In general, parasympathetic output to the stomach tends to increase secretions and enhance the patterns of smooth muscle contractility that are required for processing a meal (5–7). In contrast, sympathetic output to the stomach tends to decrease secretions and inhibit these patterns of smooth muscle contractility (8–10).
What is the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
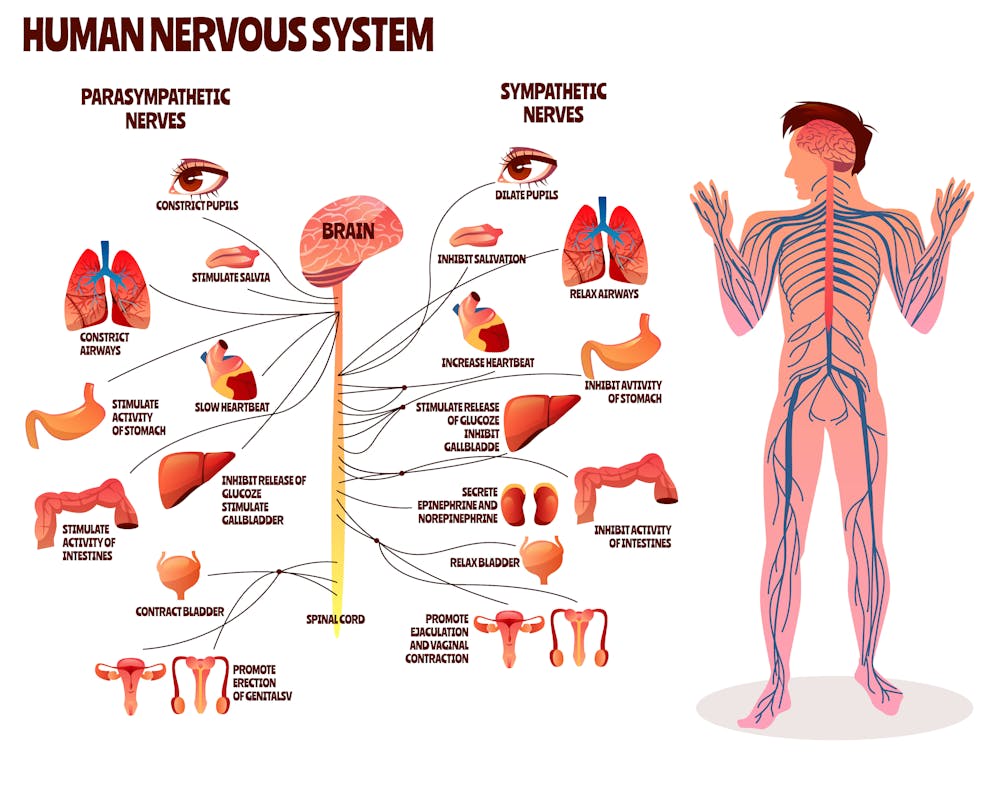
The human nervous system is a sprawling network of nerves and cells which, together, regulate all of the vital functions that take place in our bodies. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) are both components of the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic digestion?
Stomach (parasympathetic) Motility Increased; Gastric Juices Secreted Small Intestine (Sympathetic) motility reduced Small Intestine (Parasympathetic) Digestion Increased
Is the bronchial muscle sympathetic or parasympathetic?
Lung (Sympathetic) Bronchial muscle relaxed Lung (Parasympathetic) Bronchial muscle constricted Stomach (sympathetic) Peristalsis Reduced Stomach (parasympathetic) Motility Increased; Gastric Juices Secreted Small Intestine (Sympathetic)
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic salivary glands?
Iris (Sympathetic) Pupils Dilate Iris (Parasympathetic) Pupils Constrict Salivary Glands (Sympathetic) Saliva production reduced
How does sympathetic and parasympathetic affect the stomach?
The Sympathetic Nervous System controls our “fight or flight” state. It kicks-on in response to stress and stimulates blood-flow to the major muscles and the brain. The Parasympathetic Nervous System controls our “rest and digest” mode.
How does the parasympathetic system affect the stomach?
The parasympathetic nervous system, in contrast, exerts both excitatory and inhibitory control over gastric and intestinal tone and motility (i.e., milling, absorption, secretion, and defecation), implying a more finely tuned and complex influence over GI activity.
What nerve controls the stomach?
Basic Anatomy of the Vagus Nerve The vagus nerve carries an extensive range of signals from digestive system and organs to the brain and vice versa. It is the tenth cranial nerve, extending from its origin in the brainstem through the neck and the thorax down to the abdomen.
Does the autonomic nervous system control the stomach?
The parasympathetic system exerts its effects primarily via the vagus (innervates the esophagus, stomach, pancreas, upper large intestine) and pelvic nerves (innervates the lower large intestine, rectum, and anus.) The vagus nerve regulates tone and volume by activating the enteric motor neurons.
How does the parasympathetic nervous system control digestion?
The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body's rest and digestion response when the body is relaxed, resting, or feeding. It basically undoes the work of sympathetic division after a stressful situation. The parasympathetic nervous system decreases respiration and heart rate and increases digestion.
Why does parasympathetic increase digestion?
Digestion: The PSNS stimulates the release of saliva to promote digestion. It also enacts peristalsis, or the movement of the stomach and intestines, to digest food as well as release bile for the body to digest fats.
What happens when the parasympathetic nervous system is activated?
When the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is activated, it slows our heart and breathing rates, lowers blood pressure and promotes digestion. Our body enters a state of relaxation, and this relaxation breeds recovery.
Does the parasympathetic nervous system increase peristalsis?
The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) stimulates peristalsis via the myenteric plexus.
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic Background Information
To better understand sympathetic vs parasympathetic nervous systems we first have to understand nervous systems in general. Let’s take a closer loo...
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic: How They Work
Let’s look at the sympathetic vs parasympathetic systems and how they work within the autonomic nervous system. Now, this gets a little complicated...
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic Differences
It can be a little bit difficult to keep track of which effects the two nervous systems have on the human body.A key point to keep in mind is that...
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic Dangers
The parasympathetic nervous system does not pose any dangers to your health because it is simply carrying out your body’s normal functions. The sam...
Final Thoughts on Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic
Because they sound so similar, it can be confusing to remember which is which. One of the best ways to remember their differences is to look at the...
Where does the parasympathetic nervous system start?
Parasympathetic nervous system function. Your PSNS starts in your brain and extends out via long fibers that connect with special neurons near the organ they intend to act on. Once PSNS signals hit these neurons, they have a short distance to travel to their respective organs.
Where do parasympathetic nerves come from?
Trusted Source. of all parasympathetic nerve fibers in the body come from this nerve. This nerve has branches in many key organs, including the stomach, kidneys, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, bladder, anal sphincter, vagina, and penis.
What is the acronym for parasympathetic response?
Examples of parasympathetic responses. An easy acronym to remember how and where the PSNS works is SLUDD. This stands for: Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest.
What happens if your parasympathetic nervous system doesn't work?
Your PSNS is a vital part of your body’s key functions. When it doesn’t work properly, you can face a number of bodily dysfunctions that affect your health. If you think you may be having trouble with one of your body’s parasympathetic nervous system functions, talk to your doctor to find out how you can get help.
What is the nervous system?
Your nervous system is a wild and wonderful network of nerves that act in different key functions to keep your body moving, responding, sensing, and more. This article is going to examine the parasympathetic nervous system, one of two majors divisions of the larger autonomic system. In the simplest terms, the parasympathetic ...
What are the receptors in the heart?
Parasympathetic nervous system and your heart. There are a number of special receptors for the PSNS in your heart called muscarinic receptors. These receptors inhibit sympathetic nervous system action. This means they’re responsible for helping you maintain your resting heart rate.
How many halves are there in the autonomic system?
In the simplest terms, the parasympathetic and sympathetic portions of the autonomic system are two halves of the same whole.
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
Sympathetic Nervous System. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) controls homeostasis and the body at rest and is responsible for the body's "rest and digest" function. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) controls the body's responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response.
Which is faster, the sympathetic or parasympathetic?
The sympathetic nervous system is a faster system as it moves along very short neurons. When the system is activated, it activates the adrenal medullato release hormones and chemical receptors into the bloodstreams. The target glands and muscles get activated. Once the perceived danger is gone, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over to counterbalance the effects of the sympathetic nervous system's responses.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic nervous system is part of the autonomic nervous system. It originates in the spinal cord and the medulla and controls homeostasis, or the maintenance of the body's systems. The parasympathetic nervous system controls the "rest and digest" functions of the body.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
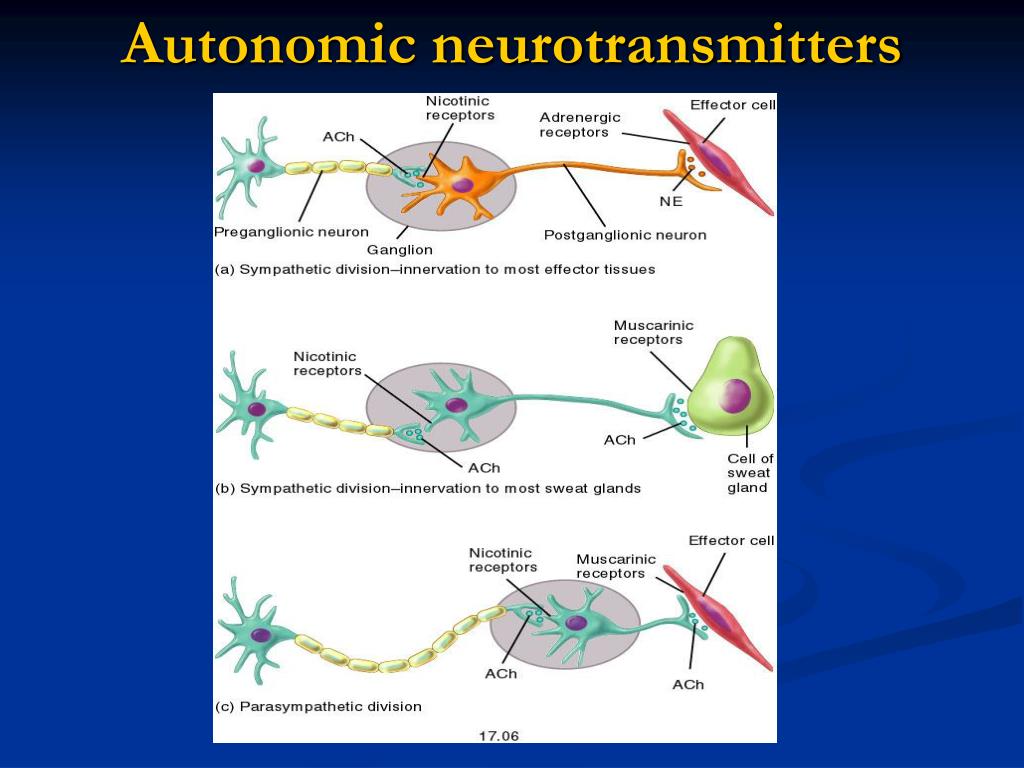
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates visceral functions, i.e. functions of the internal organs such as the heart, stomach and intestines. The ANS is part of the peripheral nervous system and also has control over some muscles within the body. The functions of the ANS are involuntary and reflexive, e.g. the beating of the heart, expansion or contraction of blood vessels or pupils, etc. — which is why we are seldom conscious of it. The parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, along with the enteric nervous system make up the ANS.
What happens to the body when the sympathetic nervous system is shut down?
With sympathetic nervous responses, the body speeds up, tenses up and becomes more alert. Functions that are not essential for survival are shut down. Following are the specific reactions of sympathetic nervous system:
Which system controls the body's responses to a perceived threat?
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) controls the body's responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response. The PNS and SNS are part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which is responsible for the involuntary functions of the human body.
Which system is responsible for involuntary functions?
The PNS and SNS are part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which is responsible for the involuntary functions of the human body.
Where is the stomach located?
The stomach lies within the superior aspect of the abdomen. It primarily lies in the epigastric and umbilical regions, however, the exact size, shape and position of the stomach can vary from person to person and with position and respiration.
Where does the sympathetic nerve supply originate?
Sympathetic nerve supply arises from the T6-T9 spinal cord segments and passes to the coeliac plexus via the greater splanchnic nerve.
What part of the stomach controls the exit of chyme?
The pyloric sphincter lies between the pylorus and the first part of the duodenum. It controls of the exit of chyme (food and gastric acid mixture) from the stomach.
What is the left gastro-omental?
Left gastro-omental – branch of the splenic artery, which arises from the coeliac trunk.
Where does gastric lymphatic fluid drain?
Lymph fluid drains into the gastric and gastro-omental lymph nodes found at the curvatures.
What is the rounded, often gas filled portion superior to and left of the cardia?
Fundus – the rounded, often gas filled portion superior to and left of the cardia.
Which direction does the pyloric antrum curve?
It curves to the right as it continues medially to reach the pyloric antrum.
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Nervous System. The human nervous system is a sprawling network of nerves and cells which , together , regulate all of the vital functions that take place in our bodies. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) are both components of the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
What Does the Parasympathetic Nervous System Do?
Put simply, the PSNS keeps your bodily functions working as they should. It keeps your heart rate and blood pressure steady while stimulating activities related to digestive and sexual function. These include the production of saliva, tears, and urine, digestion, defecation, and sexual arousal.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
The SNS and PSNS are the two main parts of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which controls the functions of our internal organs. All of the functions of the ANS are involuntary and reflexive, so we don’t always notice its effects on our bodies.
Why is the parasympathetic nervous system called the rest and digest division?
The parasympathetic nervous system division can be referred to as the rest-and-digest division because it increases the secretions from the gastric glands in the presence of food. This helps the digestive process. The sympathetic nervous system is commonly referred to as the fight-or-flight division.
How does the sympathetic nervous system help you digest food?
When the threat is gone, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over and allows you to continue digesting your meal by increasing blood flow to the digestive tract . An easy way to keep the functions of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system straight is to think of the sympathetic nervous system as the fight-or-flight division, and think of the parasympathetic nervous system as the rest-and-digest division.
What are the pits in the stomach?
The mucosa of your stomach is dotted with millions of deep gastric pits. The term 'gastric' refers to stomach, and we see that gastric pits are simply indentations in the stomach wall that lead to gastric glands. Gastric glands are the glands, or groups of cells, in the wall of the stomach that secrete components needed for digestion. These secretions are important for the chemical breakdown of many of the foods you eat, and later we will learn more about these secretions.
What is the mucosa in the digestive system?
In fact, the mucosa lines the entire length of your digestive tract. So we can say that the mucosa is the layer of the digestive system that comes in direct contact with the food mass.
How does food enter the stomach?
We previously learned that food enters the stomach through the lower esophageal sphincter, which is a ring of muscle that acts like a gatekeeper and controls the passage of food from the esophagus to the stomach. In the same fashion, food exits the stomach through another sphincter. The sphincter that controls the passage of food out of the stomach is called the pyloric sphincter. The pyloric sphincter gets its name from the fact that it lies near the pylorus, or terminal section, of the stomach. Food must be broken down to a near liquid form in order to pass through this pyloric sphincter. The sphincter never opens very wide, and it only allows about three milliliters or less of stomach contents to squirt through at a time. This strict regulation of food helps keep the small intestine, which is the next stop for food, from becoming overburdened.
Which system controls gastric glands?
Autonomic Nervous System. The secretions that come from the gastric glands are regulated closely by your body. You are totally unaware of this regulation because it's controlled, at least in part, by the division of the nervous system that is under involuntary control.
Where is the pyloric sphincter located?
The pyloric sphincter is found at the distal end of the stomach and is the sphincter that controls the passage of food out of the stomach. The stomach has the ability to stretch when it's full. When it's empty, it collapses in on itself creating a series of ridges or folds called rugae.
What are the functions of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Some of the functions of parasympathetic nervous systems are: Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) increases; digestion, intestinal motility, insulin activity, resistance to infection, rest and recuperation and endorphins ('feel good' hormone).
What is the digestive system?
The digestive system is under supervision of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS). The ANS supervise the automatic body process that is not under our conscious control. This means that when we consume food without our knowledge, our body digests it.
What is the nervous system in the body?
The SNS is in-charge for the flight or fight response of our body system. When we are fearful (flight) or anger (fight), the SNS signals to increases, our heart rate and provides more energy ...
How do intrinsic nerves stimulate the digestive system?
The intrinsic nerves are stimulated when the walls of the organs are stretch by the entry of food. They release chemical substances that speed up or delay the food movement and the secretion of juices by the digestive organs.
What nerve controls the heartbeat?
The vagus nerve regulates the heartbeat, control muscle movement, manage breathing, and transport various chemicals throughout the body. It manages the digestive tract in working condition; contracting the stomach and intestinal muscles to help digest food, and send information about what is digesting and what are the nutrients get out of it.
Does a nerve in the stomach slow down digestion?
It relaxes the stomach muscle & intestine, also decreases the blood flow to these organs, which in-turn slow down or stop digestion. The intrinsic (inside) nerves are embedding in the walls of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon.
What is the role of sympathetic and parasympathetic?
Parasympathetic. Involved in the fight or flight response. Involved in maintaining homeostasis and also, permits the rest and digest response. The sympathetic system prepares the body for any potential danger. The parasympathetic system aims to bring the body to a state of calm.
What is Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Sympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: It is the part of the autonomic nervous system, located near the thoracic and lumbar regions in the spinal cord. Its primary function is to stimulate the body’s fight or flight response. It does this by regulating the heart rate, rate of respiration, pupillary response and more.
Why is the autonomic nervous system called the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system is named so, because it works autonomously, i.e., without a person’s conscious effort. The primary function of the autonomic nervous system is homeostasis. Apart from maintaining the body’s internal environment, it is also involved in controlling and maintaining the following life processes: Digestion. Metabolism.
Where is the parasympathetic nervous system located?
Parasympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: It is located in between the spinal cord and the medulla. It primarily stimulates the body’s “rest and digest” and “feed and breed” response. Read on to explore more differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
Which body system is responsible for urination, defecation, and digestion?
Salivation, urination, lacrimation, defecation and digestion are the important body activities stimulated by the parasympathetic nervous system.
Which system prepares the body for fight and flight response?
The parasympathetic nervous system restores the body to a calm and composed state and prevents it from overworking. The sympathetic nervous system , on the other hand, prepares the body for fight and flight response.
