What countries are in Stage 3 of the demographic transition?
Which countries are in Stage 3 of the demographic transition model? As such, Stage 3 is often viewed as a marker of significant development. Examples of Stage 3 countries are Botswana, Colombia, India, Jamaica, Kenya, Mexico, South Africa, and the United Arab Emirates , just to name a few.
How realistic is the demographic transition model?
This can be attributed to a wide array of social factors, including:
- Contraception access
- Higher wages
- Fewer families participating in agriculture (meaning less need for large families to work on farms)
- Improvement in education and social status of women
What are the 4 stages of population growth?
What can we do to stop overpopulation?
- Have fewer children!
- Consider adoption!
- Read, educate yourself about population issues – read more here.
- Reduce your personal consumption: go vegan, limit flying, share your household with others, and more.
- Educate your teenage child (ren) about sex and contraception early, without taboos.
What are the 5 stages of population pyramid?
population pyramid
- Organization of data. In a population pyramid, the size of the population under investigation is depicted on the horizontal axis, and age is aligned on the vertical axis.
- Interpreting population pyramids. ...
- Population pyramids and demographic transition. ...

What are the five stages of the demographic transition?
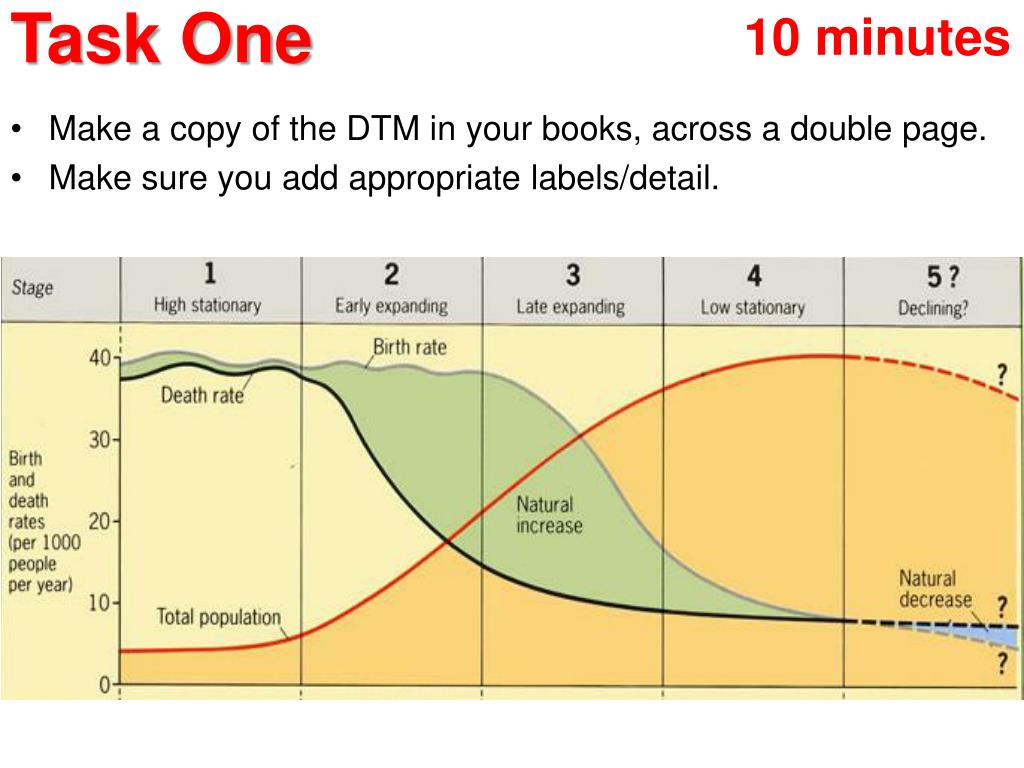
Demographic cycle(1) FIRST STAGE (High stationary) It is characterized by both. ... (2) SECOND STAGE (Early expanding) It begins with the. ... (3) THIRD STAGE (Late expanding) *Death rate declines further and. ... (4) FOURTH STAGE (Low stationary) This stage is characterized with. ... (5) FIFTH STAGE: (Declining)
How many stages are there for demographic transition?
four stagesThe original Demographic Transition model has just four stages, but additional stages have been proposed. Both more-fertile and less-fertile futures have been claimed as a Stage Five. Some countries have sub-replacement fertility (that is, below 2.1–2.2 children per woman).
What is Stage 5 of the demographic transition model called?
Answer: entry into Stage 5 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM) – theoretically. In Stage 5 of the DTM a country experiences loss to the overall population as the death rate becomes higher than the birth rate. The negative population growth rate is not an immediate effect however.
What is stage 6 of the demographic transition model?
Although it is normal for fertility decline in medium to high-HDI countries, there is evidence for fertility increase in areas of very advanced human development. Perhaps it is this that could serve as a new model of what might be called 'stage 6' of humanities ever changing demographic transition.
What are the 4 types of demographic transition?
The demographic transition model was initially proposed in 1929 by demographer Warren Thompson. The model has four stages: pre-industrial, urbanizing/industrializing, mature industrial, and post-industrial.
What is demographic transition model?
Demographic transition is a model used to represent the movement of high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system.
What is a Stage 4 country?
A country in Stage 4 will have a much smaller base of young people (fewer children), but a much larger population of elderly (decreased CDR). A nation with a large youth population is more likely to be rural with high birthrates and possibly high death rates.
What is Stage 4 demographic transition?
In Stage 4, birth and death rates are both low, stabilizing the population. These countries tend to have stronger economies, higher levels of education, better healthcare, a higher proportion of working women, and a fertility rate hovering around two children per woman. Most developed countries are in Stage 4.
What is the last stage of demographic transition?
Following the industrial stage is the final stage of the demographic transition. This stage is referred to as the post-industrial stage and is characterized by a stable human population, with both low birth rates and low death rates.
Are any countries in stage 5?
Countries currently in stage five are Japan and a number in Eastern Europe (Germany, Estonia, Ukraine). Fewer young adults are having children. Some stage 5 governments promote pro-natalist policies to try and stunt the population decrease by incentivizing having children.
What are the three stages of demographic transition class 12?
Stages of the Demographic TransitionStage 1—High birth and death rates lead to slow population growth.Stage 2—The death rate falls but the birth rate remains high, leading to faster population growth.Stage 3—The birth rate starts to fall, so population growth starts to slow.More items...•
What is a Stage 3 country?
As such, Stage 3 is often viewed as a marker of significant development. Examples of Stage 3 countries are Botswana, Colombia, India, Jamaica, Kenya, Mexico, South Africa, and the United Arab Emirates, just to name a few.
What is a Stage 4 country?
A country in Stage 4 will have a much smaller base of young people (fewer children), but a much larger population of elderly (decreased CDR). A nation with a large youth population is more likely to be rural with high birthrates and possibly high death rates.
What is Stage 5 of the epidemiological transition?
Some medical analysts argue that the world is moving into stage 5 of the epidemiologic transition, the stage of reemergence of infectious and parasitic diseases. Infectious diseases thought to have been eradicated or controlled have returned, and new ones have emerged.
What is Stage 2 of demographic transition called?
Stage two is the early expanding stage where population begins to rise. It has a high birth rate, but the death rate drops. Because of this the natural increase in population rate goes way up!
What is Stage 3 of the DTM?
Stage 3: Total population is rising rapidly. The gap between birth and death rates will narrow. Natural increase is high. Death rates will now remain low and steady (to 15 per 1,000) but birth rates will fall quickly (down to around 18 per 1,000).
What is Demographic Transition?
It was observed that in countries with high standards of living, the population grew at a slow rate, while in countries with low standards of living, the population grew more rapidly .
What is the third stage of demographic change?
The third stage of the demographic transition is the industrial stage, which is characterized by an increasing population with declining birth rates and low death rates. The death rates remain stable and low during this stage due to the continuation of the economic and social changes that improved the standard of living during the previous stage. During this stage, the birth rates begin to decline for many reasons. For the most part, people realize that they no longer have to produce large numbers of offspring because the offspring they do produce have a higher chance of surviving to adulthood. Many people also start to prefer smaller families, where they can concentrate more resources on less people and increase overall livelihood.
What is the post industrial stage?
Following the industrial stage is the final stage of the demographic transition. This stage is referred to as the post-industrial stage and is characterized by a stable human population, with both low birth rates and low death rates. The birth rates and death rates remain low due the economic and social changes of the previous stages.
What is the study of the size, density, and distribution of the human population?
Now, let's review demography, which is the study of the size, density, and distribution of the human population and the concept of demographic transition. Demographic transition is a series of stages that a country goes through when transitioning from non-industrial to industrial. The concept is used to explain how population growth and economic development of a country are connected.
Why are death rates decreasing?
The death rates are decreasing because, as the country transitions into an industrial country, there are improvements in the economy and social conditions. These changes lead to the control of diseases, the production of more food, better jobs, and improved medical care and sanitation.
What are the stages of transition?
The Four Stages of Transition 1 Stage 1: Death rates and birth rates are high and are roughly in balance, a common condition of a pre-industrial society. Population growth is very slow, influenced in part by the availability of food. The U.S. was said to be in Stage 1 in the 19th century. 2 Stage 2: This is the "developing country" phase. Death rates drop rapidly due to improvements in food supply and sanitation, which increases life spans and reduces disease. Without a corresponding fall in birth rates, countries in this stage experience a large increase in population. 3 Stage 3: Birth rates fall due to access to contraception, increases in wages, urbanization, an increase in the status and education of women, and other social changes. Population growth begins to level off. Mexico is believed to be in this stage in the early decades of the millennium. Northern Europe entered this stage in the later part of the 19th century. 4 Stage 4: Birth rates and death rates are both low in this stage. People born during Stage 2 are now beginning to age and require the support of a dwindling working population. Birth rates may drop below replacement level, considered to be two children per family. This leads to a shrinking population. Death rates may remain consistently low, or they may increase slightly due to increases in lifestyle diseases linked to low exercise levels and high obesity. Sweden has reached this stage in the 21st century.
What is the definition of demographic transition?
Demographic transition is a model used to represent the movement of high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system. It works on the premise that birth and death rates are connected to and correlate with stages of industrial development.
What is the fifth stage of fertility?
Some theorists include a fifth stage in which fertility rates begin to transition again to either above or below that which is necessary to replace the percentage of the population that is lost to death. Some say fertility levels decrease during this stage while others hypothesize that they increase. Rates are expected to increase populations in Mexico, India and the U.S. in the 21st century, and to decrease populations in Australia and China. Birth and death rates largely plateaued in most developed nations in the late 1900s.
What is stage 3 birth rate?
Stage 3: Birth rates fall due to access to contraception, increases in wages, urbanization, an increase in the status and education of women, and other social changes. Population growth begins to level off. Mexico is believed to be in this stage in the early decades of the millennium.
What is the stage 1 of the development process?
Stage 1: Death rates and birth rates are high and are roughly in balance, a common condition of a pre-industrial society. Population growth is very slow, influenced in part by the availability of food. The U.S. was said to be in Stage 1 in the 19th century. Stage 2: This is the "developing country" phase.
What is the stage of Mexico?
Mexico is believed to be in this stage in the early decades of the millennium. Northern Europe entered this stage in the later part of the 19th century. Stage 4: Birth rates and death rates are both low in this stage. People born during Stage 2 are now beginning to age and require the support of a dwindling working population.
Why do death rates drop?
Death rates drop rapidly due to improvements in food supply and sanitation, which increases life spans and reduces disease. Without a corresponding fall in birth rates, countries in this stage experience a large increase in population. Stage 3: Birth rates fall due to access to contraception, increases in wages, urbanization, ...
What are the stages of development?
First stage: The stage includes a very high growth in death rates and birth rates. The status of a country is backward and the majority of the people live in countryside areas. The society is very simple with modest means of economic development. People are underdeveloped and backward and live in dirty surroundings. Facilities like banking, modern education, transport, commerce, etc. are not even at the initial stage of development. The birth rate is very high because people are not educated about population control methods. A family with more children is regarded as a prosperous family. Due to illiteracy, ignorance and various misconceptions, the birth rate is not in control. Due to more population but fewer resources, the availability of food is very low which causes a high death rate also. The population growth is almost in equilibrium. These economic and social factors are retarding the state of living standards.
What is the fourth stage of the population?
Fourth stage: Once again the population has become sluggish. Previously we see that birth rate is declining but less than that of the death rate. But now both concepts are equally decreasing. Due to this, the standard of living rises with more economic and social developments. Superstitions are being rejected by the people and the nuclear family is a priority now. Sources of income become available but expenses of various facilities like health, education, transport, etc. also rise. Men and women indulge in several family planning schemes. Now the population is growing less comparatively.
What is the term for a cycle that starts with a decline in the death rate, then a perpetual phase?
The demographic transition theory is a cycle that starts with a decline in the death rate, then a perpetual phase of population growth and ends with a fall in the birth rate.
What is the 5 stage theory?
However, it is a 5 stage theory now. We come across a very famous term called ‘demographic dividend’. It is very important to know about the country’s death rate and the birth rate for our economy and society. The demographic transition theory is a cycle that starts with a decline in the death rate, then a perpetual phase ...
Is population growth in equilibrium?
The population growth is almost in equilibrium. These economic and social factors are retarding the state of living standards. Second stage: After living in isolation and static state of the economy, now people start entering into the economic growth phase.
Is the population cycle only a theory?
This theory is not an only theory about the population cycle but it is the most accepted one. But there are many criticisms regarding it. The stages are not sequential and explanations about the decline birth rate vary from area to area. We cannot generalize this concept. The theory takes various economic and social factors but ignores many others. However, this theory is applicable in almost all European countries.
What is the fourth stage of demographic transition?
The fourth stage of demographic transition is characterised by a low birth rate and a low death rate of population, leading to a stationary population. It is, therefore, known as the stage of stationary population where both the birth rate and death rate remain at a low level leading to a very little growth in population.
Why is the demographic transition called demographic transition?
This theory is known as demographic transition because it will require a period ...
Why is demographic transition important?
This theory is known as demographic transition because it will require a period of transition in order to adjust with the imbalance resulted from a fall in death rate and a more or less stable birth rate. With the changes in the outlook of the society, the birth and death rates gradually reduce to a lower ebb and also become balanced resulting in fall in the rate of growth of population. India is now in the second stage of demographic transition where it has been able to reduce the death rate considerably but is facing a tardy fall in its birth rate.
What is the difference between Stage III and Stage IV?
Again the Stage III is subjected to a falling birth rate and low and stationary death rate leading to a rapid ly rising population. Finally, the Stage IV is characterised by a low birth rate and a low death rate leading to a stationary population at a very low level.
What is the gradual attainment of economic development?
With the gradual attainment of economic development, the economy of the country started to experience a change in its structure from a purely agrarian to an industrialised one. During this stage people become conscious about the size of the family and also on limiting the size of the family. There will be exodus of population from rural to urban areas in search of food and job.
Why is the rate of growth of population not high?
In this economy, the rate of growth of population is not high as high birth rate is compensated by high death rate. 2. With the gradual attainment of economic development, the living condition of people started to improve due to better and regular diet, better medical and sanitation facilities leading to fall in the death rate.
What are the endogenous factors that reduce birth rates?
But to reduce the birth rate, some endogenous factors such as changes in customs, social attitudes, beliefs and dogmas about marriage and also about size of the family etc. are playing important role. But such changes are very difficult to occur and time consuming.
How many stages are there in the Demographic Transition Model?
The original Demographic Transition model has just four stages, but additional stages have been proposed. Both more-fertile and less-fertile futures have been claimed as a Stage Five.
How many stages are there in the transition?
The transition involves four stages, or possibly five. In stage one, pre-industrial society, death rates and birth rates are high and roughly in balance. All human populations are believed to have had this balance until the late 18th century, when this balance ended in Western Europe.
What happens to the population during the second stage of the demographic transition?
The decline in death rate and birth rate that occurs during the demographic transition may transform the age structure. When the death rate declines during the second stage of the transition, the result is primarily an increase in the child population. The reason being that when the death rate is high (stage one), the infant mortality rate is very high, often above 200 deaths per 1000 children born. When the death rate falls or improves, this may include lower infant mortality rate and increased child survival. Over time, as individuals with increased survival rates age, there may also be an increase in the number of older children, teenagers, and young adults. This implies that there is an increase in the fertile population proportion which, with constant fertility rates, may lead to an increase in the number of children born. This will further increase the growth of the child population. The second stage of the demographic transition, therefore, implies a rise in child dependency and creates a youth bulge in the population structure. As a population continues to move through the demographic transition into the third stage, fertility declines and the youth bulge prior to the decline ages out of child dependency into the working ages. This stage of the transition is often referred to as the golden age, and is typically when populations see the greatest advancements in living standards and economic development. However, further declines in both mortality and fertility will eventually result in an aging population, and a rise in the aged dependency ratio. An increase of the aged dependency ratio often indicates that a population has reached below replacement levels of fertility, and as result does not have enough people in the working ages to support the economy, and the growing dependent population.
Why is the existence of a demographic transition widely accepted in the social sciences?
However, the existence of some kind of demographic transition is widely accepted in the social sciences because of the well-established historical correlation linking dropping fertility to social and economic development. Scholars debate whether industrialization and higher incomes lead to lower population, or whether lower populations lead to industrialization and higher incomes. Scholars also debate to what extent various proposed and sometimes inter-related factors such as higher per capita income, lower mortality, old-age security, and rise of demand for human capital are involved.
What is demographic transition?
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high infant death rates in societies with minimal technology, education, and economic development, to low birth rates and low death rates in societies with advanced technology, education and economic development, as well as the stages between these two scenarios. Although this shift has occurred in many industrialized countries, the theory and model are frequently imprecise when applied to individual countries due to specific social, political and economic factors affecting particular populations.
What countries changed from 1820 to 2010?
Demographic change in Germany, Sweden, Chile, Mauritius, China from 1820 to 2010.
What was the impact of the decline in the death rate in England between 1750 and 1975?
A major factor was the sharp decline in the death rate due to infectious diseases, which has fallen from about 11 per 1,000 to less than 1 per 1,000.
What stage of the demographic transition model is Europe in?
Today, Europe and North America have moved to Stage 3 of the demographic transition model. A nation moves from Stage 2 to Stage 3 when CBRs begin to drop while CDRs simultaneously remain low or even continue to fall. It should be noted that the natural rate of increase in nations within Stage 3 is moderate because CBRs are somewhat higher than CDRs. The United States, Canada, and countries in Europe entered this stage in the early 20th Century. Latin American nations entered this stage later in the century.
What is the process of demographic transition?
Human geographers have determined that all nations go through a four-stage process called the demographic transition model (DTM). Developed in 1929 by American demographer Warren Thompson, the DTM’s function is to demonstrate the natural sequence of population change over time, depending on development and modernization. This can help geographers, and other scientists examine the causes and consequences of fertility, mortality, and natural increase rates. Though controversial, the DTM is used as the benchmark for forecasting human population growth regionally and globally.
Why did CBRs and CDRs fluctuate over time?
In this first stage, CBRs and CDRs fluctuated significantly over time because of living conditions, food output, environmental conditions, war, and disease. However, the natural increase of the world was pretty stable because ...
What causes a decrease in IMR and overall CDR during Stage 2?
Latin American nations entered this stage later in the century. Advances in technology and medicine cause a decrease in IMR and overall CDR during Stage 2. Social and economic changes bring about a reduction in CBR during Stage 3.
Why is the natural rate of increase in nations within Stage 3 moderate?
It should be noted that the natural rate of increase in nations within Stage 3 is moderate because CBRs are somewhat higher than CDRs. The United States, Canada, and countries in Europe entered this stage in the early 20th Century. Latin American nations entered this stage later in the century.
What stage of the demographic transition model did Latin America and Africa move into?
Africa, Asia, and Latin America moved into Stage 2 of the demographic transition model 200 years later for different reasons than their European and North American counterparts. The medicine created in Europe and North America was brought into these emerging nations, creating what is now called the medical revolution.
Why is the DTM important?
Though controversial, the DTM is used as the benchmark for forecasting human population growth regionally and globally.
What is the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
The Demographic Transition Model is a model that studies population trends in every country across the globe.
What is an example of a country in Stage 4 of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
The United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada are all very common examples of a country in stage 4 of the DTM.
What is Stage 1 of the DTM?
The first stage of the DTM is a stage where there are high birth rates and death rates. Many countries were here prior to the Industrial Revolution.

What Is The Demographic Transition Model?
What Are The Stages of The Demographic Transition Model?
- In Stage 1, which applied to most of the world before the Industrial Revolution, both birth rates and death rates are high. As a result, population size remains fairly constant but can have major swings with events such as wars or pandemics. In Stage 2, the introduction of modern medicine lowers death rates, especially among children, while birth rates remain high; the result is rapid p…
Limitations of The Demographic Transition Model
- Like any model, there will be outliers and exceptions to the rule and the Demographic Transition Model is no different. Additionally, there are things the DTM cannot reveal: the impact of other demographic variables such as migration, are not considered, nor does the model predict how long a country will be in each stage. But even so, the relationship between birth rate and death ra…