the rupee drop in 2009?
From February 2008 to March 2009, the Indian rupee moved from 39 rupees/dollar ito 51 rupees/dollar, a decline of more than one-fourth in the value of the rupee on foreign exchange markets.
Why are banks important?
Banks play a vital role in any economy in facilitating transactions and in making loans to firms and consumers. When most of a country’s largest banks become bankrupt simultaneously, a sharp decline in aggregate demand and a deep recession results. Since the main responsibilities of a central bank are to control the money supply and to ensure that the banking system is stable, a central bank must be concerned about whether large and unexpected exchange rate depreciation will drive most of the country’s existing banks into bankruptcy.
Why does Country C import a lot of food from other countries?
Country C imports a lot of its food from other countries because it has very little agriculture. If its currency depreciates relative to its trading partners, then. Multiple Choice Question. imports of food will be less expensive and households will be able to afford more food and other goods.
How does demand affect currency?
These relative values are influenced by the demand for currency, which is in turn influenced by trade. If a country exports more than it imports, there is a high demand for its goods, and thus, for its currency. The economics of supply and demand dictate that when demand is high, prices rise and the currency appreciates in value. In contrast, if a country imports more than it exports, there is relatively less demand for its currency, so prices should decline. In the case of currency, it depreciates or loses value.
What is the exchange rate of a currency?
Currency exchange rates are quoted as relative values; the price of one currency is described in terms of another. For example, one U.S. dollar might be equal to 11 South African rand. In other words, an American business or person exchanging dollars for rand would buy 11 rand for every dollar sold, and a South African would buy $1 for every 11 rand sold.
What happens when a country has a high demand for its goods?
A country with a high demand for its goods tends to export more than it imports, increasing demand for its currency. A country that imports more than it exports will have less demand for its currency. Trade balances, and as a result, currencies can swing back and forth, assuming each are floating currencies.
What happens when currencies are fixed?
If one or both currencies are fixed or pegged, the currencies don’t move as easily in response to a trade imbalance.
How much rand does an American get for every $1 sold?
Now, for every $1 sold, an American gets 15 rand. To buy $1, a South African has to sell 15 rand. Trade influences the demand for currency, which helps drive currency prices.
When a country's trade account does not net to zero, what is the difference?
When a country's trade account does not net to zero—that is, when exports are not equal to imports— there is relatively more supply or demand for a country's currency , which influences the price of that currency on the world market.
Can currencies move back and forth?
Trade balances, and as a result, currencies can swing back and forth, assuming each are floating currencies. If one or both currencies are fixed or pegged, the currencies don’t move as easily in response to a trade imbalance.