Key Points
- Legumes can fix substantial quantities of nitrogen (N) and this can be maximised by ensuring low plant available N in the soil at sowing and inoculating the seed if a paddock has not had a host legume nodulated by the same rhizobia in the last four years.
- Acid soils will require more regular inoculation or liming (except for narrow-leaf lupin).
How is nitrogen fixation carried out naturally in soil?
Nitrogen fixation is carried out naturally in the soil by a wide range of nitrogen fixing Bacteria and Archaea, including Azotobacter. Some nitrogen-fixing bacteria have symbiotic relationships with some plant groups, especially legumes.
How do plants convert nitrogen in the air to soil?
In order for plants to use the nitrogen in the air, it must be converted in some way to nitrogen in the soil. This can happen through nitrogen fixation, or nitrogen can be “recycled” by composting plants and manure.
How is nitrogen fixed in the environment?
Nitrogen is fixed, or combined, in nature as nitric oxide by lightning and ultraviolet rays, but more significant amounts of nitrogen are fixed as ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates by soil microorganisms. More than 90 percent of all nitrogen fixation is effected by them.
How is nitrogen recycled from soil?
Nitrogen is continuously recycled through plant and animal waste residues and soil organic matter. Nitrogen is removed from the soil by crops, gaseous loss, runoff, erosion and leaching. The magnitude and mechanism responsible for nitrogen losses depend upon the chemical and physical properties of a given soil.

Who fixes nitrogen in the soil?
Many heterotrophic bacteria live in the soil and fix significant levels of nitrogen without the direct interaction with other organisms. Examples of this type of nitrogen-fixing bacteria include species of Azotobacter, Bacillus, Clostridium, and Klebsiella.
How does nitrogen-fixing work?
How Does Nitrogen Fixation Work? Nitrogen-fixing plants form a mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship with soil bacteria. These microorganisms serve as a microbial inoculant, infecting the host plant's root system and causing it to form nodules where the bacteria can thrive.
What are the 3 processes that fix nitrogen?
There are three processes that can fix nitrogen: atmospheric, Haber Process and biological. Atmospheric fixation occurs when the high temperature of lightning splits the nitrogen gas so it bonds with oxygen and moisture in the air to form nitrates that fall to the earth with rain.
What is the most common way that nitrogen fixation occurs?
What is the most common way that nitrogen fixation occurs? Atmospheric nitrogen (N2 gas) is easily taken up and used by plants and animals. Ammonium (NH4) stays in soil, while nitrate (NO3) is easily leached out.
Where does nitrogen fixation occur?
Nitrogen fixation takes place in a wide variety of bacteria, the best known of which is rhizobium which is found in nodules on the roots of leguminous plants such as peas, beans, soya and clover.
What are the 2 ways nitrogen can be fixated?
Nitrogen fixation in nature Nitrogen is fixed, or combined, in nature as nitric oxide by lightning and ultraviolet rays, but more significant amounts of nitrogen are fixed as ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates by soil microorganisms.
What are two ways nitrogen fixation occurs?
There are three major ways in which this happens: first, by lightning, when the energy of lightning strikes breaks apart the N2 bonds; second, by industrial methods, when humans break the bonds with high pressure and temperatures, and hydrogen; finally, by biological fixation, with bacteria living in the soil.
What is nitrogen fixation simple definition?
Definition of nitrogen fixation : the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into a combined form (such as ammonia) through chemical and especially biological action (such as that of soil rhizobia)
What is nitrogen fixation and why is it important?
Nitrogen fixation is a process whereby bacteria in the soil convert atmospheric nitrogen ( N2 gas) into a form that plants can use. The reason this process is so important is that animals and plants cannot use atmospheric nitrogen directly.
What is a nitrogen fixing plant?
Nitrogen-fixing plants are those whose roots are colonized by certain bacteria that extract nitrogen from the air and convert or “fix” it into a form required for their growth. When the bacteria are done with this nitrogen, it becomes available to the plants, themselves.
What are the three types of nitrogen fixation?
1. Biological nitrogen fixation 2. Atmospheric nitrogen fixation 3. Industrial nitrogen fixation
What are the 7 steps of the nitrogen cycle?
1. Nitrogen fixation. 2. Assimilation 3. Ammonification 4. Nitrification 5. Denitrification 6. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium 7. Anaer...
How nitrogen fixation takes place in the soil?
Nitrogen fixation is carried out naturally in soil by microorganisms that are termed diazotrophs. These include bacteria such as Azotobacter and Ar...
What is nitrogen fixation, and why is it important?
The process of fixing atmospheric nitrogen into the soil through various means such as lightning or by certain organisms is called nitrogen fixatio...
What is an example of nitrogen fixation?
Nitrogen fixation in the root nodules of leguminous plants or by the symbiotic association of Azolla and Anabaena in the paddy fields are two examp...
How does nitrogen fixation occur?
Nitrogen fixation occurs with the help of microorganisms as a part of the nitrogen cycle either by natural means or via industrial methods.
What is the process of converting nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds?
The process of conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogenous compounds by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi and algae is known as Biological Nitrogen Fixation (BNF) or diazotrophy. Some prokaryotes such as bacteria and cyanobacteria that can fix atmospheric nitrogen are called nitrogen fixers or diazotrophs.
What are the Types of Nitrogen Fixation?
Nitrogen fixation is carried by physicochemical and biological means. Only 10 % of natural nitrogen fixation takes place by physicochemical means, whereas 90 % is carried out by biological means. Thus, we can classify nitrogen fixation in following two types:
How is nitrogen converted into ammonia?
Nitrogen needs to be converted into different forms like ammonia, nitrites or nitrates through nitrogen fixation via various means as the molecular form of nitrogen is of no use to plants and animals. Nitrogen plays a vital role in the life of living organisms. Hence nitrogen fixation is a very necessary and crucial process. Nitrogen fixation is carried by physicochemical (only 10 % and biological 90 % means. Biological nitrogen fixation is mainly performed by a set of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, cyanobacteria, etc.
Why is nitrogen fixation important?
The process of nitrogen fixation is very important as the molecular form of nitrogen is of no use to plants and animals.
What is the name of the enzyme that reduces nitrogen to ammonia?
The atmospheric nitrogen is reduced to ammonia in the presence of a catalyst known as nitrogenase. This enzyme is found naturally in certain microorganisms like symbiotic ( Rhizobium and Frankia) and non-symbiotic or free-living ( Azospirillum, Azotobacter and BGA).
Where are nitrogen fixers found?
1. Symbiotic nitrogen fixers are found in a large number of legume plants, mainly the genus Rhizobium .
Why is nitrogen important?
Available nitrogen in the soil is the essential nutrient for green leaves, and new roots and shoots.
Can you use inoculants with legumes?
We advise using inoculants with raw legume cover crop seeds to give an extra boost of rhizobacteria. Average soil has some rhizobacteria, but not enough to fix a large amount of nitrogen. Some of our legume cover crop seeds come pre-coated with inoculant ("rhizocoated" or "nitrocoated") and others need to have it added just before planting. For more information on the wonders of soil, and how cover crops help build healthy soil, take a look at Teaming with Microbes, an award-winning book that tells the scientific story of soil in easy to understand language -- with action photos too. Wait till you see the photo of the nematode being lassoed by a fungal hypha. You'll be glad you're as tall as you are.
What is nitrogen fixation?
nitrogen fixation, any natural or industrial process that causes free nitrogen (N 2 ), which is a relatively inert gas plentiful in air, to combine chemically with other elements to form more-reactive nitrogen compounds such as ammonia, nitrates, or nitrites. Under ordinary conditions, nitrogen does not react ...
What is the most economical nitrogen fixation process?
The Haber-Bosch process directly synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydro gen and is the most economical nitrogen-fixation process known. About 1909 the German chemist Fritz Haber ascertained that nitrogen from the air could be combined with hydrogen under extremely high pressures and moderately high temperatures in the presence ...
What is nitrogen used for in agriculture?
Nitrogenous materials have long been used in agriculture as fertilizers , and in the course of the 19th century the importance of fixed nitrogen to growing plants was increasingly understood. Accordingly, ammonia released in making coke from coal was recovered and utilized as a fertilizer, as were deposits of sodium nitrate (saltpetre) from Chile. Wherever intensive agriculture was practiced, there arose a demand for nitrogen compounds to supplement the natural supply in the soil. At the same time, the increasing quantity of Chile saltpetre used to make gunpowder led to a worldwide search for natural deposits of this nitrogen compound. By the end of the 19th century it was clear that recoveries from the coal-carbonizing industry and the importation of Chilean nitrates could not meet future demands. Moreover, it was realized that, in the event of a major war, a nation cut off from the Chilean supply would soon be unable to manufacture munitions in adequate amounts.
What are the two types of nitrogen fixers?
Two kinds of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms are recognized: free-living (nonsymbiotic) bacteria, including the cyanobacteria (or blue-green algae) Anabaena and Nostoc and genera such as Azotobacter, Beijerinckia, and Clostridium; and mutualistic (symbiotic) bacteria such as Rhizobium, associated with leguminous plants, and various Azospirillum species, associated with cereal grasses.
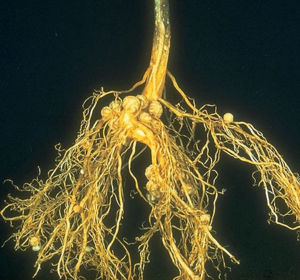
What are root nodules?
root nodules. The roots of an Austrian winter pea plant ( Pisum sativum) with nodules harbouring nitrogen-fixing bacteria ( Rhizobium ). Root nodules develop as a result of a symbiotic relationship between rhizobial bacteria and the root hairs of the plant.
What is the function of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in plants?
The symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria invade the root hairs of host plants, where they multiply and stimulate the formation of root nodules, enlargements of plant cells and bacteria in intimate association. Within the nodules, the bacteria convert free nitrogen to ammonia, which the host plant utilizes for its development. To ensure sufficient nodule formation and optimum growth of legumes (e.g., alfalfa, beans, clovers, peas, and soybeans ), seeds are usually inoculated with commercial cultures of appropriate Rhizobium species, especially in soils poor or lacking in the required bacterium. ( See also nitrogen cycle .)
What are the three most productive approaches to nitrogen?
The three most-productive approaches were the direct combination of nitrogen with oxygen, the reaction of nitrogen with calcium carbide, and the direct combination of nitrogen with hydrogen. In the first approach, air or any other uncombined mixture of oxygen and nitrogen is heated to a very high temperature, and a small portion ...
How does nitrogen fixation work?
The nitrogen fixation (N 2 -fixation) process between the legume plant and rhizobia bacteria is referred to as a symbiotic (mutually beneficial) relationship. Each organism receives something from the other and gives back something in return. Rhizobia bacteria provide the legume plant with nitrogen in the form of ammonium and the legume plant provides the bacteria with carbohydrates as an energy source. The rate of N 2 -fixation is directly related to legume plant growth rate. Anything that reduces plant growth such as drought, low temperature, limited plant nutrients, or disease will also reduce N 2 -fixation. Maintaining sufficient leaf area in a legume stand to intercept most of the sunlight is also critical to maintaining a high growth rate to support N 2 -fixation.
Where does nitrogen come from in soil?
A common misconception is that the nitrogen is released into the soil from the legume roots. Research has shown there is a release of some soluble nitrogen compounds such as amino acids and ammonium from intact legume roots and nodules, but it is an insignificant amount.
What factors affect the quantity of nitrogen fixed?
Factors that influence the quantity of nitrogen fixed are the level of soil nitrogen, the rhizobia strain infecting the legume, amount of legume plant growth, how the legume is managed, and length of growing season. If given a choice, a legume plant will remove nitrogen from the soil before obtaining nitrogen from the air through N 2 -fixation.
What is the nitrogen source for a legume plant?
Rhizobia bacteria provide the legume plant with nitrogen in the form of ammonium and the legume plant provides the bacteria with carbohydrates as an energy source. The rate of N 2 -fixation is directly related to legume plant growth rate.
What is the most limiting nutrient for legumes?
Nitrogen is the most limiting nutrient for plant growth. A legume plant’s ability to use nitrogen from the air is the best known benefit of growing legumes but the least understood. Approximately 79% of the air is nitrogen gas. However, it is not in a form that plants can use. In reality it is not the plant that removes nitrogen from the air but Rhizobium bacteria which live in small tumor like structures called nodules on the legume plant roots. These bacteria can take nitrogen gas from the air in the soil and transform it into ammonia (NH 3) that converts to ammonium (NH 4) which can be used by the plant. This ammonium is the same form as in ammonium nitrate (34-0-0) and ammonium sulfate (21-0-0) fertilizer.
How much nitrogen does a legume need?
General estimates of the amount of nitrogen fixed range from 50 to 100 lb N/acre for annuals and about 200 lb N/acre for alfalfa.
Why drill in soil for rhizobia?
It is desirable to drill the inoculated seed in the soil instead of broadcasting on the soil surface to help protect the bacteria from sunlight and high temperatures. Poor nodulation may occur even if good seed inoculation practices were used. Rhizobia bacteria begin dying as soon as the inoculated seed are planted.
How is nitrogen removed from the soil?
Nitrogen is removed from the soil by crops, gaseous loss, runoff, erosion and leaching. The magnitude and mechanism responsible for nitrogen losses depend upon the chemical and physical properties of a given soil.
Why is nitrogen used in soil?
The rates of nitrogen used and the time of application should be related to soil conditions and crop requirements to minimize leaching losses. Numerous research studies show that because of plant uptake, little nitrate nitrogen (NO3 – -N) leaches from soils on which a crop is actively growing.
What are the sources of nitrogen?
Common sources of inorganic nitrogen include ammonia (NH3), ammonium (NH4 +), amine (NH2 +) and nitrate (NO3 – ). Most fertilizer materials contain or will form NH4 + which is converted rapidly to NO3 – once in the soil.
Why is nitrogen important for agriculture?
However, the use of commercial nitrogen (N) fertilizers to increase production, maintain profits and provide low cost food and fiber is a necessity of modern agriculture. In general, crops need nitrogen in the greatest quantity of all plant nutrients.
What is the most common nitrogen in soil?
Commercial fertilizers, plant residues, animal manures and sewage are the most common sources of nitrogen addition to soils. Rates of application vary widely. Single application rates may be as high as 150 pounds of nitrogen equivalent per acre for crops such as coastal bermudagrass. However, such high application rates should be limited to soils with a low potential for erosion and runoff.
What is the first step in mineralization?
The first step of mineralization is “ammonification.”. The ammonium (NH4 +) derived from ammonification is then converted to nitrate-nitrogen (NO3 – -N) by “nitrifying” bacteria in the soil through the process called “nitrification.”. The locations of the ammonification and nitrification reactions in the nitrogen cycle are shown in Figure 1.
How to use nitrogen in agriculture?
To effectively use nitrogen and to limit its adverse impact on the environment, producers need to develop an awareness of the chemistry of nitrogen and how it is added to and removed from the soil. Commercial fertilizers used by agricultural producers are a significant source of nitrogen addition to soils.
Where does nitrogen fixation occur?
Nitrogen fixation occurs between some termites and fungi. It occurs naturally in the air by means of NO x production by lightning. All biological reactions involving the process of nitrogen fixation are catalysed by enzymes called nitrogenases.
Why is nitrogen fixation important?
Nitrogen fixation is essential to life because fixed inorganic nitrogen compounds are required for the biosynthesis of all nitrogen-containing organic compounds , such as amino acids and proteins, nucleoside triphosphates and nucleic acids.
What is the role of nitrogenase in a cell?
The protein complex nitrogenase is responsible for catalyzing the reduction of nitrogen gas (N 2) to ammonia (NH 3 ). In Cyanobacteria, this enzyme system is housed in a specialized cell called the heterocyst. The production of the nitrogenase complex is genetically regulated, and the activity of the protein complex is dependent on ambient oxygen concentrations, and intra- and extracellular concentrations of ammonia and oxidized nitrogen species (nitrate and nitrite). Additionally, the combined concentrations of both ammonium and nitrate are thought to inhibit N Fix, specifically when intracellular concentrations of 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) exceed a critical threshold. The specialized heterocyst cell is necessary for the performance of nitrogenase as a result of its sensitivity to ambient oxygen.
What is the nitrogenase complex?
The protein complex nitrogenase is responsible for catalyzing the reduction of nitrogen gas (N 2) to ammonia (NH 3 ). In Cyanobacteria, this enzyme system is housed in a specialize cell called the heterocyst. The production of the nitrogenase complex is genetically regulated, and the activity of the protein complex is dependent on ambient oxygen concentrations, and intra- and extracellular concentrations of ammonia and oxidized nitrogen species (nitrate and nitrite). Additionally, the combined concentrations of both ammonium and nitrate are thought to inhibit N Fix, specifically when intracellular concentrations of 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) exceed a critical threshold. The specialized heterocyst cell is necessary for the performance of nitrogenase as a result of its sensitivity to ambient oxygen.
How much nitrogen does red clover fix?
For example, nitrogen fixation by red clover can range from 50 to 200 lb./acre.
How is ammonia produced?
The most common ammonia production method is the Haber process. The Haber-Bosch nitrogen reduction process for industrial fertilizer production revolutionized modern day technology. Fertilizer production is now the largest source of human-produced fixed nitrogen in the terrestrial ecosystem. Ammonia is a required precursor to fertilizers, explosives, and other products. The Haber process requires high pressures (around 200 atm) and high temperatures (at least 400 °C), which are routine conditions for industrial catalysis. This process uses natural gas as a hydrogen source and air as a nitrogen source. The ammonia product has resulted in an intensification of nitrogen fertilizer globally and is credited with supporting the expansion of the human population from around 2 billion in the early 20th century to roughly 8 billion people now.
What was the first species to use diatomic nitrogen?
In 1901 Beijerinck showed that azotobacter chroococcum was able to fix atmospheric nitrogen. This was the first species of the azotobacter genus, so-named by him. It is also the first known diazotroph, species that use diatomic nitrogen as a step in the complete nitrogen cycle .
How Does Nitrogen Fixation Work?
Inside these root nodules, the bacteria draw nitrogen gas from the air, turning it into fixed nitrogen that is able to be absorbed and used by the plant host.
Why do plants need nitrogen?
Nitrogen is the element responsible for lush green plant growth, but plants aren't actually able to use the nitrogen gas in Earth's atmosphere. Certain plant species, though, harbor bacteria in their roots that convert nitrogen from the atmosphere into a form that plants can absorb. Farmers and gardeners use these plants as cover crops—inedible species grown in the off-season for the purpose of replacing the nutrients consumed by harvested crops—to produce nitrogen.
What is the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen into a soluble form usable by plants as fertilizer?
Biological nitrogen fixation is the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen into a soluble form usable by plants as fertilizer; bacteria living on the roots of leguminous plants perform this essential ecological function.
What happens to the nitrogen in the root nodules?
Inside these root nodules, the bacteria draw nitrogen gas from the air, turning it into fixed nitrogen that is able to be absorbed and used by the plant host. Once the host plant dies, the bacteria are released back into the soil where they either stay put or infect another legume.
What are the three types of nitrogen-fixing plants?
3 Types of Nitrogen-Fixing Plants. Legumes (members of the plant species Fabaceae) are common nitrogen-fixing plants. Legume plants form a symbiotic relationship with a type of nitrogen-fixing bacteria called Rhizobium. Actinorhizal plants are certain species of non-legume trees and shrubs that have a symbiotic association with a nitrogen-fixing ...
What is the name of the plant that is nitrogen-fixing?
Legumes (members of the plant species Fabaceae) are common nitrogen-fixing plants. Legume plants form a symbiotic relationship with a type of nitrogen-fixing bacteria called Rhizobium. Actinorhizal plants are certain species of non-legume trees and shrubs that have a symbiotic association with a nitrogen-fixing bacteria called Frankia. Popular types of nitrogen-fixers for home gardens include:
What are some examples of non-legume plants that have nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
Popular types of nitrogen-fixers for home gardens include: Ground cover plants: Vetch, cowpea, lupine flower, soybean, clover, peanut, alfalfa, and Austrian winter pea.
How to fix nitrogen deficiency?
Some organic methods of adding nitrogen to the soil include: Adding composted manure to the soil. Planting a green manure crop, such as borage. Planting nitrogen fixing plants like peas or beans.
Why Do Plants Need Nitrogen?
To put it in simple terms, plants need nitrogen to make themselves. Without nitrogen, a plant cannot make proteins, amino acids, and even its very DNA. This is why when there is a nitrogen deficiency in the soil, plants are stunted. They simply cannot make their own cells.
Why do my plants look yellow?
Your garden isn’t growing as well as it used to and some of the plants in the garden are starting to look a little yellow. You suspect a nitrogen deficiency in the soil, but you are unsure how to correct it. “Why do plants need nitrogen anyway?”, you may be wondering.
How can nitrogen be recycled?
In order for plants to use the nitrogen in the air, it must be converted in some way to nitrogen in the soil. This can happen through nitrogen fixation, or nitrogen can be “recycled” by composting plants and manure.
Can you test soil for nitrogen?
There is no homemade way to test the nitrogen of soil. You will either have to have your soil tested or purchase a soil testing kit. Typically, your local extension office will gladly test your soil for a small fee or even for free, depending on where you live.
Is nitrogen a chemical fertilizer?
Non-organic. Nitrogen as a plant fertilizer is common when purchasing chemical fertilizers. When looking to specifically add nitrogen to your garden, choose a fertilizer that has a high first number in the NPK ratio. The NPK ratio will look something like 10-10-10 and the first number tells you the amount of nitrogen.
What is the role of nitrogen in soil?
Since nitrogen (along with potassium and phosphorus) is one of the three nutrients used by plants in the highest quantities, it can be one of the first nutrients lacking from the soil. Plants can easily deplete all the nitrogen available in the soil in a given area.
Why do you need to fix nitrogen in your garden?
Incorporating nitrogen fixing plants in your garden can help maintain a natural balance. It can help prevent soil from becoming depleted of this vital plant nutrient. If you do not pay attention to the nitrogen cycle, you may find that productivity decreases over time.
What is Nitrogen and Why Do Plants Need It?
Nitrogen, (along with potassium and phosphorus) is essential for plant growth.
How do people use nitrogen fixing trees?
People use nitrogen fixing trees as pioneer species to reclaim and enhance damaged or degraded land. You can spread them across a piece of land, along swales, or use them in the creation of shelter belts of wind-break hedging, for example. Over time, these plants fix nitrogen and improve the soil.
Why do plants co-operate with bacteria in their roots?
Certain plants co-operate with bacteria in their roots to take nitrogen from the atmosphere and make it available in the soil.
How does lightning affect soil?
Lightning can be one way in which atmospheric nitrogen is turned into bio-available nitrates in the soil. But most atmospheric nitrogen is ‘fixed’ into the soil through the agency of soil microbiota.
What happens if you don't pay attention to the nitrogen cycle?
If you do not pay attention to the nitrogen cycle, you may find that productivity decreases over time. You may even find that plants develop deficiencies and fail to thrive.